Living Robots, is the Github repository for the new Ebook "Living Robots with EV3".
"Living Robots with EV3" is a ebook designed to learn about development of Robots with modern techniques and technologies. The book put the focus in the platform Lego Mindstorms EV3.
If you enjoyed the previous ebook (http://juanantonio.info/lejos-ebook/) then book your copy now: http://juanantonio.info/about.htm
05/04/2014: First commit
05/25/2014: RPLIDAR Support for LeJOS
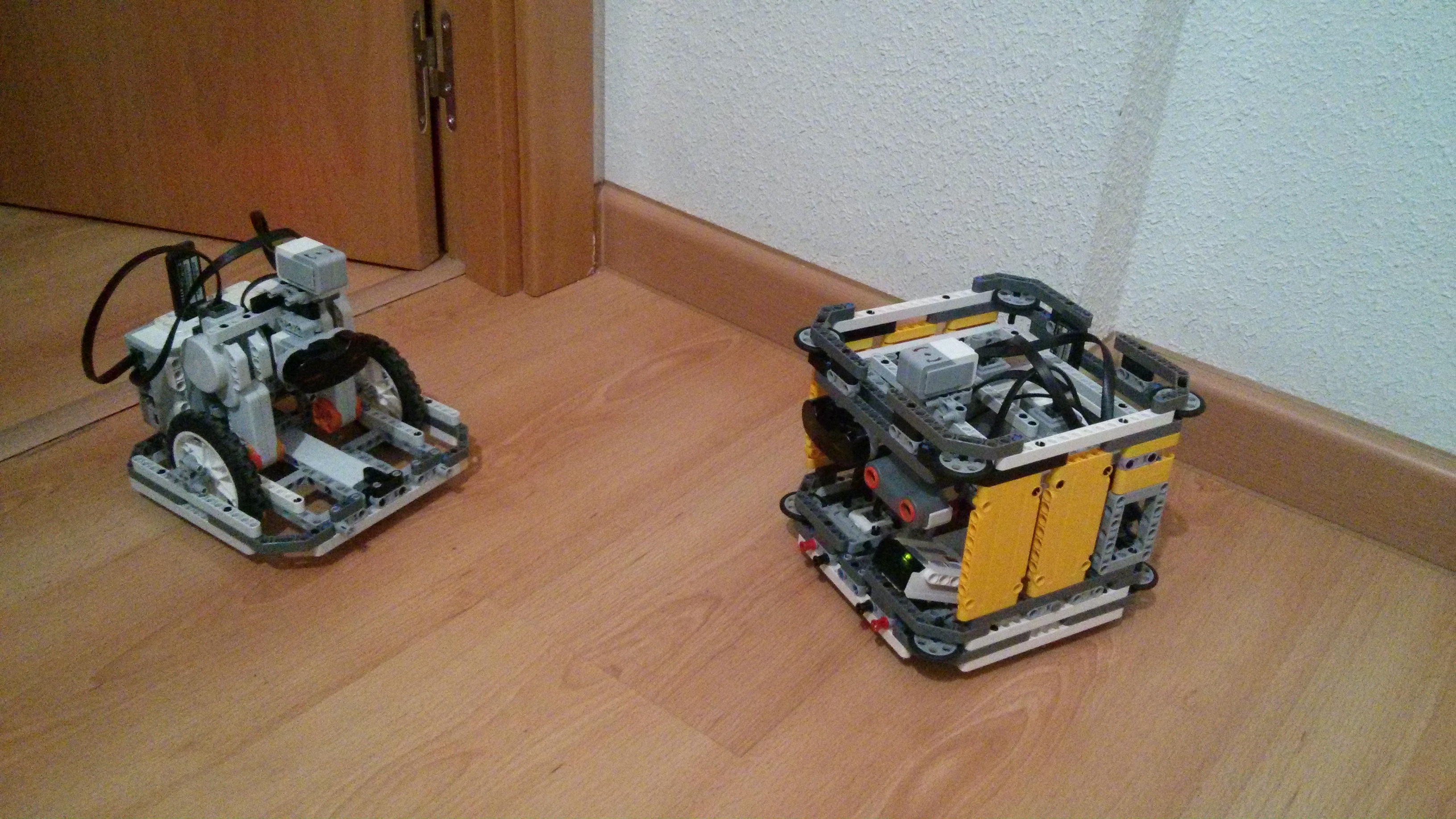
04/26/2015: 2 Britys tries to communicate.
