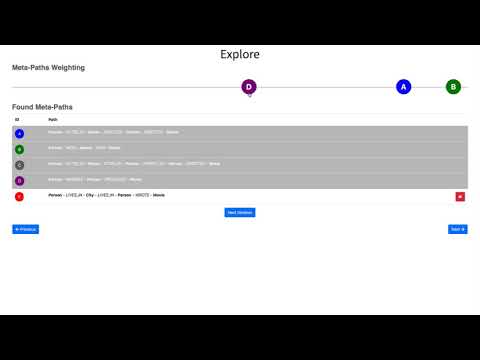
We present MetaExp, a system that assists the user during the exploration of large knowledge graphs, given two sets of initial nodes. At its core, MetaExp presents a small set of meta-paths to the user, which are sequences of relationships among node types. Such meta-paths do not overwhelm the user with complex structures, yet they preserve semantically-rich relationships in a graph. MetaExp engages the user in an interactive procedure, which involves simple meta-paths evaluations to infer a user-specific similarity measure.
More information can be found in
You can deploy the software with docker-compose. Detailed information and deployment scripts can be found in our metaexp-deployment repository
Our deployment is based on several docker containers, please install docker:
-
Neo4j is already running
-
New Neo4j Instance
In graph-algorithms repository:
mvn clean install
cp algo/target/graph-algorithms-algo-*.jar $NEO_HOME/plugins
# allow low level API access in neo4j.conf
dbms.security.procedures.unrestricted=algo.*
- start sockercontainer
- deploy redis server
- call route test_import
To build your own local code use deployment/build-ui.sh /path/to/code (e.g. deployment/build-ui.sh .),
set the environment variable REACT_APP_API_HOST according to you API (e.g. export REACT_APP_API_HOST=[API Endpoint]) and
to run a single container deployment/run-ui.sh [PORT] (e.g. ./deployment/run-dev-ui.sh).
Cross-Browser Usablity: Please use Mozilla Firefox.
The input range slider-thumb styling only works with Firefox
Architectural Approach: Flux-Pattern
Following, according to the Flux-Pattern, we describe the API-Communication, the most important stores and components and to which stores, i.e. data changes, they listen to and which actions they trigger.
- /src/utils/MetaPathAPI.js holds all relevant actions regarding API-Communication
- Actions provided according to each component's functionality
- process.env.REACT_APP_API_HOST React env-variable holds API-Endpoint
- AccountStore: Stores data regarding login information, e.g. username, chosen dataset, login state
- AppStore: Navigation data, like current page and previous and next page (footer navigation)
- SetupStore: Data of setup page, i.e. chosen node sets, cypher queries for neo4j graph visualization through forked third party neo4j-graph-renderer
- ExploreStore: Meta-Paths and rating information, chosen rating interface, batch size
- ResultStore: Holds explanatory data as a similarity score, top-k contributing meta-paths and additional meta-path information
Main Parts: Setup page, Explore page, Result page
- SearchNodesSection: Component for executing a cypher query in CypherEditor-Component with syntax highlighting and auto-completion
- ResultSetSection: Component for visualizing query response and selecting node candidates for both node sets
- NodeSetsSection: Component for visualizing both selected candidate node sets and saving them
- MetaPathDisplay: General Component for displaying meta-path batches and rating scala, handling their rating change , batch size and rating interface change, displaying refrence meta-paths over all batches
- MetaPath: Textual visualization of meta-path
- MetaPathRater: Input range slider for rating a certain meta-path
- IndividualRatingInterface: Table with meta-path and absolute rating slider for each meta-path
- CombinedRatingMetaPathTable: Table with Meta-Path ID Button, which can be clicked to add Meta-Path to batch-global relative rating slider
- SimilarityScore: Component for displaying initially chosen node sets and a score for their similarity or 'connectedness'
- ContributingMetaPaths: Component for visualizing a pie chart, that holds information abut how much each of the top-k meta-paths contribute to the similarity score
- MetaPathDetails: Component for displaying details of a certain meta-path, i.e. structural and domain value and exemplary meta-path instances
The python backend is structured into several components, each is responsible for either serving the api or part of the algorithmic backbone. The algorithmic parts are in their basic functionality. Work on the individual components is conducted outside of the MetaExp-Project, but might be referenced here in the future.
-
Serving Modules
server: Serve API endpoints with a flask/gunicorn serverredis_own: Provide access to a redis database where node embeddings are storedneo4j_own: Connector to the neo4j database
-
Algorithmic Modules
active_learning: Provide active learning functionality for interactively learning a preference model of meta-pathsdomain_scoring: Calculate the similarity of two node sets given a preference over meta-pathsembeddings: Compute vector-embeddings of MetaPathsexplaination: Explain the similarity score
The API is not stateless, the image below describes the process of interating with the API. Users need to login to the system for a specific dataset. This is followed by the input-set selection and then the iterative rating of paths. Finally the user can view the similarity. These phases are sequential. Since this is a prototype, it is likely that the system will crash if they are called arbitrarily.
-
get-available-datasets- Returns a list of all available neo4j-datasets in the backend.
- IN
None - OUT
{[dataset1, dataset2, ...]}
-
login- Login into the system.
- IN
{'username': username, 'dataset': datasetname, 'purpose': purpose_of_similarity} - OUT
{'status': 200}
-
node-types- Select the input node types for both sets for the algorithm.
- IN
{'start_label': label_of_start_node, 'end_label': label_of_end_node, 'start_node_ids': list_of_node_ids, 'end_node_ids': list_of_node_ids} - OUT
{'status': 200}
-
next-meta-paths/<int:batch_size>- Retrieve the next batch_size MetaPaths that should be labelled by the user.
- IN
None - OUT
{'metapaths': [path1, path2, ... ], 'next_batch_available': bool}
-
rate-meta-paths- Send metapaths that have been rated.
- IN
{'meta_paths': [{'id': 3, 'metapath': ['Phenotype', 'HAS', 'Association', 'HAS', 'SNP', 'HAS', 'Phenotype'], 'rating': 0.75},...], 'min_path':{'id': ,...}, 'max_path':{'id': ,..}} - OUT
{'status': 200}
-
stop-rating- Finish the rating process.
- IN
None - OUT
{'status': 200}
-
get-similarity-score- Retrieve the similarity score for the previously defined node sets and preferences.
- IN
None - OUT
{'similarity_score': score}
-
contributing-meta-paths- Retrieve the most contributing MetaPaths for this similarity score.
- IN
None - OUT
{'contributing_meta_paths': [pie_chart_vis1,...]}
-
similar-nodes- Retrieve the most similar nodes to those in the set.
- IN
None - OUT
{'similar_nodes': [node1, node2,...]}
-
logout- Logout of the system.
- IN
None - OUT
{'status': 200}
The neo4j-graph-algorithms library was extended by a procedure that computes all meta-paths on a given graph.
computeAllMetaPaths()- This extracts all meta-paths from the graph that have the given length or are smaller. For each meta-path the count of paths fitting it is also computed.
- IN
{'meta-path-length': maximal length computed meta-pahts should have} - OUT
{'meta-paths with counts': a map of meta-paths and their path-counts}
Forked and extended third party react component for visualizing neo4j graphs and interact with the nodes.
Freya Behrens, Sebastian Bischoff, Pius Ladenburger, Julius Rückin, Laurenz Seidel, Fabian Stolp, Michael Vaichenker and Adrian Ziegler.
This work was conducted with our project partners neo4j, helmholz zentrum münchen and knowing health.
All work is licensed under MIT License.