Proof of concept used for phishing multi-factor authentication on O365.
This is a proof of concept. It is not a click-and-pwn tool. You will need to read the code
The JavaScript files included are not the entire phishing pages. The phishing page should be a cloned page of your target's login page / Microsoft / whatever MFA service you are targeting. It is up to you to create a good clone (hint: wget), to host them (nginx works great), then to integrate the required JavaScript. The files have notes on where to drop in the code on the clones.
There are 3 components to this PoC:
- mfa_slipstream.py - This tool sits running on the attacker's machine. It handles collecting username and password data, it facilitates the transition from the username and password to the collection of MFA tokens, as well as handles collecting the MFA tokens themselves.
- collect_userpass.js - This only contains 1 JavaScript function that sends a request back to your attacker box to do the initial login in real-time.
- collect_mfa.js - This contains 2 pieces of JavaScript. Part 1 handles sending the MFA code back to your attacker machine, part 2 parses information from the url set by collect_userpass.js (part 2 appears in the cloned page second, though it is actually executed first during the attack).
For an overview of how the PoC code is organized see: MFA Slipstream - Phishing MFA PoC Walkthrough
For a demo of the attack please see this blogpost: Phishing Your Way Past Multi-Factor Authentication
Or just the video here:
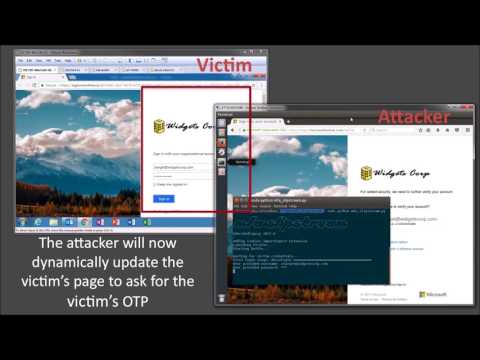
Here is an overview of how these pieces fit together:
It can be run on Windows or Linux (have successfully used it on both)
git clone https://github.com/decidedlygray/mfa_slipstream_poc.git
pip install selenium
cd mfa_slipstream_poc
# If on Windows, you'll need to figure out a different way to self-sign a cert. Otherwise
# LetsEncrypt is always your friend. This may need to be a real cert for production
openssl req -new -x509 -keyout mfa_slipstream.pem -out mfa_slipstream.pem -days 365 -nodes
Download and put into your PATH: https://github.com/mozilla/geckodriver/releases Why Firefox? I originally started with Chrome, but it was buggy and kept freezing up on me.
Again, this is not a proper tool, but a PoC, so setup is a tiny bit messy.
Line 47 of mfa_slipstream.py needs to be set to something that will redirect the attacker to the target's login page:
PROTECTED_RESOURCE='https://targetsite.sharepoint.com/SitePages/Home.aspx'
Line 48 of mfa_slipstream.py should be set to the target's email domain (e.g. for user@widgetscorp.co):
TARGET_EMAIL_DOMAIN='widgetscorp.co'
Instances of portal.widgetscorp.co in both files should be updated with the domain pointing to your attack box
You should review and understand both files, update them to suite your target. Wherever you see 'widgetscorp.co' replace it with your target's domain.
You will see 2 URL patters in these files of things you need to update:
- https://login.mymicrosoftphish.com/4bf18ef2-86a7-4b76-b63f-80a89cde4657/login?bunch_of_stuff_here This needs to point to wherever you have your Phishing Stage 2 page is hosted. Stage 1 performs the transition, using information supplied by an XHR call to mfa_slipstream.py to land the user on a believable MFA collection page.
- https://login.mymicrosoftphish.com/error?bunch_of_stuff_here This is an error page you need to create, or however you want to handle the "dump off" after the user fails to get a session. This is called by code in collect_mfa.js.