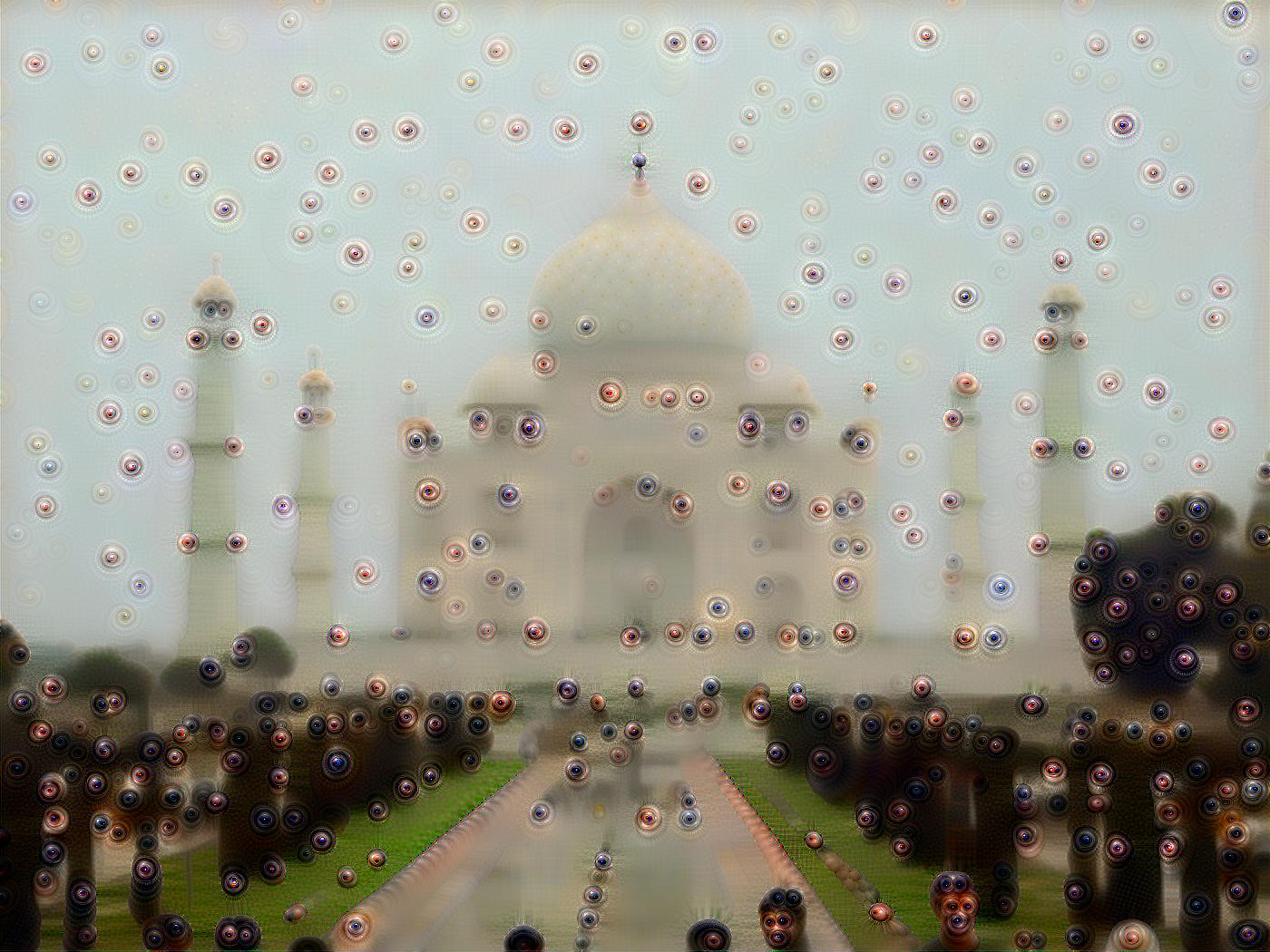See also: https://github.com/google/deepdream
Blog entry: https://www.bonaccorso.eu/2017/07/09/keras-based-deepdream-experiment-based-vgg19/
This experiment (which is a work in progress) is based on some suggestions provided by the Deepdream team in this blog post but works in a slightly different way. I use a Gaussian Pyramid and average the rescaled results of a layer with the next one. A total variation loss could be employed too, but after some experiments, I've preferred to remove it because of its blur effect.
