Simple Django Rest Framework (sdrf) is django based app used to provide abstraction that combines both django rest framework with drf_yasg a swagger generator to implement good looking and well documented apis using djang
- assuming you already have a django project that you need to add this app to you need to start with installing the package using
pip install sdrf
- install required apps to INSTALLED_APPS in django settings
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
"rest_framework",
"drf_yasg",
'sdrf',
]- add swagger docs url to your project urls
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path,include
urlpatterns = [
...
path('',include('sdrf.urls'))
]- check out if everything is okay by visting default swagger docs url at
http://<your-project-url>/rest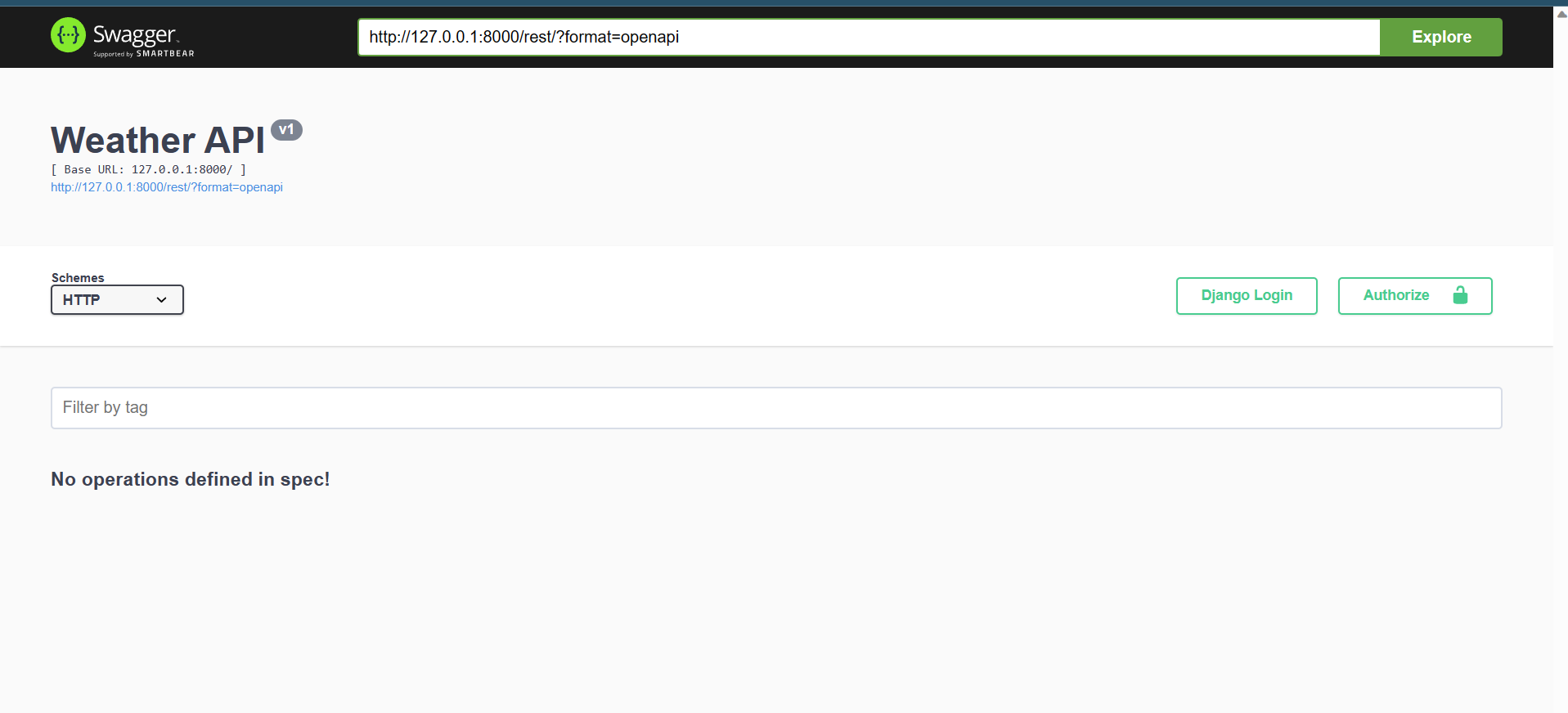
now you have an rest app up and running you can configure it as you want. addtionally for django rest framework configuration and drf_yasg configuration you have our sdrf configs you can make with these default values
| config variable name | default value | description |
|---|---|---|
| REST_APP_NAME | Weather API |
the app name used in swagger docs view |
| REST_APP_VERSION | v1 |
the api version used in swagger docs view |
| REST_APP_CREATOR | {'name': '','email': '','url': ''} |
the contact information for communicating the rest app creator used in swagger docs view |
| REST_APP_BASE_URL | rest/ |
the base url that the swagger docs will be viewd on and a prefix for default api endpoint |
- assuming you have an django app that already exsist create and an API endpoint class that inheiret APIEndPoint class for example see out hello world here
from sdrf.api_endpoint import APIEndpoint
from sdrf.endpoint_config import APIEndpointConfig
class HelloEndPoint(APIEndpoint):
def configure(self, config: APIEndpointConfig) -> APIEndpointConfig:
...
