Welcome back to my another projet based staff. Here I am going to discuss all this project from the very beginning to the end. So Hopefully, you will really enjoy it. So let's get started.
As it's clear from the name Heart diseases prediction app creation using cloud platforms & MLOps tools, I am going to create a health-related application with an industry approach. So let's see step by step all my activities for deploying this project in the production environment.
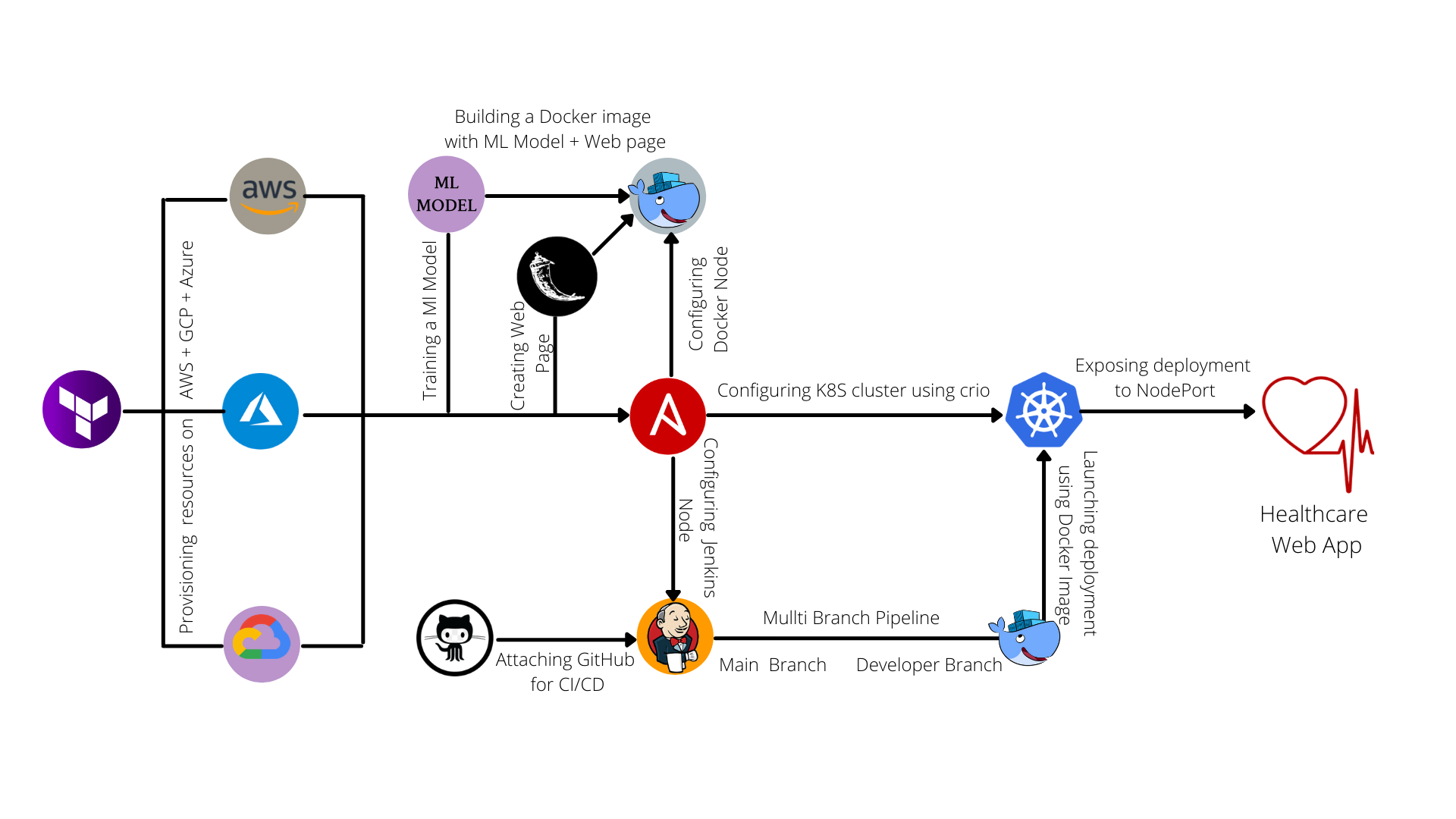
I will create this type of architecture to deploy my web app. so let see step by step.
Here I mentioned my git link where you can find all the related codes and stuff. https://github.com/hackcoderr/heart-diseases-predictor
To create this project, having good knowledge of the following tools and platforms is a prerequisite.
- Terraform
- Cloud Platforms
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Ansible
- Kubernetes
- Machine Learning
- Git and Github
- Docker
- Jenkins
- flask
these all tools and platforms will help us how we can automate this project. So let's see the usages of all mentioned staff one by one and why we are using them here. So let's started with terraform.
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as a code software tool that provides a consistent CLI workflow to manage hundreds of cloud services. Terraform codifies cloud APIs into declarative configuration files.
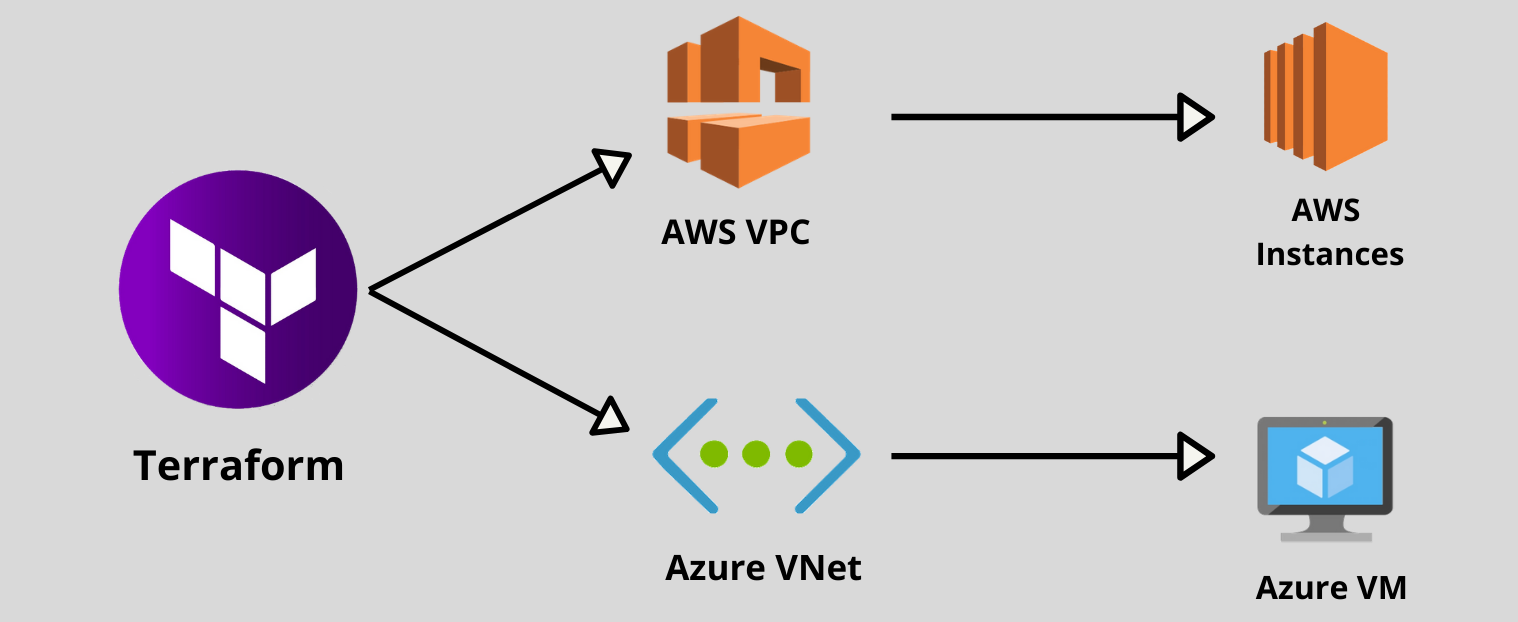
As it's mentioned in the above introduction of Terraform that we use this to manage the cloud services So I want to use some cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, and GCP) here so that I can create the below-mentioned reproducible infrastructure.