Last release: 1/6/2014
Download: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/raw/master/chapter0/docs/LRWE_Chapter0.pdf
Read the following docs to install leJOS in your EV3 Brick:
http://sourceforge.net/p/lejos/wiki/Getting%20started%20with%20leJOS%20EV3/ http://sourceforge.net/p/lejos/wiki/Creating%20a%20bootable%20SD%20card/ http://www.lejos.org/ev3/docs/
After you have installed leJOS on your PC, you will need to create an SD card. To do this you need an empty SD card with a FAT32 partition of at least 200MB. The card itself should be at least 1GB and no more than 32GB. SDXC cards are not supported by the EV3 hardware. If your card does not have a FAT32 partition, you can use a partition utility to reformat it as FAT32, or write the sd500.img file in the sd500.zip file (which is part of the distribution) to the disk as an image file (using dd or a disk image writing utility). You should then unzip the lejosimage.zip file from the leJOS home directory to the root directory of the card, and download and copy the Oracle JRE .tar.gz file to the card. The file is available at http://java.com/legomindstorms You should use the Java 7 version at this release. You will need to create a free Oracle account, if you do not have one. When you have written these files to the card, safely remove it, put it in the EV3 and boot the EV3. leJOS will then reformat your card to have a 500MB FAT32 partition and a Linux ext2 partition using the rest of the card. It will prepare the card for use by leJOS showing you its progress as it goes. This process takes about 8 minutes.
Once, you have LeJOS installed in your MicroSD, add it and plug your Wifi dongle and turn on. In this case, EV3 Brick will detect the MicroSD with a OS and LeJOS will run.
Once you have a EV3 brick running leJOS with a WIFI Dongle (For exampe a Netgear WNA 1100), turn on the brick and connect with your computer using a USB wire. Open a shell window and type:
ssh root@10.0.1.1
root@10.0.1.1's password:
root@(none):/etc# adduser lejos
adduser: /home/lejos: File exists
Changing password for lejos
Enter the new password (minimum of 5, maximum of 8 characters)
Please use a combination of upper and lower case letters and numbers.
Enter new password:
Bad password: too short.
Warning: weak password (continuing).
Re-enter new password:
Password changed.
root@(none):/etc#
If you need to execute a command with root priviligies, you could use the following example:
soulFactory:bin jabrena$ ssh lejos@10.0.1.1
lejos@10.0.1.1's password:
lejos@(none):~$ su -c /sbin/reboot
Password:
Broadcast message from root (pts/0) (Sun Nov 2 22:31:21 2014):
The system is going down for reboot NOW!
lejos@(none):~$ Connection to 10.0.1.1 closed by remote host.
Connection to 10.0.1.1 closed.
lejos@(none):~/programs$ su -c "jrun -jar HelloWorld.0.1.jar"
Password:
Hello World
##### Set up your WIFI connection
To configurate your WIFI connection edit the file wpa_supplicant.conf
path: /home/root/lejos/bin/utils
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant
network={
ssid="YOUR_SSID"
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
psk=YOUR_PSK
}
if your computer is not able to create a psk, use the following online tool: https://www.wireshark.org/tools/wpa-psk.html
later, execute the following command: /home/root/lejos/startwlan
root@(none):~/lejos/bin# ./startwlan
Start WiFi...
Check configuration...
hostname is (none)
searching for wlan
using lejos config
wpa_state=DISCONNECTED
Searching for AP...
wpa_state=ASSOCIATING
Searching for AP...
wpa_state=COMPLETED
bssid=58:23:8c:03:6f:cc
ssid=YOUR_SSID
Request IP address...
udhcpc (v1.13.2) started
Sending discover...
Sending select for 192.168.0.13...
Lease of 192.168.0.13 obtained, lease time 3600
adding dns 62.81.16.213
adding dns 62.81.29.254
Once you have a WIFI connection with your Router, you connect with your EV3 brick using the IP, in this case: 192.168.0.13
ssh root@192.168.0.13
root@192.168.0.13's password:
Clone this GIT repository and install Eclipse IDE to import the following project:
https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/tree/master/chapter8/ev3/HelloWorldWSS
Once you have the example in your eclipse, run ANT file to install the application in your brick and the web application.
