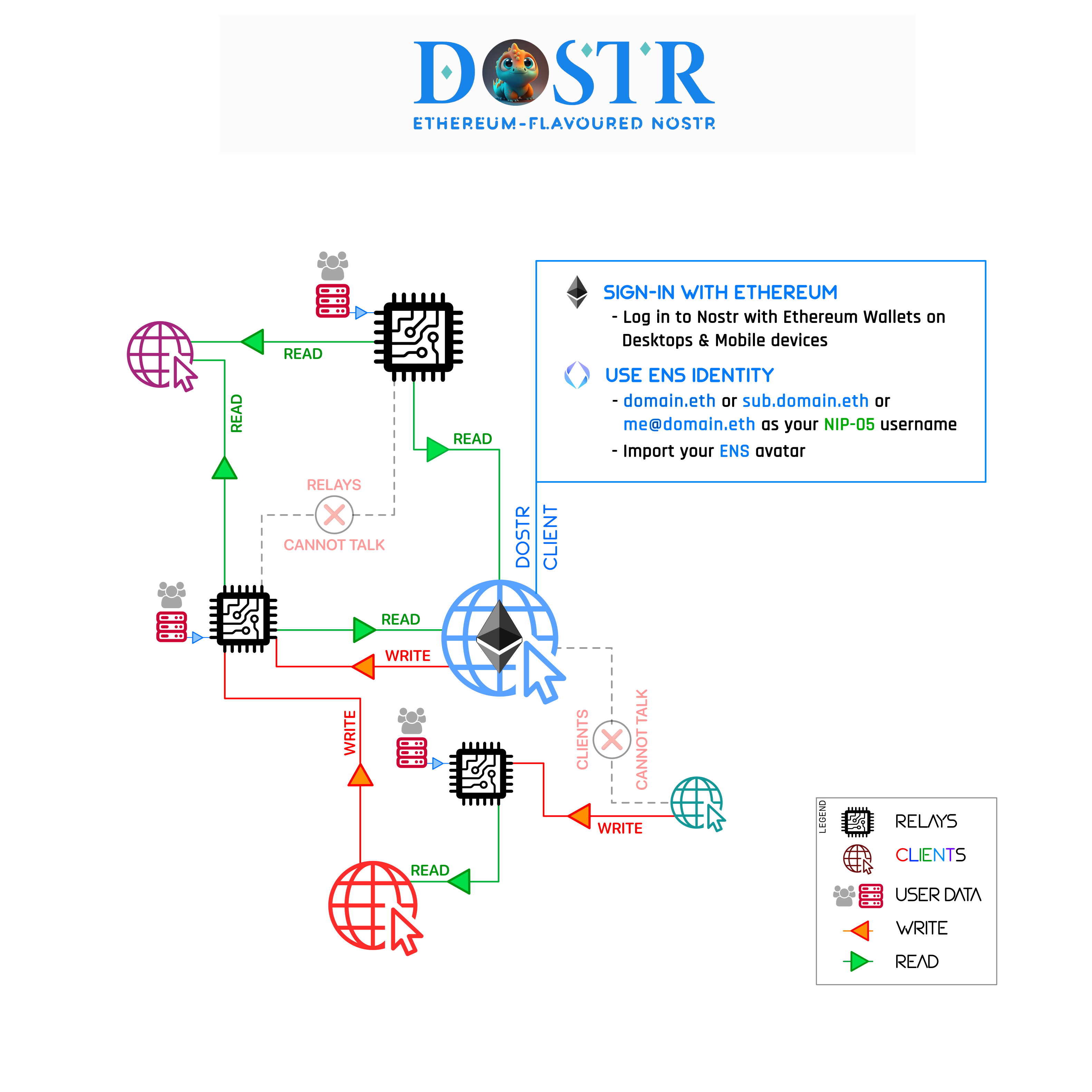
Dostr is an Ethereum-flavoured Nostr client. Dostr is an optional Ethereum-native side-stack to Nostr which allows users to generate deterministic Nostr-specific private keys from Ethereum-native ECDSA signatures. This allows Nostr to function with Ethereum wallets and leverage properties of ENS (Ethereum Name Service) protocol in Dostr client infrastructure and vice-versa. Consequently, Dostr provides an optional side-stack of Ethereum-based services for Nostr users, e.g. allows them to use their ENS identity on Nostr or attach to Helix2 as a submodule hook. Alternatively, Ethereum users may find that Dostr is a minimal implementation of Sign In With X (SIWx) - an alternative to SIWE.