Now it's time to install the terraform. So let see its installation.
If you're using Linux os as terraform workstation then run the below commands otherwise go with the mentioned link and install terraform according to your OS. https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
sudo yum install wget -y
sudo wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.15.3/terraform_0.15.3_linux_amd64.zip
sudo yum install unzip -y
sudo unzip terraform_0.15.3_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/
Now check to terraform version with terraform -version command.
Before going onward, let me create a workspace where I will save all the things related to this project.
Amazon web service is an online platform that provides scalable and cost-effective cloud computing solutions. It is a broadly adopted cloud platform that offers several on-demand operations like compute power, database storage, content delivery, etc., to help corporates scale and grow.
But if you want to more about it then visit the below link. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amazon_Web_Services
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service that helps you securely control access to AWS resources. You use IAM to control who is authenticated (signed in) and authorized (has permissions) to use resources.
Now we will need access key and secret key for creating VPC and launch AWS instances by terraform tool that why we have to create AWS IAM User with AmazonVPCFullAccess and AmazonEC2FullAccess. So download your IAM credential file.
Now install AWS CLI in your terraform workstation that will help to create making AWS profile and other staff. So if you are using linux then run the below commands and for others os visit the mentioned link. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-chap-install.html
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install
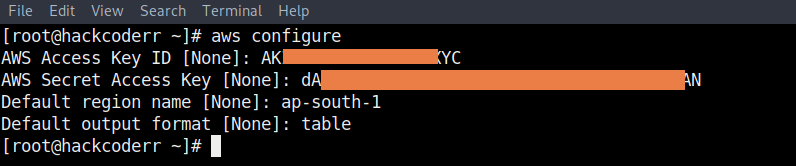
Now you can easily make an AWS CLI profile which we will use in aws.tf file as a profile. So let's see.
- First of all log in with AWS CLI.
aws configure
- After running the above command, give your
access key&secret keywhich you downloaded during the creating AWS IAM User.
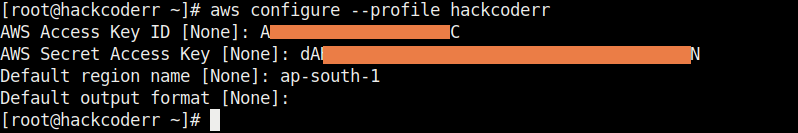
- Now run the below command to make your profile and the same is here, give your access and secret key.
aws configure --profile profilename
aws configure --list-profiles
Now time is to move towards terraform code so make your workspace. Note: I am following mentioned workspace for terraform staff for easy understanding so you also can follow this.
/root/hdp-project/terraform/aws/
- So create
aws.tffile inside above mentioned and write the below code.
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-south-1"
profile = "hackcoderr"
}
Here you can set any region at the place ap-south-1 according to your need and give your profile name instead of my profile hakcoderr.
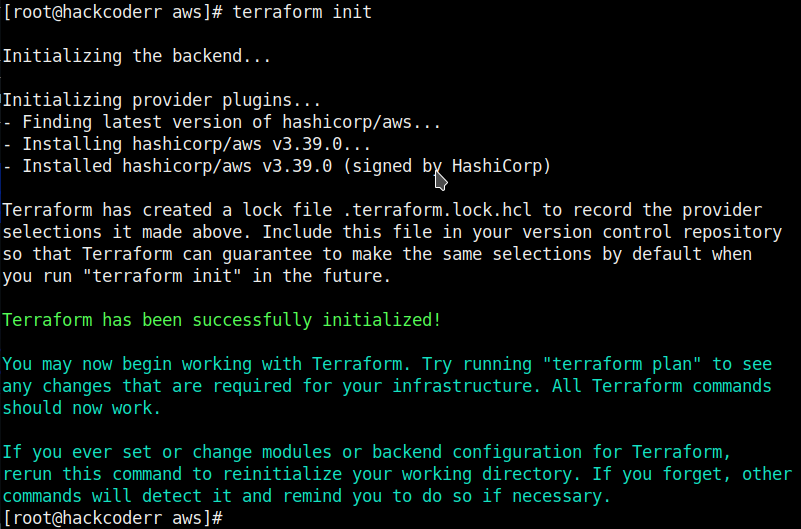
The terraform init command is used to initialize a working directory containing Terraform configuration files. This is the first command that should be run after writing a new Terraform configuration or cloning an existing one from version control. It is safe to run this command multiple times. You can initialize using terraform init.
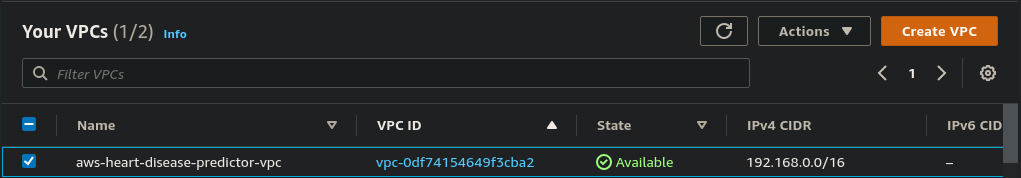
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) enables you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network closely resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS.
resource "aws_vpc" "vpc" {
cidr_block = "192.168.0.0/16"
instance_tenancy = "default"
enable_dns_support = "true"
enable_dns_hostnames = "true"
tags = {
Name = "aws-heart-disease-predictor-vpc"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
In the above code, you can choose Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) block range according to your desired and if you don't want to DNS support then you can write false to enable_dns_support. and give any tag as you want.