Open a shell terminal and execute ssh to connect with your EV3 Brick. In the path: /home/lejos/programs/ execute the following command:
lejos@(none):~/programs$ jrun -jar HelloWorld.0.1.jar
lejos@(none):~$ su -c "jrun -jar HelloWorld.0.1.jar"
lejos@(none):~/programs$ su -c "jrun -jar HelloWorld.0.1.jar demo"
Open your web browser Chrome and type:
http://192.168.0.13/HelloWorld/
Connect with your EV3 Brick and Speak with it. Enjoy!!!
Example: A set of Examples evolving the class HelloWorld
Example: A program using LeJOS API
Example: Example running a Web Socket Server
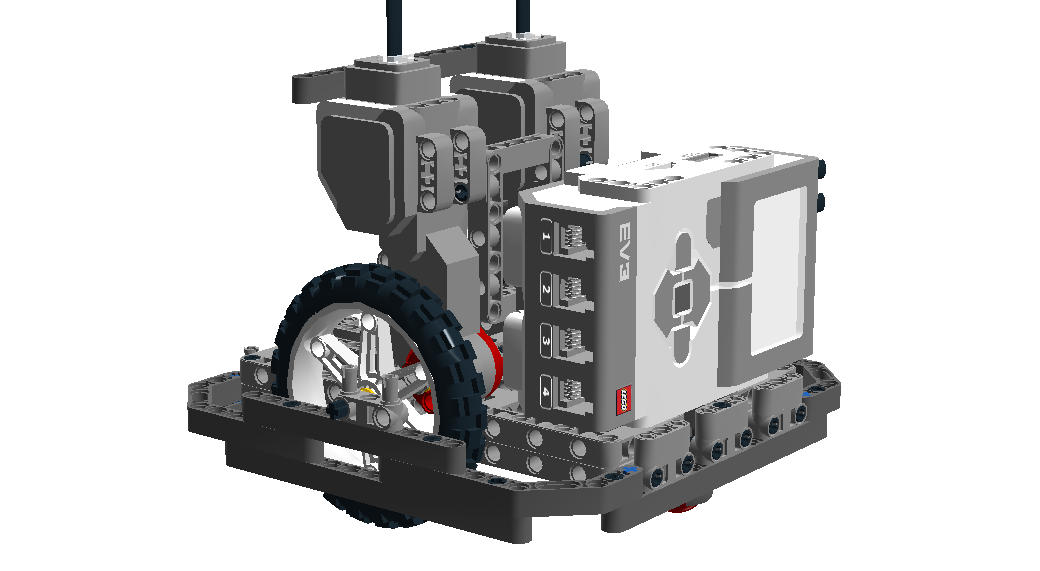
In the first stages, you don't need to use a robot structure to follow the book. I recommend that you have:
Specifications:
1x Lego Mindstorms EV3 Brick + EV3 Rechargable battery + Netgear WNA 1100
1x Smartphone + Chrome Web browser
1x Computer (A better experience with MAC OS or Ubuntu)
Specifications:
1x Lego Mindstorms EV3 Brick + EV3 Rechargable battery + USB Hub + Netgear WNA 1100
1x Hitechnic Compass sensor
1x EV3 IR Sensor
1x Arduino One + Arduino Proto shield + Dexter breadboard adapter
1x Robopeak RPLIDAR
1x Smartphone + Chrome Web browser
Pending
In this chapter, we will cover the most popular and useful sensors compatible with EV3 Brick.
### Exteroceptors sensors
Exteroceptors are sensors that measure the positional or force-type interaction of the robot with its environment.
Sensors tested:
Robopeak RPLIDAR
EV3 IRSensor
Hitechnic Compass Sensor
Dexter GPS
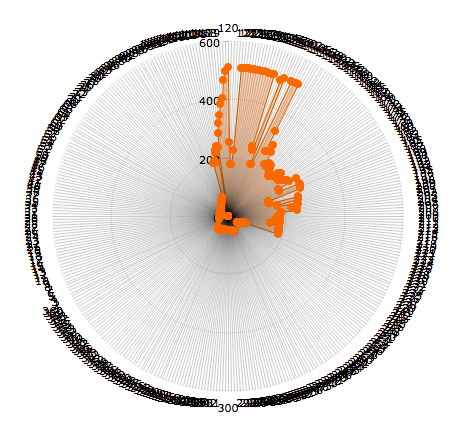
RPLIDAR is a low cost 360 degree 2D laser scanner (LIDAR) solution developed by RoboPeak. The system can perform 360 degree scan within 6 meter range. The produced 2D point cloud data can be used in mapping, localization and object/environment modeling.
