Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
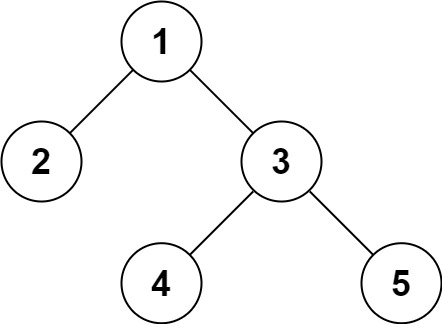
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. 1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
給定一個二元樹結點 root 要求要實作 serial, deserial 方法
可以透過 DFS 實作 Pre-order format
如下圖
class Solution {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
DFS(root, list);
return String.join(",", list);
}
public void DFS(TreeNode root, List<String> list) {
if (root == null) {
list.add("N");
return;
}
list.add(String.valueOf(root.val));
DFS(root.left, list);
DFS(root.right, list);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
int count;
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] list = data.split(",");
count = 0;
return DE_DFS(list);
}
public TreeNode DE_DFS(String[] list) {
if (list[count].equals("N")){
count++;
return null;
}
int rootValue = Integer.parseInt(list[count]);
count++;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
root.left = DE_DFS(list);
root.right = DE_DFS(list);
return root;
}
}- Understand DFS
- Understand what problem need to solve
- Analysis Complexity