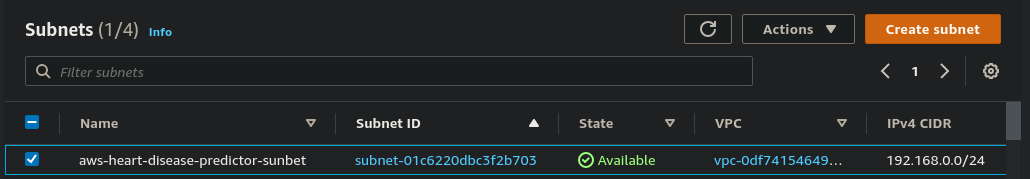
Subnetwork or subnet is a logical subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting. AWS provides two types of subnetting one is Public which allows the internet to access the machine and another is private which is hidden from the internet.
resource "aws_subnet" "subnet-1a" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
cidr_block = "192.168.0.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-south-1a"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "true"
tags = {
Name = "aws-heart-disease-predictor-sunbet"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
Here CIDR range should be under your VPC CIDR range otherwise it doesn't work and map_public_ip_on_launch is used to assign public IP to instance after launching, choose any availability_zone available your selected region. You can give tags for easy recognition after creating subnets.
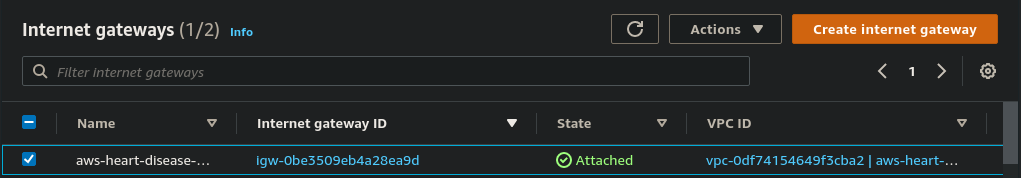
An internet gateway serves two purposes: to provide a target in your VPC route tables for internet-routable traffic and to perform network address translation (NAT) for instances that have been assigned public IPv4 addresses.
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "gw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
tags = {
Name = "aws-heart-disease-predictor-internet-gateway"
}
}
the above code will create your respective internet gateway. you need to specify on which VPC you want to create an internet gateway. Also, you can give a name using a tag block.
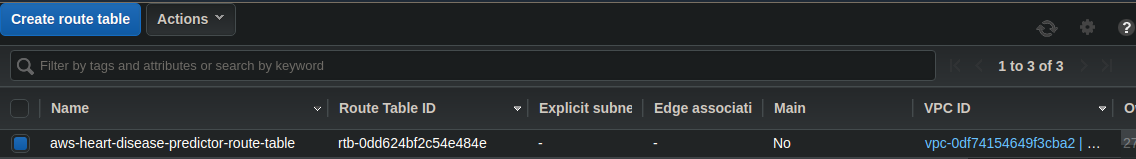
A routing table contains a set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic from your subnet or gateway is directed.
resource "aws_route_table" "route_table" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.vpc.id
route {
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.gw.id
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
}
tags = {
Name = "aws-heart-disease-predictor-route-table"
}
}
You need to create a routing table for the internet gateway you have created above. Here, I am allowing all the IP rage. So my ec2 instances can connect to the internet world. we need to give the vpc_id so that we can easily allocate the routing table to the respective VPC. You can specify the name of the routing table using a tag block.
We need to connect the routing table created for internet gateways to the respective subnets inside the vpc.
// Route Table Association
resource "aws_route_table_association" "route-association" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.route_table.id
}
You need to specify which subnets you want to take to the public world. As if the subnets get associated(connected) to the Internet Gateway it will be a public subnet. But if you don’t associate subnets to the Internet gateway routing table then it will be known as private subnets. The instances which are launched in the private subnet are not able to connect from outside as it will not having public IP, also it will not be connected to the Internet Gateway. You need to specify the routing table for the association of the subnets. If you don’t specify the routing table in the above association block then the subnet will take the vpc’s route table. So if you want to take the ec2 instances to the public world then you need to specify the router in the above association block. It's upon you which IP range you want your ec2 instances to connect. Here I have to give 0.0.0.0/0 means I can access anything from the ec2 instances.
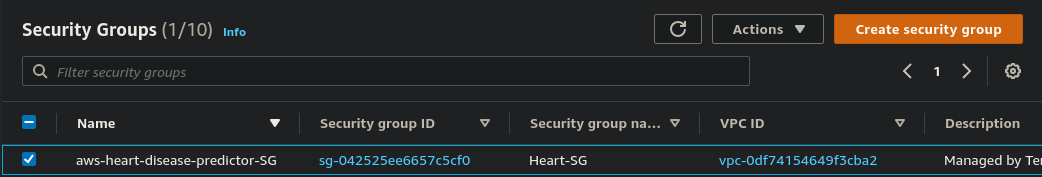
A security group acts as a virtual firewall for your EC2 instances to control incoming and outgoing traffic. If you don’t specify a security group, Amazon EC2 uses the default security group. You can add rules to each security group that allows traffic to or from its associated instances.
resource "aws_security_group" "SG" {
name = "Heart-SG"
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.vpc.id}"
ingress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags ={
Environment = "Production"
Name= "aws-heart-disease-predictor-SG"
}
}
The above will create a security group that works as a firewall. So which type of traffic want to engress& ingress you can set here. But I want to all types of traffic SO here I have given all traffic. -1 means all. from_port= 0 to_port=0 (0.0.0.0) that means we have disabled the firewall and(0.0.0.0/0) means all traffic I can able to access from this outbound rule. You can give the name of the respective Security Group.
An EC2 instance is nothing but a virtual server in Amazon Web services terminology. It stands for Elastic Compute Cloud. It is a web service where an AWS subscriber can request and provision a compute server in the AWS cloud. AWS provides multiple instance types for the respective business needs of the user.
resource "aws_instance" "Ansible_Controller_Node" {
ami = "ami-0a9d27a9f4f5c0efc"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id}"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.SG.id}"]
key_name = "key"
tags ={
Environment = "${var.environment_tag}"
Name= "Ansible_Controller_Node"
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "K8S_Master_Node" {
ami = "ami-04bde106886a53080"
instance_type = "t2.medium"
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id}"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.SG.id}"]
key_name = "key"
tags ={
Environment = "${var.environment_tag}"
Name= "K8S_Master_Node"
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "K8S_Slave1_Node" {
ami = "ami-04bde106886a53080"
instance_type = "t2.medium"
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id}"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.SG.id}"]
key_name = "key"
tags ={
Environment = "${var.environment_tag}"
Name= "K8S_Slave1_Node"
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "K8S_Slave2_Node" {
ami = "ami-04bde106886a53080"
instance_type = "t2.medium"
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id}"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.SG.id}"]
key_name = "key"
tags ={
Environment = "${var.environment_tag}"
Name= "K8S_Slave2_Node"
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "JenkinsNode" {
ami = "ami-0a9d27a9f4f5c0efc"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id}"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.SG.id}"]
key_name = "key"
tags ={
Environment = "${var.environment_tag}"
Name= "JenkinsNode"
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "DockerNode" {
ami = "ami-0a9d27a9f4f5c0efc"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.subnet-1a.id}"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.SG.id}"]
key_name = "key"
tags ={
Environment = "${var.environment_tag}"
Name= "DockerNode"
}
}
The above will launch EC2 instance so ami count and instance_type you can choose according to your desired and write tags as you want.
