| THA's | Title | Status |
|---|---|---|
| THA 1 | Letter | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 2 | Letter with CSS | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 3 | Resume | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 4 | Clock | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 5 | Calulator | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 6 | Arrays | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 7 | Objects | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 8 | CSS Pixel Art | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 9 | Book Your Seat | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 10 | Memory Game Horimiya Edition | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 11 | Quiz | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 12 | Todo List with LocalStorage | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 13 | Website with API - Anime | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 14 | Use Events - Pig Game | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 15 | Functional Component | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 16 | Meme Card | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 16 | Checker Board | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 17 | Calorie Counter With Props | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 18 | Checker Board with Conditionals and Loops | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 18 | Calorie Counter with Conditionals and Loops | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 19 | Buttons With their Own State | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 20 | Calorie List with Delete Feature | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 21 | Calorie with Add, Delete, Edit | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 22 | Meme Generator | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 23 | Anime Quote | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| THA 24 | Route Conditional Login | ✅ (Visit Here) |
| Title | Link |
|---|---|
| Guess Number Game | Visit Here |
Bad Notes :Warning
- Positions
- Display
- Overflow
- Semantic Elements
- Section
- Article
- Header
- Footer
- Nav
- Details - Summary
- Time
- Aside
- document - A global Object of a javascript
- window.onload , document.getElementById(), getQuerySelectorAll()
- addEventListener, parseInt,
- Event Bubbling - In css = OnClick= "function()"
- In addEventListner function we can use event.stopPropogation
- Event Capturing
- var are by default initialized undefined but let gives an error
- typeof,console.log,for loop, let ,array, forEach, for item of arr,
- if else, variable dont have type values have,
- coersion to number ->Number() way, +n way, parseInt way
- coersion to boolean -> !!() way or Boolean
- coersion to string -> toString or concatenate with empty string
- a==b, a===b
- Global Scope -
- Lexical scope -
- Functional scope -
- Block scope - { }
- Diff between let var const - var can be accessed from outside of block
- var can have acceess in whole function
- let doesnt have access outside of block
-
Array and Accessing Elements
-
Javascript Arrays, Accessing, .concat, .join, slice, indexOf(value), lastIndexOf(value),
-
Iterating List
- forEach, forOf, forIn, Simple For,
- a.some(item=> item===10),a.every(item=>item===1),a.filter(item=>item==1),map(item=>item=10)
-
a.reduce((acc,item)=>{acc=acc+item; retun acc;},0);
-
Mutating List
-
.pop,.reverse,.push,.sort, splice,shift,unshift,.length()
-
sort((a,b)=> a-b);
-
splice(start,delete count, items);
-
shift - pop from front
-
unshift - push from front
-
toString
-
toLocaleString
-
isArray
-
sort
-
splice
-
length
-
- Syntax - Create an Object ={},=new Object({});,=Object.Create(prototype object);,
- Dot Notation, Bracket Notation, Methods in Objects -
- Create Properties from outside object, Object are Mutable,
- for in loop, Nested Objects, Object.Keys(objectName), Object.Values(objectName),
- Object.freeze(objectName), Object.getOwnPropertyNames(objectName),objectName.splice(),
- Json.stringify, Json.parse
- get and set on objects, delete property
- Object Constructors
- Object.assign(target,source);
- spread operator for clone objects or arrays - newobje = {...source}
- rest Parameters - a,b,...x fun(a,b,x,c,c,d,d) a b will be assign rest will store in x array
- Arguments Object -
- what if number of parameters we pass are higher than required - ans - it will only take required number of - parameters
- rest parameter must be the last in parameter
-
console.log(window), const new=window.open(), new.close(), new.location="https://google.in",
-
global scope ==> variables become property in window, function become method in window,
-
This Keyword,
-
global scope, function scope var with this keyword
-
call keyword with parameter,
-
apply keyword same as call keyword parameter are passed as array
-