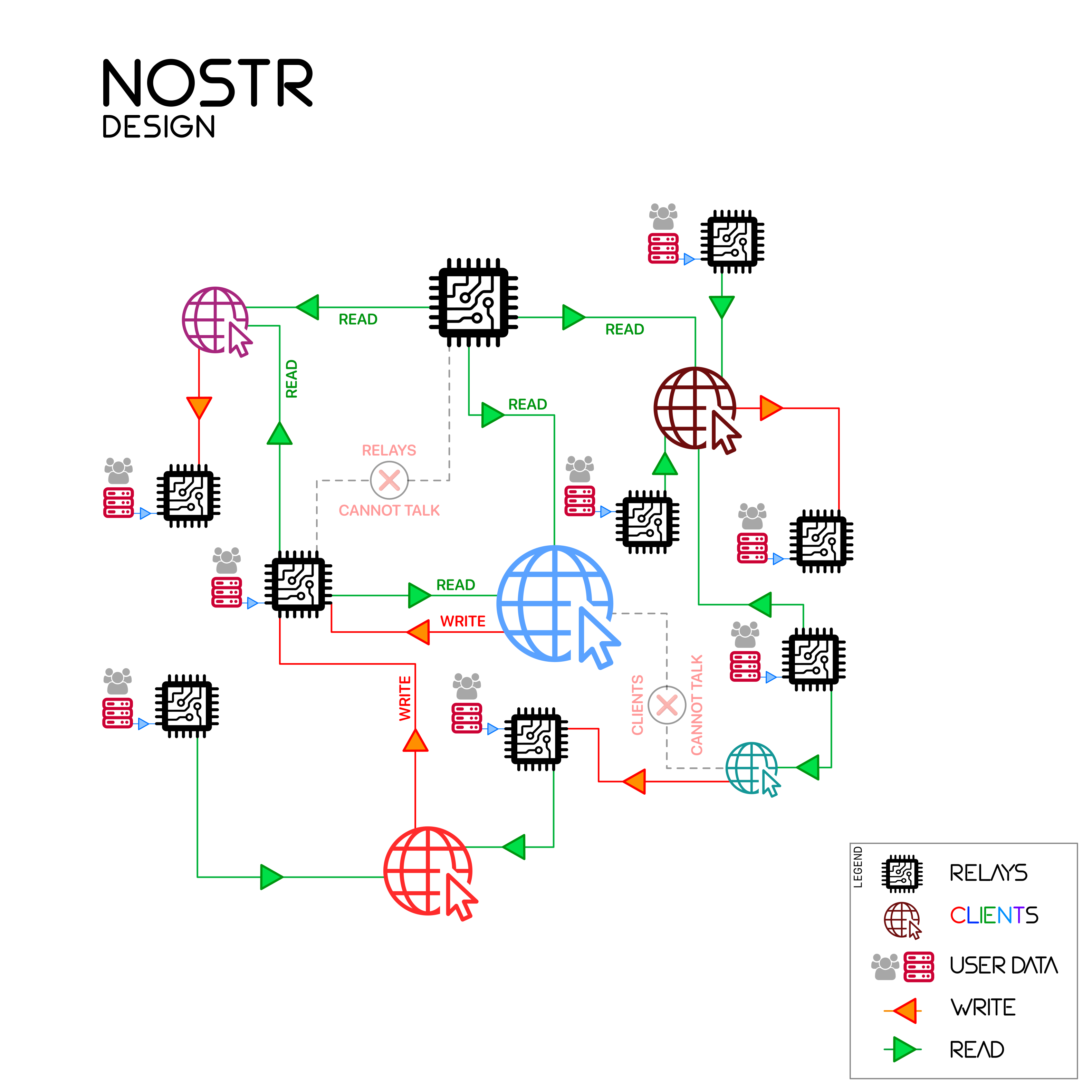
Dostr is a Nostr client with Ethereum-based side-stack. To understand Dostr, one must understand Nostr. Nostr is a minimal peer-to-peer networking protocol with following properties:
- Nostr consists of Clients and Relays. Clients are local instances run by users and relays are websocket servers which communicate between clients.