Note: If you want to see complete code at a time then go through my git repo. https://github.com/hackcoderr/heart-diseases-predictor/blob/master/terraform/aws/aws.tf
With your Terraform template created, the first step is to initialize Terraform. This step ensures that Terraform has all the prerequisites to build your template in Azure.
terraform init
The next step is to have Terraform review and validate the template. This step compares the requested resources to the state information saved by Terraform and then outputs the planned execution. The Azure resources aren't created at this point.
terraform plan
If everything looks correct and you're ready to build the infrastructure in Azure, apply the template in Terraform.
terraform apply
Once Terraform completes, your VM infrastructure is ready.
It's also a public cloud provider and provides resources and services as AWS provides. So hopefully, you have an idea about it otherwise you want to more about it then visit mentioned link. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsoft_Azure
Here, we have to also install Azure CLI for the Azure profile So that run the terraform code for azure. So If you're using RHEL, CentOS, or Fedora as a linux then run the below commands otherwise follow this link.
sudo rpm --import https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc
echo -e "[azure-cli]
name=Azure CLI
baseurl=https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/azure-cli
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc" | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/azure-cli.repo
sudo dnf install azure-cli -y
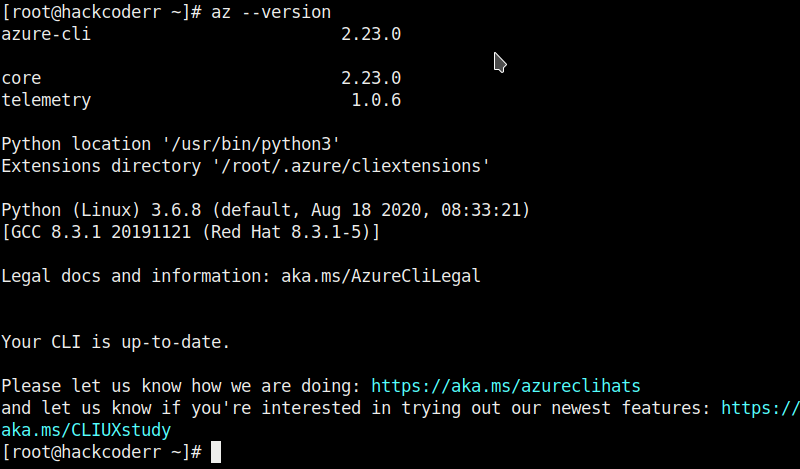
So let's check the Azure CLI version just for confirmation.
When we will work terraform, we have to provide the azure credentials for the Azure profile so that we can login with azure. so there are many ways to login with it and Azure CLI is one of them that I am going to use. So let's move ahead and login.
az login
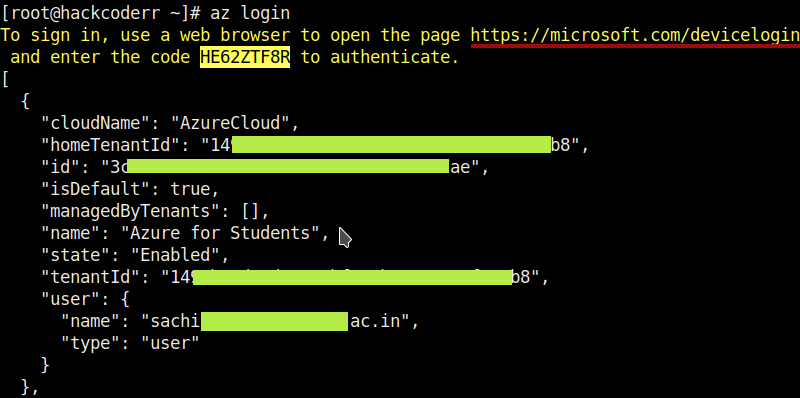
Note: If you get more than one subscription id then you can simply select one id with the below command.
az account set --subscription "My Demos"
So now time is to move towards writing the terraform code.
The provider section tells Terraform to use an Azure provider. It will use your azure credentials like subscription_id, client_id, client_secret, and tenant_id behind the scene.
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
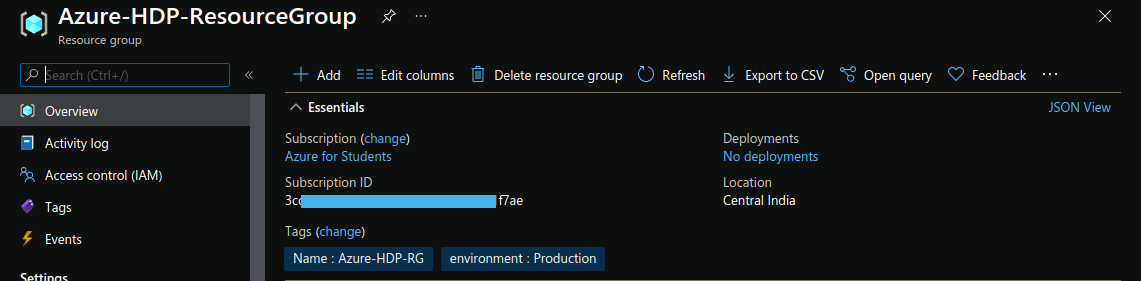
A resource group is a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. The resource group can include all the resources for the solution, or only those resources that you want to manage as a group.
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "hdp-rg" {
name = "Azure-HDP-ResourceGroup"
location = "Central India"
tags = {
Name = "Azure-HDP-RG"
environment = "Production"
}
}
The above section creates a resource group named Azure-HDP-ResourceGroup in the Central India location. But these things you can manage according to your desire.
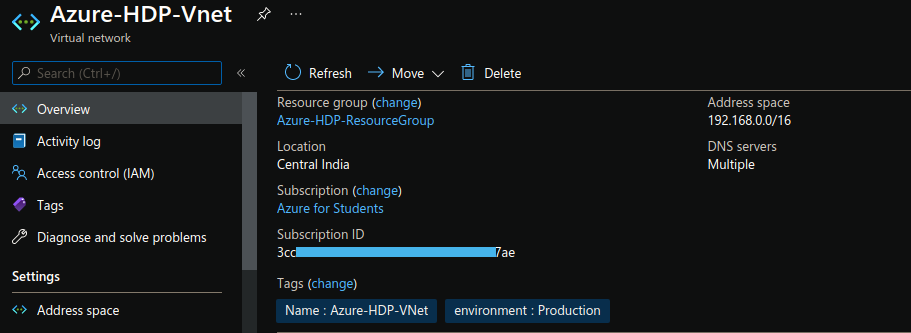
It has the same concept as AWS VPC so let understand the template code for it.