RPLIDAR Arduino Library: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/raw/master/chapter3/arduino/RPLIDAR/Driver/RPLidarDriver_r1.0.zip
Arduino Sketch: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/blob/master/chapter3/arduino/RPLIDAR/Sketches/simple_connect6/simple_connect6.ino
LeJOS Sensor Class: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/blob/master/chapter3/ev3/java/RPLIDARTest/src/lejos/hardware/sensor/RPLIDARSensor.java
#### Data Visualization
I have added a simple example to generate a JSON file to view LIDAR data in a polar chart in any web browser.
http://192.168.0.101/Radar/amcharts/polarChart.htm
Proprioception in robotics means sensing the internal state of the robot or a part of it . For example the posture of a mechanical manipulator, leg or other jointed mechanism or the battery level.
Sensors tested:
EV3 Battery
Example: IRSensor to detect a Beacon
Example: The magic 8 ball using a EV3GyroSensor
Example: How to use the sensor RPLIDAR
Example: How to generate JSON data to view LIDAR data
Pending
In this chapter, user will learn basic concepts about Local & Global navigation
### Local navigation
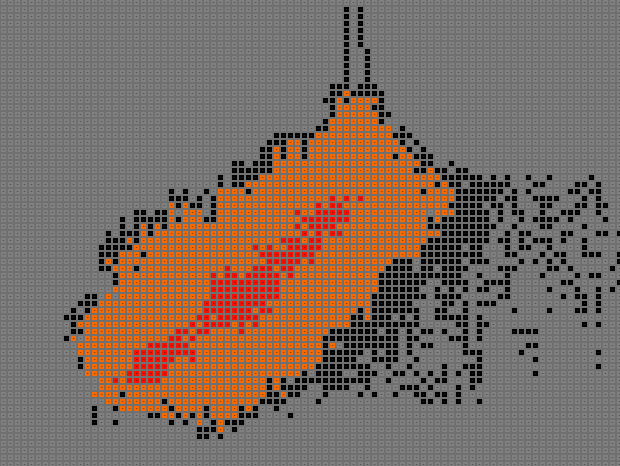
I am working in a better support for Occupancy grid map. Current leJOS support is poor and the implementation doesn't cover Bayes theory.
http://www.lejos.org/ev3/docs/lejos/robotics/mapping/OccupancyGridMap.html
To solve this Gap, I am trying to develop a better support to upgrade the class and add Bayes support using some papers as:
http://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/people/michael.wooldridge/teaching/robotics/lect05.pdf
Current solution start showing a real map about a real space using a EV3 Robot with a 2D LIDAR in few minutes.
http://192.168.0.101/ogm/index2.htm
I am thinking in some kind of solution to export the map to use later in next session. User could choose the map using some kind of web tool.
http://www.cs.mcgill.ca/~hsafad/robotics/
https://code.google.com/p/deadreckoning/
http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/device/orientation/deviceorientationsample.html
http://www.albertosarullo.com/demos/accelerometer/
http://perso-etis.ensea.fr/~pierandr/cours/M1_SIC/AN3397.pdf
http://letsmakerobots.com/content/dead-reckoning-algorithms-solutions
http://www.cs.bris.ac.uk/Publications/Papers/2000009.pdf
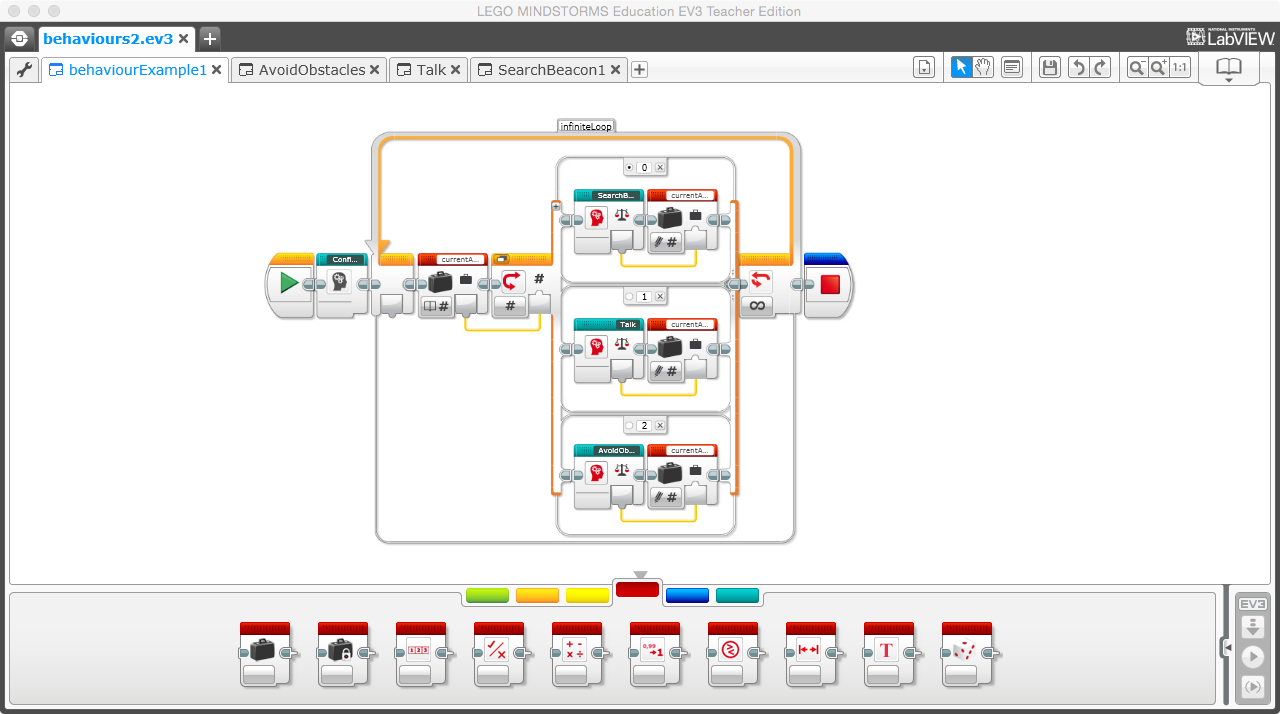
Using EV3G, is possible to develop behaviours.
Example: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/blob/master/chapter6/ev3/ev3g/behaviours2.ev3
Example: http://sourceforge.net/p/lejos/ev3/ci/master/tree/EV3BumperCar/src/EV3BumperCar.java
### Deliberative Control
The behaviours are modelled with a HFSM using Apache Commons SCXML.
Examples: https://github.com/jabrena/liverobots
Example: Simple bumper car
Example: Track color objects with your Smarphone
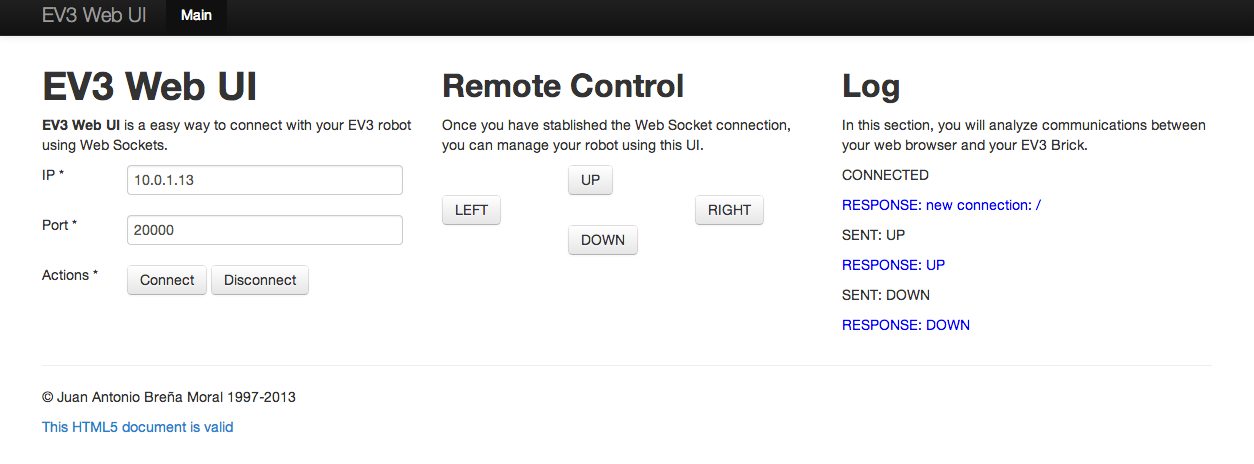
In this Chapter, the reader will learn many stuff about Web Servers and Web interfaces for robots with EV3 Brick.