- Nostr clients have the ability to talk to relays and make requests for filtered information, which the relay fetches from another client and returns to the original requester.
- Nostr clients are identified by their private keys and may have a Petname. Nostr clients must sign the information they send and relays must validate the information before transmitting it.
More details about the Nostr protocol may be found here (and here). In native Nostr implementation, Schnorr signature scheme over secp256k1 is used as per Bitcoin-native BIP-340 standard. Dostr adds to this standard by deriving the Nostr-specific private keys from Ethereum-native ECDSA signature scheme outlined in EIP-191 and EIP-712 using HMAC Key Derivation Function (HKDF). In Dostr clients, ENS names of the signing wallets become the petnames of the users.
Implementing an Ethereum-based side-stack to Nostr has several utilities. Firstly, it allows Nostr to work with Ethereum-based wallets and leverage the rich UX of Ethereum ecosystem. For instance, most Ethereum-wallets implement ENS by default and Dostr is the first and only protocol that allows users to uitlise their NIP-02 compatible ENS names on Nostr. Dostr further leverages properties of ENS such as its DNS resolution via a gateway (https://vitalik.eth.limo) to store NIP-05 compatible public client information. The cross-chain utility of Dostr is not limited to ENS and extends beyond to other Ethereum-native naming and linking protocols such as (https://github.com/helix-coupler/resources/blob/master/yellow-paper/README.md) or Woolball.
Dostr design is identitical to the Nostr specifications described in NIP-01 except for two main differences - using ECDSA signatures to derive user keys, and use of ENS via a gateway to access the user properties instead of a web2 DNS server. The detailed NIP-XX proposal covering these two aspects is currently under review. In summary, the Dostr implementation can be summarised with the following pseudo-code.
Dostr uses HMAC-based Extract-and-Expand Key Derivation Function (HKDF) coupled with sha256.
import { hkdf } from '@noble/hashes/hkdf';
import { sha256 } from '@noble/hashes/sha256';
import * as secp256k1 from '@noble/secp256k1';
let username = 'petname@domain.eth.limo'; // chosen username as per NIP-02 and/or NIP-05
let optPassword = "horse staple battery"; // optional password
let address = wallet.getAddress(); // get checksum'd address from eth wallet
let signature = wallet.signMessage(message); // request signature from eth wallet (v, r, s)
let inputKey = sha256(signature);
let salt = sha256(`nostr:${username}:${optPassword}:${signature.slice(68)}`); // generate salt with username, password & signature
let info = `nostr:${username}:${address}`; // HKDF() arg
let dkLen = 42; // HKDF() arg
let hashKey = hkdf(sha256, inputKey, salt, info, dkLen); // calculate keyhash with HKDF function
let privKey = nobleSecp256k1.hashToPrivateKey(hashKey); // private key from (keyhash ⊕ secp256k1)
let pubKey = nobleSecp256k1.getPublicKey(privKey); // public key from (keyhash ⊕ secp256k1)Nostr username can be either of the following:
petname or petname@domain.eth.limo or domain.eth.limo or sub.domain.eth.limo, where,
petnameis a name/identifier compatible with NIP-02,petname@domain.eth.limois an identifier compatible with NIP-05,domain.eth.limois NIP-05 equivalent of_@domain.eth.limo, andsub.domain.eth.limois NIP-05 equivalent of_@sub.domain.eth.limo.
Note that petname can be the same as domain.
Password is optional value used in HKDF salt,
let username = "petname@domain.eth.limo"
let password = "horse staple battery"
let signature = wallet.signMessage(message)
let salt = sha256(`nostr:${username}:${password}:${signature.slice(68)}`);
// generate password if none provided by user
if(!password || password == ""){
salt = sha256(`nostr:${username}:${signature.slice(68)}`)
}let message = `Login to Nostr as ${username}\n\nWARNING : DO NOT SIGN THIS REQUEST FROM UNTRUSTED NOSTR CLIENTS.\n${address}`let signature = wallet.signMessage(message); // request ECDSA signature from eth wallet in (v, r, s) struct