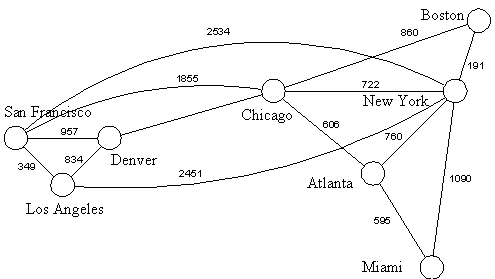
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of vertices or nodes or points and edges or arcs or lines that connect them. A graph may be undirected, meaning that there is no distinction between the two vertices associated with each edge, or its edges may be directed from one vertex to another. Graphs are one of the prime objects of study in discrete mathematics.
You can read about this here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_theory
#Setup ##1. Download the file graph.h below
##2. Copy graph.h to the correct location
Obs: The graph.h you have to stay in the same file directory that will use it
##3. Include the header file
#include "graph.h"Great. Your graphs library is now ready to use.
#Additional Setup ##Creating an Graph instance
int main()
{
//Graph Instance
Graph<Integer> my_graph = new Graph<Integer>();
system("pause");
return 0;
}##Add Vertex item
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
my_graph->addVertex(new Vertex<Integer>(new Integer(i+1)));##Add Edge item
Integer *i = new Integer(first_int);
Integer *j = new Integer(second_int);
Vertex<Integer> *v1 = my_graph->getVertex(i);
Vertex<Integer> *v2 = my_graph->getVertex(j);
my_graph->addEdge(v1,v2,distance);##Print Graph
my_graph->print();#FAQ ###How can i create a non-directed graph
//Create a constant
#define DISTANCE = 0;
//When adding an edge
my_graph->addEdge(v1,v2,DISTANCE);
my_graph->addEdge(v2,v1,DISTANCE);#Developed By
- Eduardo Castro
- eduhrcastro.github.io - eduardo@nucleus.eti.br
#License Copyright 2015 Eduardo Castro