B.Eng. Tobias Niggemeyer, currently a student of biomechatronic at Bielefeld University
B.Eng. Maximilian Exner, currently a student of biomechatronic at Bielefeld University
The "Turing Bombe Dependent Benchmark Project" is an elaboration of a comparison between a CPU and an FPGA. The aim of this project is to show the advantages and disadvantages of a CPU and a FPGA using the solution algorithm of the Turing Bombe. The Turing Bombe is an electro-mechanical machine that was used to decrypt messages which were encrypted by the Enigma. The implementation of the Turing bombe is based on informations and examples of the following website:
https://www.lysator.liu.se/~koma/turingbombe/
Because of the high complexity of the Turing Bombe and its configuration , this implementation is validated by the example described in the documentation of the referenced website.
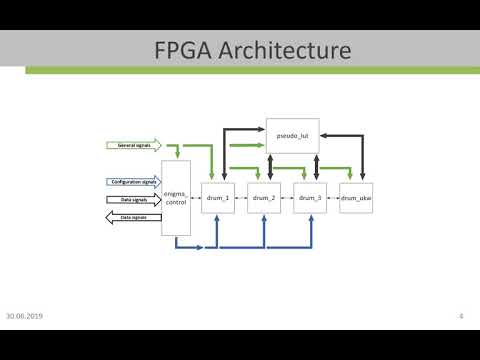
The following image shows the structure of the implementation of the project. In the first step the configuration of the Turing Bombe is calculated.It is realized in C/C++ and is based on the description of the referenced website. In the second step the information of the calculated configuration is either passed to a C/C++ object, which represents the Turing Bombe or transmitted to an FPGA via a serial communication. In both cases the configuration is used to adjust the settings of the respective Turing Bombe. The selection of the C/C++ Turing Bombe or the accelerated version implemented on the FPGA can be made by passing the corresponding parameters to the function (see section "Instructions To Test The Design")
If the Turing Bombe transmits a possible solution, it is passed to another C/C++ object called Checking Machine. This Object calculates the configuration of the plugboard of the Enigma. If the calculation is possible,it is passed to one more C/C++ object which represents the Enigma. The Enigma is used to decrypt the message and is also used to readjust the ring settings of the Enigma to encrypt the whole message. The readjustment is not implemented in this project.
To run the CPU implementation, do the following steps (please use the Linux GCC toolchain):
- Open the MAIN
- Use the makefile in the c_implementation directory to build the application.
- Use the following call to run the CPU implementation (from the c_implementation directory):
./bin/TURBOdeb -m "<Path_of_the_message_json>"
To run the FPGA implementation, do the following steps:
- Open the Vivado project (this project is created with Vivado 2018.3)
- Generate the Bitstream for the turing_bombe_final_wrapper
- Export the Hardware (File->Export->Export Hardware)
- include Bitstream
- /turing_bombe_project/xsdk/hw_export
- Lauch SDK
- Workspace: /turing_bombe_project/xsdk/workspace
- Exported Location: /turing_bombe_project/xsdk/hw_export
- Create new application project and use the helloworld example
- Replace helloworld.c with /turing_bombe_project/src/sw/TURBOdeb_com.c
- Build Application
- Choose the created Project and run as "Launch in Hardware (system debugger)" (right click on project -> Run As -> Run Configurations ... -> Xilinx C/C++ application (System Debugger))
- Make sure that the "Reset entire System" and "Programm FPGA" checkboxes are checked
- Press run to flash the bitstream and start the FPGA application
- After flashing the FPGA application to the FPGA the hardware can be used for the acceletration
- Use the following call to run the FPGA implementation (from the c_implementation directory):
- make sure that the ZYBO-Z7-20 board is connected and configured
- use the right device port in the /dev/.. - directory
./bin/TURBOdeb -m "<Path_of_the_message_json>" -p "/dev/ttyUSBX"
One example message is in the software directory. The message is stored in a json file. The console prints will give you feedback on the decryption process and the timing. Now the C implementation is supported by the FPGA implementation. This will cause a faster processing time.
The function of the FPGA implementation could also be shown with a simulation. This could be done with Vivado. Please do the following steps:
- Open the Vivado project
- Choose with a right-click on the simulation source "turing_bombe_wrapper_TB", "Set as Top"
- Run Simulation in Vivado
- The simulation stops when the right Enigma configuration is found.
As described in the section "Project Architecture" the implementation of the project is based on the information and description of the referenced website. Moreover the implementation is tested and validated with the example shown on the website. The encryption of other sentences has shown, that there are problems in the calculation of the configuration of the Turing Bombe.
Furthermore, the decryption of the sentence is limited to the known crip. To decrypt the whole sentence a function has to be implemented which calculates the right ring position of the three Enigma-Drums.
All in all the following functions have to be improved/created to achieve a complete encryption of random sentences:
- Improve the calculation of the configuration (graph theory necessary)
- Create function to find the right ring settings of the enigma
- Test/Validate the function of the Turing Bombe with the improved/created functions
- Accelerate of further functions (FPGA implementation of the calculation of the configuration)
This project is licensed under the MIT License.