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "hdp-vnet" {
name = "Azure-HDP-Vnet"
address_space = ["192.168.0.0/16"]
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
tags = {
Name = "Azure-HDP-VNet"
environment = "Production"
}
}
The above section creates a virtual network named Azure-HDP-Vnet in the 192.168.0.0/16 address space.
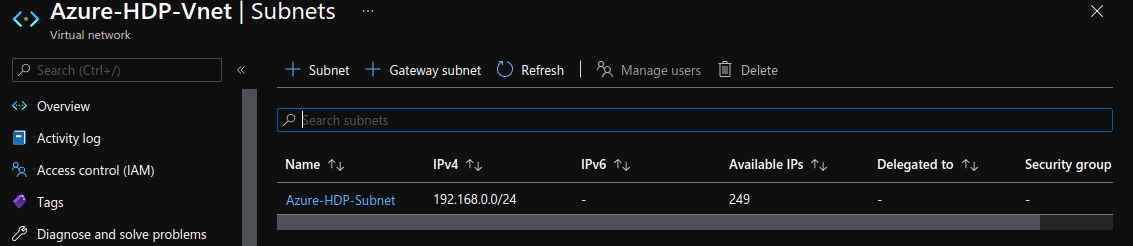
It also works as AWS Subnet so let's see code directly.
resource "azurerm_subnet" "hdp-subnet" {
name = "Azure-HDP-Subnet"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.hdp-vnet.name
address_prefixes = ["192.168.0.0/24"]
}
The above section creates a subnet named Azure-HDP-Subnet in the Azure-HDP-Vnet virtual network.
To access resources across the Internet, create and assign a public IP address to your VM. So I'm going to 3 VM's that's why I will need 3 Public IPs.
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "hdp-publicip-1" {
name = "Azure-HDP-PublicIP-1"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
allocation_method = "Dynamic"
tags = {
Name = "HDP-Public-IP-1"
environment = "Production"
}
}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "hdp-publicip-2" {
name = "Azure-HDP-PublicIP-2"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
allocation_method = "Dynamic"
tags = {
Name = "HDP-Public-IP-2"
environment = "Production"
}
}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "hdp-publicip-3" {
name = "Azure-HDP-PublicIP-3"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
allocation_method = "Dynamic"
tags = {
Name = "HDP-Public-IP-3"
environment = "Production"
}
}
The above section creates 3 public IP address named Azure-HDP-PublicIP-1 and so on.
Network Security Groups control the flow of network traffic in and out of your VM.
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "hdp-sg" {
name = "Azure-HDP-SG"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
security_rule {
name = "SSH"
priority = 1001
direction = "Inbound"
access = "Allow"
protocol = "Tcp"
source_port_range = "*"
destination_port_range = "22"
source_address_prefix = "*"
destination_address_prefix = "*"
}
tags = {
Name = "Azure-HDP-SG"
environment = "Production"
}
}
The above section creates a network security group named Azure-HDP-SG and defines a rule to allow SSH traffic on TCP port 22.
A virtual network interface card (NIC) connects your VM to a given virtual network, public IP address, and network security group.
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "hdp-nic-1" {
name = "myNIC-1"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
ip_configuration {
name = "myNicConfiguration"
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.hdp-subnet.id
private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"
public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.hdp-publicip-1.id
}
tags = {
Name = "HDP-NIC-1"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "hdp-nic-2" {
name = "myNIC-2"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
ip_configuration {
name = "myNicConfiguration"
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.hdp-subnet.id
private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"
public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.hdp-publicip-2.id
}
tags = {
Name = "HDP-NIC-2"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "hdp-nic-3" {
name = "myNIC-3"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
ip_configuration {
name = "myNicConfiguration"
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.hdp-subnet.id
private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"
public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.hdp-publicip-3.id
}
tags = {
Name = "HDP-NIC-3"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
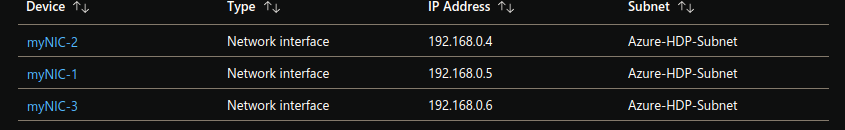
The above section in a Terraform template creates 3 virtual NIC named myNIC-1 and so no, connected to the virtual networking resources you've created.
Now you can connect your nic cards with the security group which you have created.
resource "azurerm_network_interface_security_group_association" "hdp-nic-sg-1" {
network_interface_id = azurerm_network_interface.hdp-nic-1.id
network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.hdp-sg.id
}
resource "azurerm_network_interface_security_group_association" "hdp-nic-sg-2" {
network_interface_id = azurerm_network_interface.hdp-nic-2.id
network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.hdp-sg.id
}
resource "azurerm_network_interface_security_group_association" "hdp-nic-sg-3" {
network_interface_id = azurerm_network_interface.hdp-nic-3.id
network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.hdp-sg.id
}
The above section in a Terraform template creates 3 security group associations connected to the nic cards you've created.
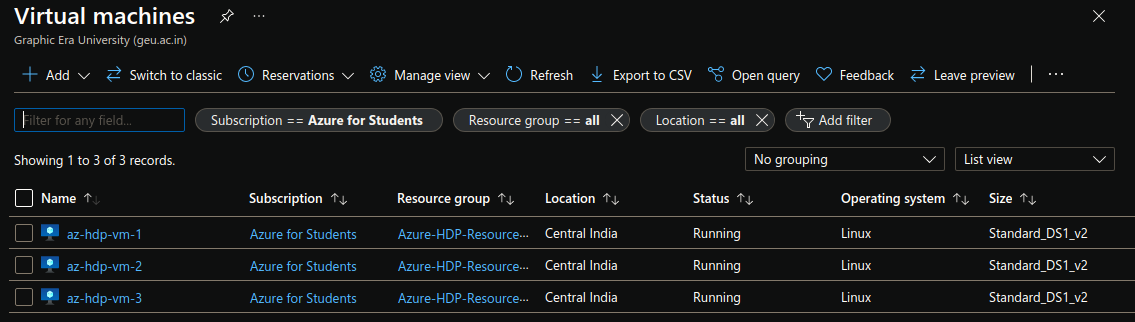
The final step is to create VMs and use all the resources created. So you see here 3 VMs named as az-hdp-vm-1 and so no.
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine" "main-1" {
name = "az-hdp-vm-1"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.hdp-nic-1.id]
vm_size = "Standard_DS1_v2"
delete_os_disk_on_termination = true
delete_data_disks_on_termination = true
storage_image_reference {
publisher = "RedHat"
offer = "RHEL"
sku = "8.1"
version = "latest"
}
storage_os_disk {
name = "hdp-disk-1"
caching = "ReadWrite"
create_option = "FromImage"
managed_disk_type = "Standard_LRS"
}
os_profile {
computer_name = "hostname"
admin_username = "hdpAdmin"
admin_password = "Password1234!"