bind keyword, same as call, but we can create kind of const for it and store the call and call whenever - needed, functionname.call(object), functioname me this keyword,
-
Hoisting - access variable before define => undefined, same for arrow function
-
call funciton before define => correct output,
-
spread operator - creates clone not reference, create copy of two array and merge,
-
overwrite when two object copy, update values of object using spread operator
-
Events and Event Listeners
var x=document.querySelcctor(.classname);
x.addEventListener('click',()=>{ box.classlist.contains('classname') });- Functions
- function expression
- (function(){});
- array function
- anonymous function
- arrow function
- diffrence in arrow and normal function declaration - this value
- no execution context is made in case of arrow function. ex
- default parameters
- callback function
- setTimeOutput(fun,time);
- setTimeOutput(fun,time,more funs); more fun will run first
- asynchronous programming
- Function Chaining
-
Prototypal Inheritance
-
let shape = { height: 10, widhth: 10, }; let circle = { radius: 2, }; circle.__proto__ = shape; console.log(circle.height, circle.radius); // 10, 2
-
Object.getPrototypeOf
-
Derived Class
-
Base Class
-
super keyword
- Event Loop
- setTimeout and setInterval
- Blocking vs Non Blocking
- localStorage
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let a = 2;
if (a === 2) {
// resolve(); // promise fulfilled
resolve("Success"); // can also pass json data
} else {
// reject(); // uncaught error
reject("Failed");
}
});
promise.then((data)=>{
console.log("Promise was Resolved");
console.log(data);
});
.catch(()=>{
console.log("Promise was Rejected");
})- 3 types of states = resolve, pending, reject
- works asynchronously
- then executes when promise resolved
- catch executes when promise rejects
fetch("https://api.github.com/users/nikhilnagrale2")
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => console.log(data));async function hello() {
return "Hello";
}
var a = hello(); // returns promise
console.log(a); // promise
a.then((data) => {
console.log(data); //hello
});function resolveAfter2Seconds(x) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(x);
}, 2000);
});
}
async function f1() {
var x = await resolveAfter2Seconds(10);
console.log(x); // 10
}
f1();- Set Data
localStorage.setItem("username", "op");- remove Data
localStorage.removeItem("username");- Get Data
localStorage.getItem("username");- Clear Data
localStorage.clear();- Set Data
sessionStorage.setItem("username", "op");- remove Data
sessionStorage.removeItem("username");- Get Data
sessionStotage.getItem("username");- Event Listner - what type
- Event Handler
- click, mouseOver, mouseOut, keyup, keydown, keypress, focus, blur, change, submit, onformsubmit, onoffline, onload, onresize, onvideoplay,
- Fast, Large community, OpenSource, blah blah React JS
- How to install create react app
npm install -g create-react-app- How to create react app
npx create-react-app "AppName"- How to start Server
npm start- What is BabelJs
- How to import React and ReactDOM
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";- Render ReactDOM
ReactDOM.render(<h1>Hello Wordl</h1>, document.getElementById("root"));function Navbar() {
return <h1>Navbar</h1>;
}
function App() {
return (
// jsx
<div>
<Navbar />
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
</div>
// jsx
);
}
// Prop -> FC -> JSX
// Call App
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));export default App; // Export Jsx
import App from "./App";- create file in src
- import css file
- instead of class use className
const Card = () => { // parent component
const Image = () => { // child component
return <img src="https://cubettech.com.jpg" alt="" />;
};
return (
<div className="card">
<Image />
</div>
<h2>React Card</h2>
);
};- JSX is an extension to the JavaScript language syntax
const componentWithoutJSX = React.createElement(
"h1",
{
// attributes,
className: "text",
},
"Hello World"
);
const componentWithJSX = <h1 className:"text">Hello World</h1>; // babel converts to above
function App() {
return componentWithoutJSX;
}function App(){
return (
<div className="card" style="{{backgroundColor:"blue"}}">
<h1>Title</h1>
</div>
)
}function App(props){
return (
<div className="card" style="{{backgroundColor:"blue"}}">
<h1>Title</h1>
</div>
)
}
<App img="xyz" title="xyzs"/><button style={{ backgroundColor: "green", color: "blue" }}>Download</button>- or simply create object and assign
- we can also use conditionals to give different class
- Class based components
- Life cycle methods
- Webpacks: Transpiler
class MyComponent extends Component {
render() {
return <h1> Hello world </h1>;
}
}class Sample extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "Harshith",
};
}
render() {
return <h1>{this.state.name}</h1>;
}
}
export default Sample;- In a React component, props are variables passed to it by its parent component.
- State on the other hand is still variables, but directly initialized and managed by the component.