- Python 2.7-3.5
- Keras
- Theano/Tensorflow
- SciPy
- Scikit-Image
(With different settings in terms of layers and number of iterations)
|
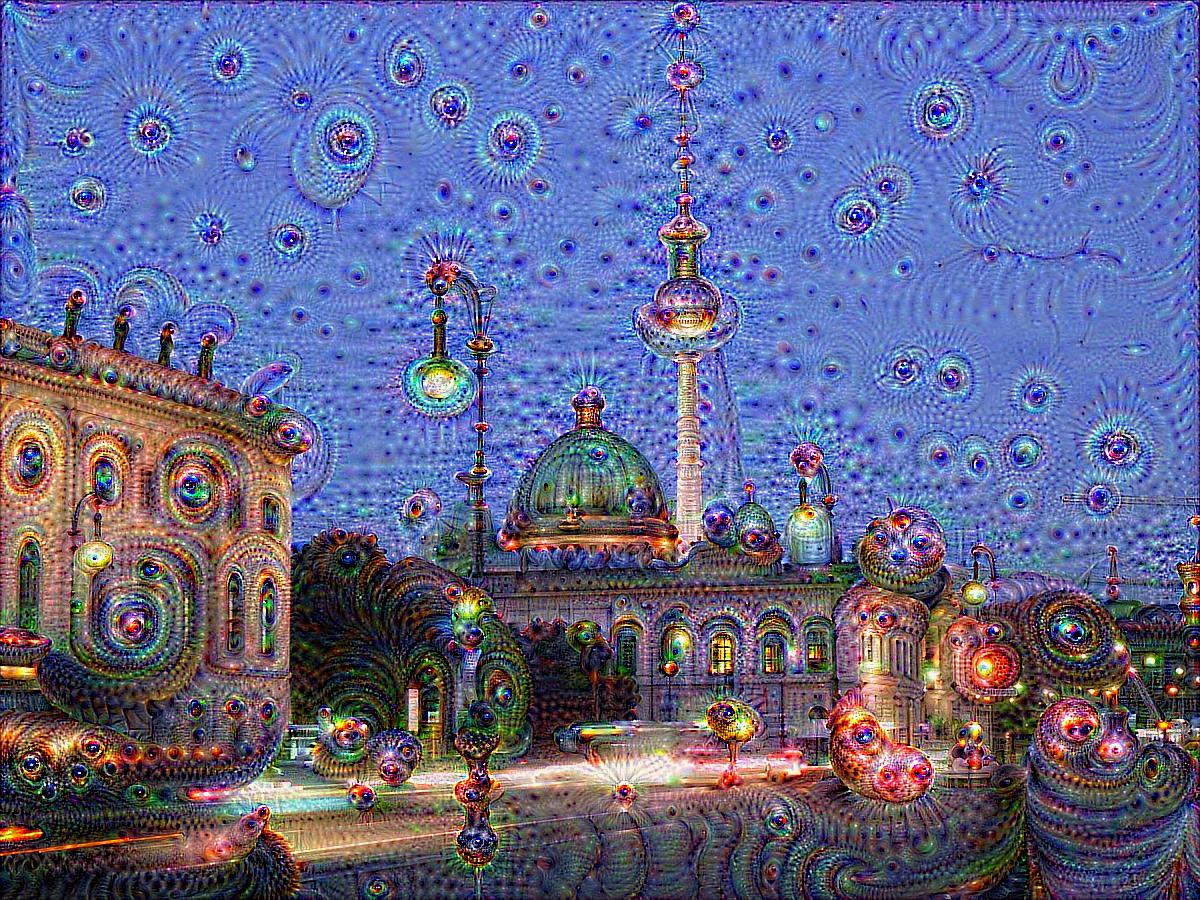
Berlin |
Berlin |
|
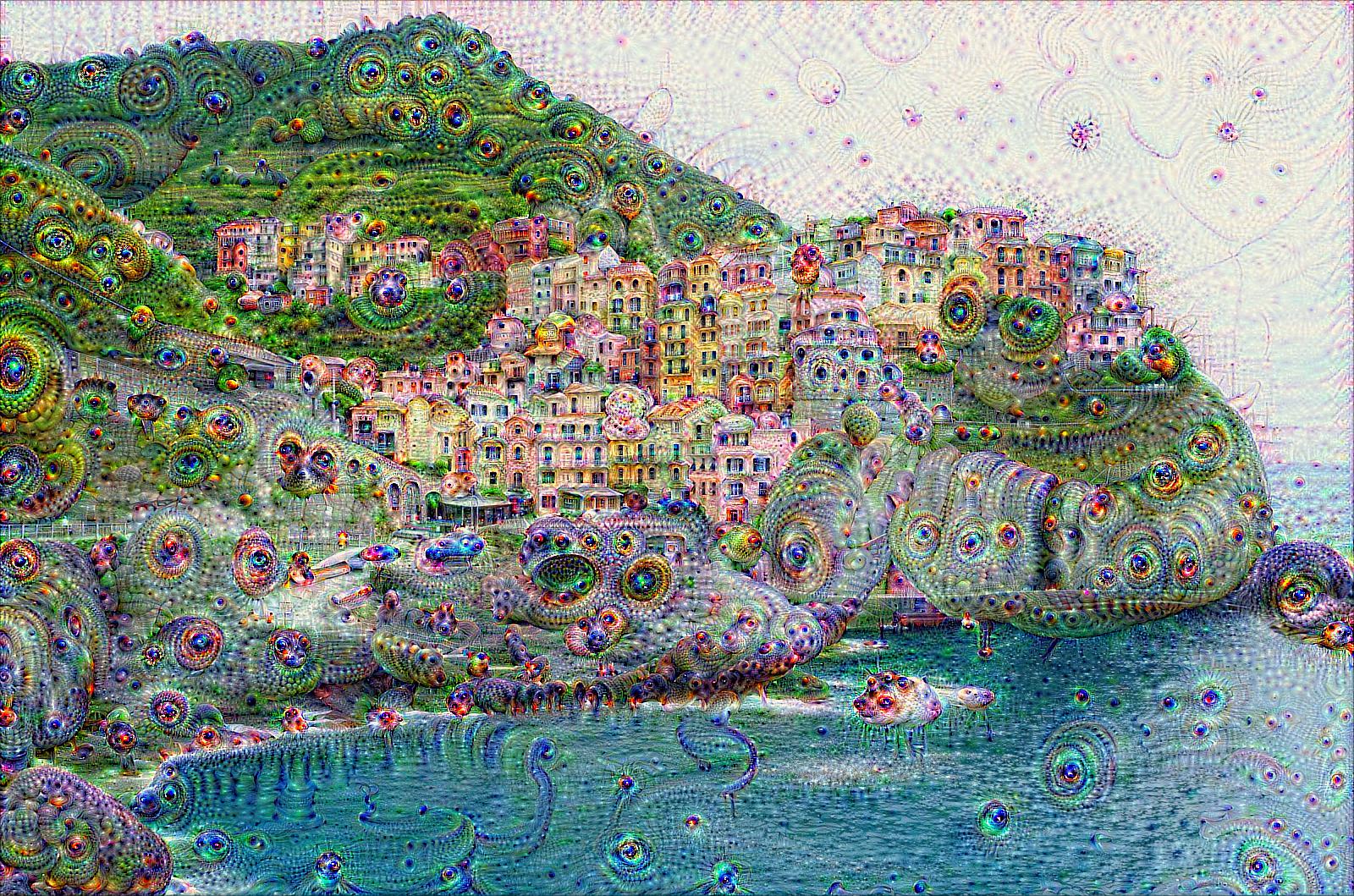
Cinque Terre |
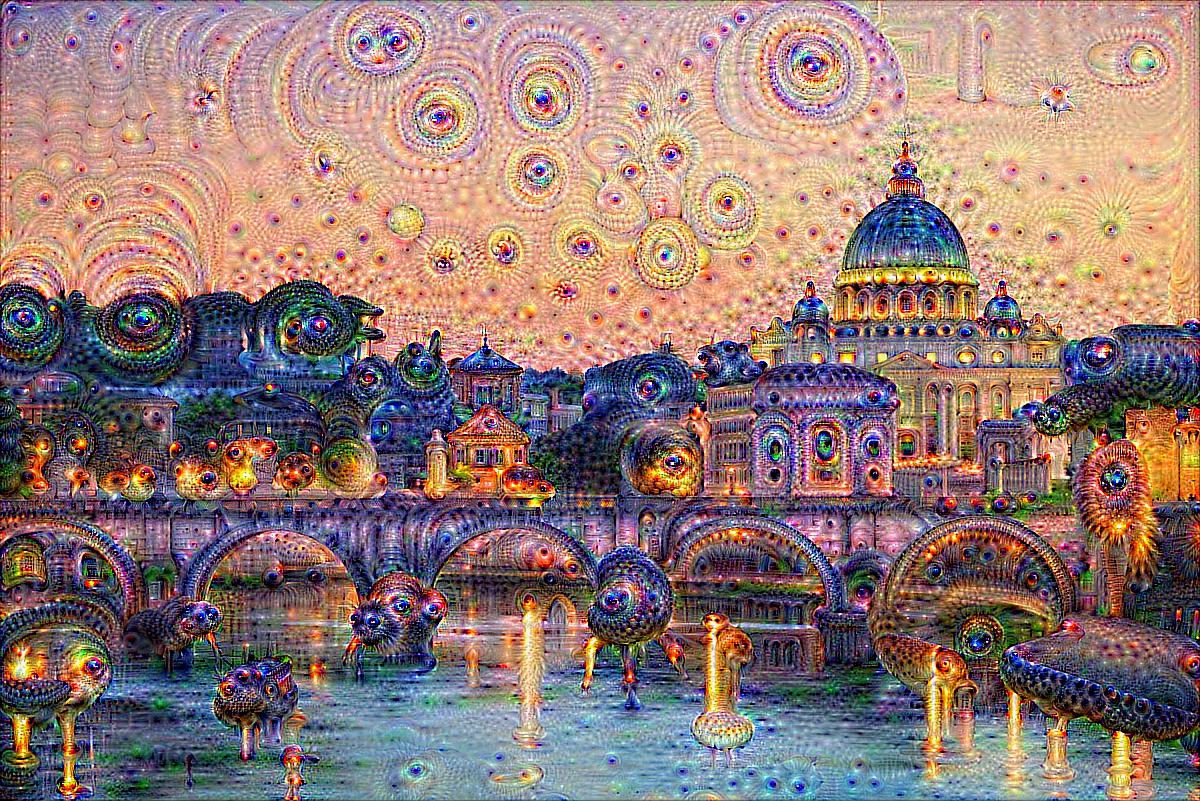
Rome |
|
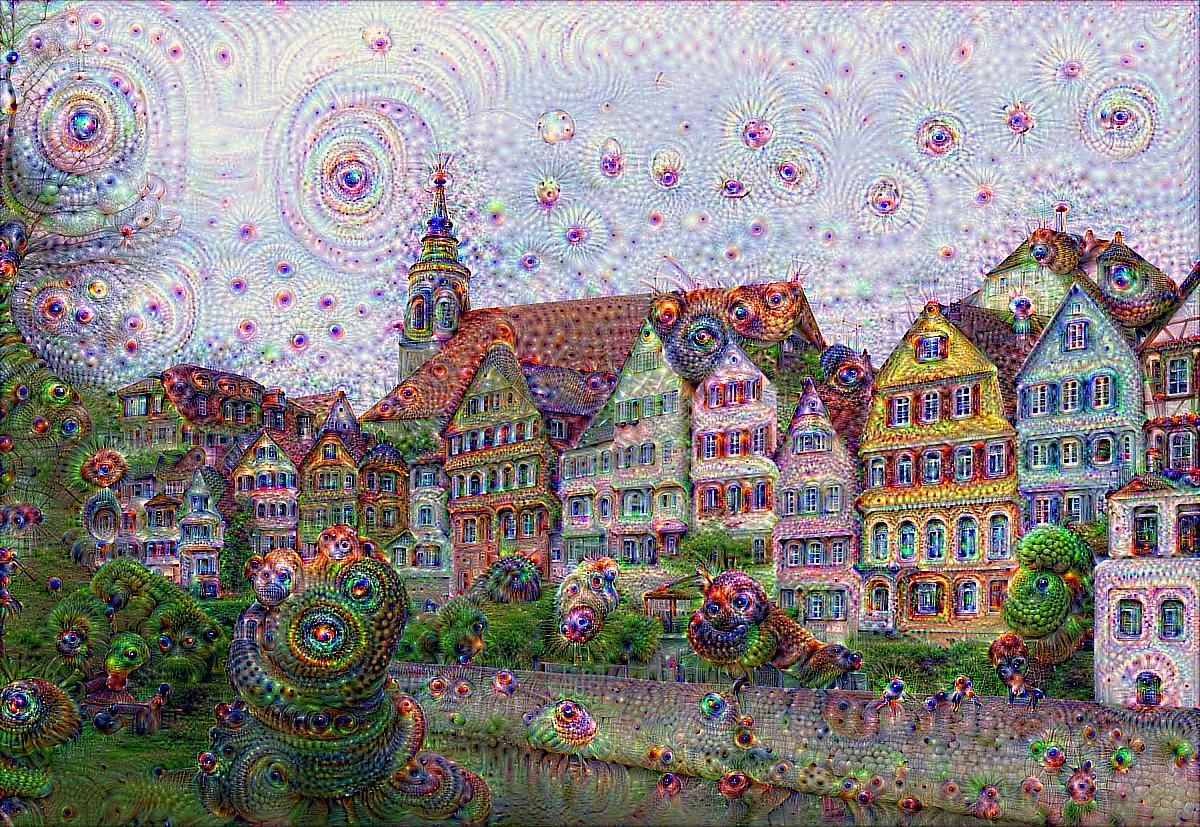
Tubingen |
Taj Mahal |
A good suggestion provided in this blog post is adding some noise to the original image. In this way there's a stronger activation of