}
os_profile_linux_config {
disable_password_authentication = false
}
tags = {
Name = "Az-HDP-Slave-1"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine" "main-2" {
name = "az-hdp-vm-2"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.hdp-nic-2.id]
vm_size = "Standard_DS1_v2"
delete_os_disk_on_termination = true
delete_data_disks_on_termination = true
storage_image_reference {
publisher = "RedHat"
offer = "RHEL"
sku = "8.1"
version = "latest"
}
storage_os_disk {
name = "hdp-disk-2"
caching = "ReadWrite"
create_option = "FromImage"
managed_disk_type = "Standard_LRS"
}
os_profile {
computer_name = "hostname"
admin_username = "hdpAdmin"
admin_password = "Password1234!"
}
os_profile_linux_config {
disable_password_authentication = false
}
tags = {
Name = "Az-HDP-Slave-2"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine" "main-3" {
name = "az-hdp-vm-3"
location = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.hdp-rg.name
network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.hdp-nic-3.id]
vm_size = "Standard_DS1_v2"
delete_os_disk_on_termination = true
delete_data_disks_on_termination = true
storage_image_reference {
publisher = "RedHat"
offer = "RHEL"
sku = "8.1"
version = "latest"
}
storage_os_disk {
name = "hdp-disk-3"
caching = "ReadWrite"
create_option = "FromImage"
managed_disk_type = "Standard_LRS"
}
os_profile {
computer_name = "hostname"
admin_username = "hdpAdmin"
admin_password = "Password1234!"
}
os_profile_linux_config {
disable_password_authentication = false
}
tags = {
Name = "Az-HDP-Slave-3"
Environment = "Production"
}
}
The above section creates 3 VMs named az-hdp-vm-1 and az-hdp-vm-2 and az-hdp-vm-3 and attaches the virtual NICs named myNIC-1, myNIC-2 and myNIC-3 respectlly. The latest RHEL 8.1 image is used, and a user named azureuser is created.
With your Terraform template created, the first step is to initialize Terraform. This step ensures that Terraform has all the prerequisites to build your template in Azure.
terraform init
The next step is to have Terraform review and validate the template. This step compares the requested resources to the state information saved by Terraform and then outputs the planned execution. The Azure resources aren't created at this point.
terraform plan
If everything looks correct and you're ready to build the infrastructure in Azure, apply the template in Terraform.
terraform apply
Once Terraform completes, your VM infrastructure is ready.
Here now, we have to create a machine learning model. As the dataset is of classification problem then we have to choose classification algorithms. Here i trained the model with Logistic Regression, RandomForestClassifier, DecisionTree Classsifier, GradientBoostingClassifier.
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
lr_model=LogisticRegression()
lr_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
lr_y_model= lr_model.predict(X_test)
lr_y_model
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print("Logistic Regression Accuracy: ", accuracy_score(y_test, lr_y_model))
Logistic Regression Accuracy: 0.9180327868852459/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/sklearn/linear_model/_logistic.py:765: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge (status=1):
STOP: TOTAL NO. of ITERATIONS REACHED LIMIT.
Increase the number of iterations (max_iter) or scale the data as shown in:
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/preprocessing.html
Please also refer to the documentation for alternative solver options:
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#logistic-regression
extra_warning_msg=_LOGISTIC_SOLVER_CONVERGENCE_MSG)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rfc_model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10000, max_depth=100)
rfc_model
rfc_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
rfc_y_pred = rfc_model.predict(X_test)
rfc_y_pred
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print("Random Forest Accuracy: ", accuracy_score(y_test, rfc_y_pred))
Random Forest Accuracy: 0.7704918032786885
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
dt_model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
dt_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
dt_y_pred=dt_model.predict(X_test)dt_y_pred
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print("Decision Tree Accuracy: ", accuracy_score(y_test, dt_y_pred))
Decision Tree Accuracy: 0.6721311475409836
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
GB_model = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=1000)
GB_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_GB = GB_model.predict(X_test)
y_pred_GB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_GB)
GradientBoostingClassifer Accuracy: 0.7868852459016393
From the above model creation and comparision Logistic Regression is giving much accuracy but i am taking model of Random Forest and saving it to .h5 extension.
import joblib
joblib_file = "LogisticRegression_Heart_Prediction.h5"
joblib.dump(lr_model, joblib_file)
This above code will create a file named RandomForest_Heart_Prediction.h5 and we have to use this model while create a docker image in which flask we have to install. Below is the code for dockerfile. Code link→
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1hr2igd-gjnjGn335g8VWosY5i1LuEDZY
Now we need to build the image using below dockerfile code.
FROM centos:latestRUN yum install python3 python3-devel gcc-c++ -y && \
python3 -m pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pip && \
yum install sudo -y && \
yum install --assumeyes python3-pip && \
pip install keras && \
pip install tensorflow --no-cache-dir tensorflow && \
pip install --upgrade pip tensorflow && \
pip3 install flask && \
pip3 install joblib && \
pip3 install sklearn && \
mkdir /heart_app && \
mkdir /heart_app/templatesCOPY LogisticRegression_Heart_Prediction.h5 /heart_app
COPY app.py /heart_app
COPY myform.html /heart_app/templates
COPY result.html /heart_app/templates
EXPOSE 4444
WORKDIR /heart_app
CMD export FLASK_APP=app.py
ENTRYPOINT flask run --host=0.0.0.0 --port=4444
To build the docker image use below command. docker build -t image_name:version .
https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/hackcoderr/heart-diseases-predictor
Ansible is an open-source software provisioning, configuration management, and application-deployment tool enabling infrastructure as code.
I'm going to install an ansible setup AWS Instance named ansible-controller-node which I have launched before. So run mentioned commands.
sudo yum install python3 git -y
git clone https://github.com/hackcoderr/Ansible-Setup.git
cd Ansible-Setup/
python3 script.py
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname ansible-controller
Note: If you want to know more about it then you can visit my Ansible Steup Repository.
Before creating playbooks we have create roles to manage the code properly. So, here i am creating three roles i.e master, slaves and jenkins configuration. you can create roles via below commands:
ansible-galaxy init master # master role
ansible-galaxy init slaves # slave role
ansible-galaxy init jenkins # jenkins role
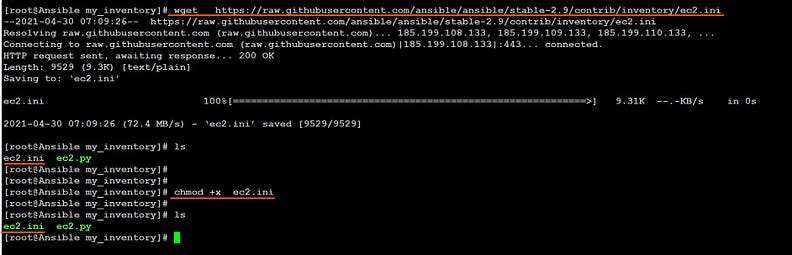
Now create a directory eg. /myinventory in Ansible controller node. and you need use dynamic inventory plugins. using wget command download the ec2.py and ec2.ini plugins inside /myinventory folder.