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
property: "value",
};
}
render() {
return <h1> {this.state.property} </h1>;
}
}- There is a designated way to change states. To change state, we use this.setState() method. Let’s change the property property to 'hussain'
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "Constructor Method",
};
}
render() {
<div
onClick={() => {
this.setState({ name: "Harshith" });
}}
>
<p>This is a {this.state.name}</p>
</div>;
}
}- constructor() method is called when the component is initiated and it’s the best place to initialize our state. The constructor method takes props as an argument and starts by calling super(props) before anything else.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "Constructor Method",
};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p> This is a {this.state.name}</p>
</div>
);
}
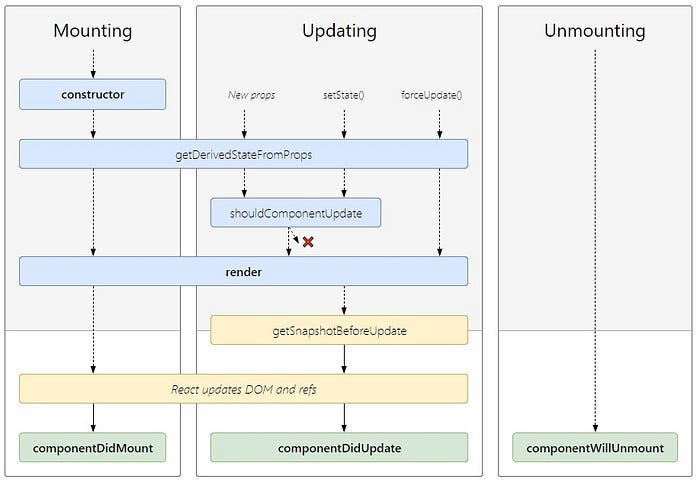
}- The getDerivedStateFromProps method is called right before rendering the element in our DOM. It takes props and state as an argument and returns an object with changes to the state.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export class ChildComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "Constructor Method",
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
return { name: props.nameFromParent };
}
render() {
return <div>This is a {this.state.name}</div>;
}
}
export default class getDerivedStateFromPropsMethod extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<ChildComponent nameFromParent="getDerivedStateFromProps Method" />
</div>
);
}
}- This is the only compulsory method required by the React. This method is responsible to render our JSX to DOM
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class renderMethod extends Component {
render() {
return (
<>
<p>This is a render method</p>
</>
);
}
}- The most common and widely used lifecycle method is componentDidMount. This method is called after the component is rendered. You can also use this method to call external data from the API.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class componentDidMountMethod extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "This name will change in 5 sec",
};
}
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ name: "This is a componentDidMount Method" });
}, 5000);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>{this.state.name}</p>
</div>
);
}
}- This lifecycle method is used when you want your state or props to update or not. This method returns a boolean value that specifies whether rendering should be done or not. The default value is true.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class shouldComponentUpdateMethod extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "shouldComponentUpdate Method",
};
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
return false; //Change to true for state to update
}
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ name: "componentDidMount Method" });
}, 5000);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>This is a {this.state.name}</p>
</div>
);
}
}- This method is called right before updating the DOM. It has access to props and state before the update. Here you can check what was the value of your props or state before its update. So let see how it works.
Note: componentDidUpdate() should be included otherwise you will get an error.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class getSnapshotBeforeUpdateMethod extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "constructor Method",
};
}
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ name: "componentDidMount Method" });
}, 5000);
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
document.getElementById("previous-state").innerHTML =
"The previous state was " + prevState.name;
}
componentDidUpdate() {
document.getElementById("current-state").innerHTML =
"The current state is " + this.state.name;
}
render() {
return (
<>
<h5>This is a {this.state.name}</h5>
<p id="current-state"></p>
<p id="previous-state"></p>
</>
);
}
}- The componentDidUpdate method is called after the component is updated in the DOM. This is the best place in updating the DOM in response to the change of props and state.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class componentDidUpdateMethod extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "from previous state",
};
}
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ name: "to current state" });
}, 5000);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevState) {
if (prevState.name !== this.state.name) {
document.getElementById("statechange").innerHTML =
"Yes the state is changed";
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
State was changed {this.state.name}
<p id="statechange"></p>
</div>
);
}
}- If there are any cleanup actions like canceling API calls or clearing any caches in storage you can perform that in the componentWillUnmount method. You cannot use setState inside this method as the component will never be re-rendered.