In this section, user will learn the different among httpd and other developments in Java to run a Web Server as NanoWeb server.
root@(none):~# start-stop-daemon -K -n httpd
stopped httpd (pid 1823)
root@(none):~# httpd -v -h /home/lejos/www/
An example when the httpd is pretty busy:
Mem: 49048K used, 11812K free, 0K shrd, 516K buff, 25556K cached
CPU: 8% usr 35% sys 0% nic 0% idle 0% io 15% irq 39% sirq
Load average: 11.89 12.35 10.50 17/101 9146
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM %CPU COMMAND
1551 1197 root S 178m 300% 16% /home/root/lejos/ejre1.7.0_55/bin/java
1735 1 root R 2880 5% 11% httpd -v -h /home/lejos/www/
EV3 brick has not enought CPU to run a real J2EE web application server as Jetty or Tomcat, so if the develop need to run a Web Socket Server, at the moment the unique solution which I have found is the following project:
https://github.com/TooTallNate/Java-WebSocket
Note: I have used for all examples this library with sucess.
Modern web browsers as Chrome, has a pretty interesting API. In this section you will learn the following APIs:
Web Speech API https://dvcs.w3.org/hg/speech-api/raw-file/tip/speechapi.html https://www.google.com/intl/en/chrome/demos/speech.html
In this section, user will learn basic stuff about Modern web development.
Example: Web remote control with Websockets
Example: Data visualization for RPLIDAR (Polar Chart)
Example: Occupancy grid map viewer
Example: JSON generation
Example: Web Speech API
Example: RMI Client & Server example
Arduino is a Excellent board to extend the capabilities of a EV3 brick
Example: How to integrate Arduino with EV3 with LeJOS & EV3G
It is very important to ensure that your robot operates in a secure environment. Learn some stuff about security for Robots and avoid future robot's hacks.
In this chapter you will learn some concepts about security for Unix. Remember that your EV3 Brick run over a Busybox distro.
Nano Web server running on EV3 and suffering a DOS Attack:
Mem: 59800K used, 1060K free, 0K shrd, 48K buff, 4288K cached
CPU: 23% usr 26% sys 0% nic 0% idle 23% io 9% irq 17% sirq
Load average: 3.60 1.78 0.77 1/373 2030
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM %CPU COMMAND
1577 1538 root S 266m 447% 43% /home/root/lejos/ejre1.7.0_55/bin/java -classpath /ho
4 2 root SW 0 0% 11% [events/0]
430 2 root DW 0 0% 8% [mmcqd]
1538 1184 root S 179m 301% 5% /home/root/lejos/ejre1.7.0_55/bin/java -classpath /ho
180 2 root DW 0 0% 4% [kswapd0]
1594 1567 root R 3072 5% 2% top
The examples included in this chapter are:
Example: Discover ports opened in your EV3 Brick
Example: Hack your SSH root account using Brute force
Example: Read /var/volatile/log/ to discover ssh attacks
Example: A mini example about a DOS Attack to the service httpd included Busybox
Example: Shell scripts to remove some no necessary processes
Example: Scheduling a task with Cron4J
Example: NTP Client (Using classes from project EV3Menu)
Exercise 1: How to add a program in the startup
Exercise 2: Create a Virus for EV3 brick
http://sourceforge.net/p/lejos/wiki/Getting%20started%20with%20leJOS%20EV3/
LeJOS project uses Busybox as the way to offer a Linux experience. It was specifically created for embedded operating systems with very limited resources. BusyBox provides several stripped-down Unix tools in a single executable file. The authors dubbed it "The Swiss Army Knife of Embedded Linux", as the single executable replaces basic functions of more than 300 common commands
In this Annex, the reader will learn how to use Busybox in a EV3 environment.
Download preview: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/raw/master/annex2/docs/LRWE_Annex2_Busybox_Preview.pdf Exercises: https://github.com/jabrena/livingrobots/raw/master/annex2/docs/LRWE_Annex2_Busybox_Exercises.pdf