This 👇 command will create a ec2.py dynamic inventory file
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible/stable-2.9/contrib/inventory/ec2.py
This 👇 command will create a ec2.ini dynamic inventory file
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible/stable-2.9/contrib/inventory/ec2.ini
You need to make executable those two above files
chmod +x ec2.py
chmod +x ec2.ini
You need to give below inputs inside ec2.ini file.
aws_region='ap-south-1'
aws_access_key=XXXX
aws_secret_access_key=XXXX
After that export all these commands so boto can use this commands freely.
export AWS_REGION='ap-south-1'
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=XXXX
export AWS_ACCESS_SECRET_KEY=XXXX
Now we have to edit inside ec2.py file. This file written in python 2 but we are using python 3 so we need to edit the header.
#!/usr/bin/python3
Updating ec2.py file from python to python3.

Install boto and boto3 libraries so ansible can connect to aws services and launch the respective services. To install boto and boto3 using below command.
pip3 install boto # installing boto
pip3 install boto3 # installing boto3
[defaults]
inventory= /my_inventory
host_key_checking=false
ask_pass=false
remote_user=ubuntu
private_key_file=/root/mykey.pem
command_warnings=False
[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
Note: Here, we have given remote_user=ubuntu because the master and slaves of the kuberenetes cluster is launched via ubuntu image. The main reson to use ubuntu image is due to we are using crio as a intermediate container runtime engine. Only ubuntu supports the repo for crio installation. Therefore we are using ubuntu image.
Now this ansible.cfg file will helps us to configure instances on AWS dynamically. inventory=/myinventory (it includes ec2.ini and ec2.py) files. private_key_file should be the key in .pem format of the instances. host_key_checking=false will allow to give proper ssh connection. privilege_escalation should be concluded in the ansible.cfg file to configure the system using sudo power. Your ansible.cfg file will look like this below snip.
Now first we have to configure Master node and then slave nodes. To configure crio in ubuntu i have created a script from below codes and saved into crio.sh and save in a /root/ directory.
OS=xUbuntu_20.04
VERSION=1.20cat >>/etc/apt/sources.list.d/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable.list<<EOF
deb https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable/$OS/ /
EOFcat >>/etc/apt/sources.list.d/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable:cri-o:$VERSION.list<<EOF
deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable:/cri-o:/$VERSION/$OS/ /
EOFcurl -L https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable/$OS/Release.key | apt-key --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/libcontainers.gpg add -curl -L https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable:cri-o:$VERSION/$OS/Release.key | apt-key --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/libcontainers-cri-o.gpg add -
# First we have to copy the crio.sh cript to master node and run it to configure crio in master.
- name: "Copying Script to K8S Master Node"
copy:
src: "/root/crio.sh"
dest: "/root/"
# Running crio.sh script
- name: "running script"
shell: "bash /root/crio.sh"
register: crioscript
- debug:
var: crioscript.stdout_lines# updating packages
- name: "Updating apt"
shell: "apt update"
ignore_errors: yes
register: yumupdate
- debug:
var: yumupdate.stdout_lines# installing crio
- name: "Instlling CRIO"
shell: "apt install -qq -y cri-o cri-o-runc cri-tools"
ignore_errors: yes
register: crioinstall
- debug:
var: crioinstall.stdout_lines# reloading daemon
- name: "Reloading System and CRIO"
shell: "systemctl daemon-reload"# enabling and starting crio
- name: "enabling CRIO"
shell: "systemctl enable --now crio"
ignore_errors: yes
register: criostart
- debug:
var: criostart.stdout_lines# Configuring repo for Kubeadm Installing Kubeadm
- name: "Installing KubeAdm"
shell: |
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -
apt-add-repository "deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main"
apt install -qq -y kubeadm=1.20.5-00 kubelet=1.20.5-00 kubectl=1.20.5-00
ignore_errors: yes
register: kubeadminstall
- debug:
var: kubeadminstall.stdout_lines# Creating a overlay network
- name: "Adding Overlay Network"
shell: |
cat >>/etc/modules-load.d/crio.conf<<EOF
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
ignore_errors: yes
register: overlay# adding filters to overlay network
- name: "Creating Overlay and Netfilter"
shell: "modprobe overlay"
- shell: "modprobe br_netfilter"
ignore_errors: yes# enabling iptables by changing values to 1
- name: "Chnaging Iptables values to 1"
shell: |
cat >>/etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf<<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
ignore_errors: yes# running sysctl --system
- name: "Running sysctl --system"
shell: "sysctl --system"
register: sysctl
- debug:
var: sysctl.stdout_lines# changing cgroup drivers to pod
- name: "Chnaging group drivers"
shell: |
cat >>/etc/crio/crio.conf.d/02-cgroup-manager.conf<<EOF
[crio.runtime]
conmon_cgroup = "pod"
cgroup_manager = "cgroupfs"
EOF# reloading daemon
- name: "Reloading System and CRIO"
shell: "systemctl daemon-reload"
ignore_errors: yes# enabling crio
- name: "enabling crio"
shell: "systemctl enable --now crio"
ignore_errors: yes# restarting crio
- name: "Restarting CRIO"
shell: "systemctl restart crio"
ignore_errors: yes# changing fstab and disabling firewall
- name: "Changing Fstab and disable ufw"
shell: |
sed -i '/swap/d' /etc/fstab
swapoff -a
systemctl disable --now ufw
ignore_errors: yes# Restarting kubelet
- name: "restarting kubelet"
shell: "systemctl restart kubelet"# initializing master node with cidr 192.168.0.0/16
- name: "Initilaizing Master"
shell: "kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.1.86 --pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16 --ignore-preflight-errors=NumCPU --ignore-preflight-errors=Mem"
ignore_errors: yes
register: master
- debug:
var: master.stdout_lines- name: "Creating .kube directory"
shell: "mkdir -p $HOME/.kube"- name: "Copying /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config"
shell: "sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config"- name: "changing owner permission"
shell: "sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config"# creating calico overlay network to create a connection between the master and slave nodes
- name: "Using Calico as Overlay Network"
shell: "kubectl --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf create -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.18/manifests/calico.yaml"
ignore_errors: yes
register: callico
- debug:
var: callico.stdout_lines# generating token
- name: "Printing token"
shell: "kubeadm token create --print-join-command"
register: token- debug:
var: token.stdout_lines
# First we have to copy the crio.sh cript to master node and run it to configure crio in slaves.
- name: "Copying Script to K8S Master Node"
copy:
src: "/root/crio.sh"
dest: "/root/"# running crio.sh script
- name: "running script"
shell: "bash /root/crio.sh"
register: crioscript
- debug:
var: crioscript.stdout_lines# updating packages
- name: "Updating apt"
shell: "apt update"
ignore_errors: yes
register: yumupdate
- debug:
var: yumupdate.stdout_lines# Installing Crio
- name: "Instlling CRIO"
shell: "apt install -qq -y cri-o cri-o-runc cri-tools"
ignore_errors: yes
register: crioinstall- debug:
var: crioinstall.stdout_lines# Reloading Deamon
- name: "Reloading System and CRIO"
shell: "systemctl daemon-reload"# enabling crio
- name: "enabling CRIO"
shell: "systemctl enable --now crio"
ignore_errors: yes
register: criostart
- debug:
var: criostart.stdout_lines# installing and configuring repo for kubeadm
- name: "Installing KubeAdm"
shell: |
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -
apt-add-repository "deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main"
apt install -qq -y kubeadm=1.20.5-00 kubelet=1.20.5-00 kubectl=1.20.5-00
ignore_errors: yes
register: kubeadminstall
- debug:
var: kubeadminstall.stdout_lines# creating overlay network
- name: "Adding Overlay Network"
shell: |
cat >>/etc/modules-load.d/crio.conf<<EOF
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
ignore_errors: yes
register: overlay# adding filters to overlay network
- name: "Creating Overlay and Netfilter"
shell: "modprobe overlay"
- shell: "modprobe br_netfilter"
ignore_errors: yes# enabling iptables by changing values to 1
- name: "Chnaging Iptables values to 1"
shell: |
cat >>/etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf<<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
ignore_errors: yes# running sysctl --system
- name: "Running sysctl --system"
shell: "sysctl --system"
register: sysctl
- debug:
var: sysctl.stdout_lines# changing cgroup drivers to pod
- name: "Changing group drivers"
shell: |
cat >>/etc/crio/crio.conf.d/02-cgroup-manager.conf<<EOF
[crio.runtime]
conmon_cgroup = "pod"
cgroup_manager = "cgroupfs"
EOF# pulling images using kubeadm
- name: "Pulling Images using KubeAdm"
shell: "kubeadm config images pull"
changed_when: false
register: kubeadm
- debug:
var: kubeadm.stdout_lines# reloading daemon
- name: "Reloading System and CRIO"
shell: "systemctl daemon-reload"
ignore_errors: yes# enabling crio
- name: "enabling crio"
shell: "systemctl enable --now crio"
ignore_errors: yes# restarting crio
- name: "Restarting CRIO"
shell: "systemctl restart crio"
ignore_errors: yes# changing fstab and disabling firewall
- name: "Changing Fstab and disable ufw"
shell: |
sed -i '/swap/d' /etc/fstab
swapoff -a
systemctl disable --now ufw
ignore_errors: yes# Restarting kubelet
- name: "restarting kubelet"
shell: "systemctl restart kubelet"# Joining Slaves with token
- name: "Joining Slaves to Master Node"
shell: "{{ master_token }}"
ignore_errors: yes
register: init
- debug:
var: init.stdout_lines
---
# tasks file for jenkins# copying jdk file in jenkins node
- name: "Copying Jdk file to jenkins Node"
copy:
src: "/root/jdk-8u281-linux-x64.rpm"
dest: "/root/"
ignore_errors: yes# copying jenkins file to jenkins node
- name: "Copying Jenkins file to jenkins Node"
copy:
src: "/root/jenkins-2.282-1.1.noarch.rpm"
dest: "/root/"
ignore_errors: yes# Installing JDK
- name: "Installing JDK"
shell: "rpm -ivh /root/jdk-8u281-linux-x64.rpm"
ignore_errors: yes
register: jdk
- debug:
var: jdk.stdout_lines# Installing Jenkins
- name: "Installing Jenkins"
shell: "rpm -ivh /root/jenkins-2.282-1.1.noarch.rpm"
ignore_errors: yes
register: jenkins
- debug:
var: jenkins.stdout_lines# Staring jenkins
- name: "Starting Jenkins Server"
shell: "systemctl start jenkins"# enabling jenkins
- name: "enabling Jenkins Server"
shell: "systemctl enable jenkins"
Now the mainplaybook will contains the roles of master, slaves and jenkins respectively.
# Configuring master node
- hosts: ["tag_Name_K8S_Master_Node"]
roles:
- name: "Configuring Master Node"
role: "/root/roles/master"# Configuring slaves node
- hosts: ["tag_Name_K8S_Slave1_Node", "tag_Name_K8S_Slave2_Node"]
vars_prompt:
- name: "master_token"
prompt: "Enter Token To Join To Master: "
private: no
roles:
- name: "Configuring Slave Node"
role: "/root/roles/slaves"# Configuring jenkins node
- hosts: ["tag_Name_JenkinsNode"]
remote_user: "ec2-user"
roles:
- role: "/root/roles/jenkins"
You can run the mainplaybook.yml using ansible-playbook mainplaybook.yml
Now login to jenkins jenkins node using public_ip:8080. We need to set the password for jenkins node intially. This process needed to be done only once. You will be landed on this page and it will ask for password.
copy the /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword the location and using cat command you can take the passowrd like this in the below image.
Now copy the password and pate in the Administrator password section and then click on continue.
After that you need to create a password because this password is too long and hard to remember. So below are the steps shown in the video to create the password and to install the restive plugins. Ensure that you have to install below plugins.
Plugins from below lists needed to be installed:
ssh: ssh plugins need to install for connecting the kubernetes servers.Gihub: Github plugins need to install to us SCM services.Pipeline: Pipline plugin will helps you to automate the jobs and make your setup easy.Multibranch pipeline: Multibranch pipeline plugin will helps you to pulls the code from different branches. In this project i have created two branch i.e main(default) and developer branch. The code should be in both the branch inJenkinsfilenamed file. So multibranch will scan the repository and both the branches and will pull the code and create jobs with names “main” job and “developer” job. If developer branch job run successfully then and if main branch wants to commit then they can.
Now you have to create a repository in github and add the pipeline code in that repo inside Jenkinsfile.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('BuildingHeartPrectionPod'){
steps {
sh 'sudo kubectl create deployment mlopsheartpred --image=hackcoderr/heart-diseases-predictor:v1 --kubeconfig /root/admin.conf'
sh 'sudo kubectl expose deployment mlopsheartpred --type=NodePort --port=4444 --kubeconfig /root/admin.conf'
sh 'sudo kubectl get pod -o wide --kubeconfig /root/admin.conf'
}
}
stage('gettingpod'){
steps {
sh 'sudo kubectl get pod -o wide --kubeconfig /root/admin.conf'
sh 'sudo kubectl get svc --kubeconfig /root/admin.conf'
}
}
}
}
Now we need to copy the url of repository and you have to create a new job with multibranch pipeline and you need to to add source “git” and paste the url and save the job.
Now you can access the webapp with the public ip of the slave node and with the exposed port.
Visit on my web app to see the result http://13.234.21.125:31207/home
So fill the required stuff and check your heart health.