return config
@staticmethod
def execute(request: Request, *args, **kwargs) -> Response:
name = request.query_params.get('name')
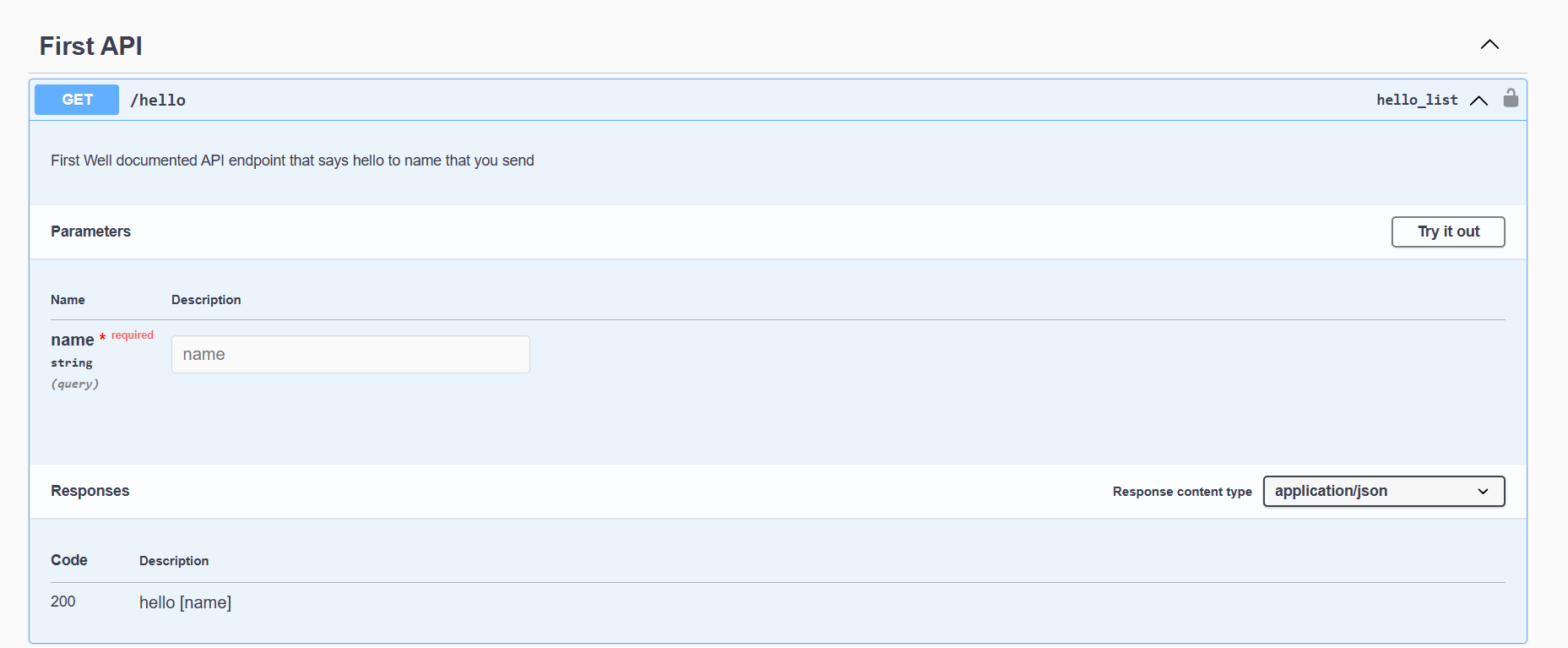
return HttpResponse(f'Hello {name}')- configure your api endpoint using configure method, in this method you have all sort of configuration that you can configure for your rest api even the auhentication and authorization configurations, http method, routing, and swagger view configs simplified with easy and nice looking config code
from sdrf.api_endpoint import APIEndpoint
from sdrf.endpoint_config import APIEndpointConfig
class HelloEndPoint(APIEndpoint):
def configure(self, config: APIEndpointConfig) -> APIEndpointConfig:
config.name = 'Hello Rest!'
config.description= """
First Well documented API endpoint that says hello to name that you send
"""
config.endpoint= 'hello'
config.http_method = 'GET'
config.set_response(200,'hello [name]')
config.add_parameter('name',self.DataType.STRING,self.ParameterTypes.QUERY_PARAM)
config.add_tag('First API')
return config
@staticmethod
def execute(request: Request, *args, **kwargs) -> Response:
name = request.query_params.get('name')
return HttpResponse(f'Hello {name}')- finally add your api endpoint to your app urls using as_url static method
from .views import HelloEndPoint
urlpatterns = [
HelloEndPoint.as_url()
]- check your output and test your api in the swagger view
just like you would do in normal django rest framework and make ViewSet you dont need to learn anything new to that but instead of inherting rest_framework.viewsets.ModelViewSetyou will inherit ourModelEndPoint`like that
from .models import Person,PersonSeralizer
from sdrf.model_endpoint import ModelEndPoint
...
class PersonEndPoint(ModelEndPoint):
queryset = Person.objects.all()
serializer_class = PersonSeralizerthen simply make it as urls in urls.py
from .views import PersonEndPoint
urlpatterns = [
...
PersonEndPoint.as_urls(),
]