different filters. I suggest to try different values and/or removing the noise from the processed image.
def process_image(image, iterations=2, noise_level=5):
# Create bounds
bounds = np.ndarray(shape=(image.flatten().shape[0], 2))
bounds[:, 0] = -128.0
bounds[:, 1] = 128.0
# Initial value
x0 = image.flatten()
# Add some noise
noise = np.random.randint(-noise_level, noise_level, size=x0.shape)
x0 = np.clip(x0 + noise, -128, 128)
# Perform optimization
result = minimize(fun=loss,
x0=x0,
args=list(image.shape),
jac=gradient,
method='L-BFGS-B',
bounds=bounds,
options={'maxiter': iterations})
return postprocess_image(np.copy(result.x.reshape(image.shape)))
It's possible to create amazing videos by zooming into the same image (I've also added an horizontal pan that can be customized). You can use the snippet below, which assumes to have already processed an existing image (processed_image):
nb_frames = 3000
h, w = processed_image.shape[0:2]
for i in range(nb_frames):
rescaled_image = rescale(processed_image, order=5, scale=(1.1, 1.1))
rh, rw = rescaled_image.shape[0:2]
# Compute the cropping limits
dh = int((rh - h) / 2)
dw = int((rw - w) / 2)
dh1 = dh if dh % 2 == 0 else dh+1
dw1 = dw if dw % 2 == 0 else dw+1
# Compute an horizontal pan
pan = int(45.0*np.sin(float(i)*np.pi/60))
zoomed_image = rescaled_image[dh1:rh-dh, dw1+pan:rw-dw+pan, :]
processed_image = process_image(preprocess_image(img_as_ubyte(zoomed_image)), iterations=2)
imsave(final_image + 'img_' + str(i+1) + '.jpg', processed_image)