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class componentWillUnmount extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
show: true,
};
}
render() {
return (
<>
<p>{this.state.show ? <Child /> : null}</p>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState({ show: !this.state.show });
}}
>
Click me to toggle
</button>
</>
);
}
}
export class Child extends Component {
componentWillUnmount() {
alert("This will unmount");
}
render() {
return <>I am a child component</>;
}
}import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function some() {
const [state, setState] = useState("Initial name");
return (
<>
{" "}
<h2 onClick={() => setState("Later name")}>{state}</h2>
</>
);
}- Events
- Hooks - useState, useEffect
- setState
class Football extends React.Component {
shoot() {
alert("Great Shot!");
}
render() {
return <button onClick={this.shoot}>Take the shot!</button>;
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Football />, document.getElementById("root"));import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function App(props) {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div className="App">
<button onClick={() => {
count newCount = count+1;
setCount(newCount);
console.log(count);
}}>{count}</button>
</div>
);
}import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function App(props) {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// useEffect(()=> {
// console.log("DOM Updated");
// },[]);
useEffect(()=> {
console.log("DOM Updated");
},[count]);
return (
<div className="App">
<button onClick={() => {
setCount({count+1});
console.log(count);
}}>{count}</button>
<button onClick={() => {
setCount(count1+1);
console.log(count1+1);
}}>{count1}</button>
</div>
);
}import React, { Component } from "react";
const Api = () => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetchItems();
}, []);
const fetchItems = async () => {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const posts = await response.json();
// const posts_text = response.text();
console.log(posts, "json");
setPosts(posts);
};
const createPost = async () => {
await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify({ title: "foo", body: "bar", userId: 1 }),
headers: { "Content-type": "application/json; charset=utf-8" },
});
};
return (
<>
<button onClick={createPost}>create post</button>
posts.map((item, index) => {
<h1 className="title" key={index}>
{item.title}
</h1>;
});
</>
)
};
export default Api;const Form = () => {
const [email, setEmail] = useState("");
const [password, setPassword] = useState("");
const [country, setCountry] = useState("India");
const [acceptedTerms, setAcceptedTerms] = useState(false);
const handleSubmit = (event) => {
console.log(`email:${email} password:${setPassword} country:${country} terms:${acceptedTerms}`);
event.preventDefault(); // prevent page refresh
// event.stopPropogation();
}
return (
<form>
<h1>Create Account</h1>
<label>
Email:
<input
type="email"
value={email}
name="email"
onChange={(e) => setEmail(e.target.value)}
/>
</label>
<label>
password:
<input
type="password"
value={password}
name="password"
onChange={(e) => setPassword(e.target.value)}
/>
</label>
<label>
Country:
<select value={country} onChange={(e) => setCountry(e.target.value)}>
<option key="india">India</option>
<option key="usa">Usa</option>
<option key="canada">Canada</option>
</label>
<label>
<input value={acceptedTerms} type="checkbox" name="acceptedTerms" onChange={(e) => setAcceptedTerms(e.target.value)}/>
</label>
<button onClick={(e) =>handleSubmit(e) }>Submit</button>
</form>
);
};
export default Form;- All About API's
- Custom hooks
- Hooks
- React Router DOM
import React, {useState} form 'react';
function Sample(props){
const {name } = props;
const [state,setState]= useState(name);
return (
<div>
<h1>{state}</h1>
<button onClick={()=>{
setState("Harshith");
}}>Click Me</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Sample;// UseArray
// useCallback
import React, {useCallback, useState} form 'react';
import { useCallback } from "react";
const memizedCallback = useCallback{
()=>{
doSomething(a,b);
},[a,b]
}// value, setValue, add, clear, removeById, removeIndex
export const useArray = (initial) => {
const [value, setValue] = useState(initial);
return {
value,
setValue,
add: useCallback((a) => setVAlue((v) => [...v, a])),
clear: useCallback((a) => setValue(() => [])),
removeById: useCallback((id) =>
setValue((arr) => arr.filter((v) => v && v.id !== id))
),
removebyIndex: useCallback((index) =>
setValue((v) => {
arr.filter((v) => v);
})
),
};
};
///////////////////////////////////////
import { useArray } from "./useArray";
function Sample(props) {
const todos = useArray(["hi", "hr"]);
return (
<div>
<h3> Todos </h3>
<button
onClick={() => {
todos.add(Math.random());
}}
>
add
</button>
<ul>
{todos.value.map((todo, i) => {
<li key={i}>
{todo}
<button
onClick={() => {
todos.removeById(todo);
}}
>
Delete
</button>
</li>;
})}
</ul>
<button onClick={() => todos.clear()}>Clear</button>
</div>
);
}export function useUnSplashPhotos(secret, query) {
const [images, setImages] = useState([]);
const [error, setError] = useState(undefined);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
const url = `https://api.unsplash.com?query=${query}`;
useEffectt(() => {
console.log("called");
}, [query]);
}
function Sample(props) {
const [query, setQuery] = useState("animals");
const [images, error, loading] = useUnSplashPhotos("secret", query);
return (
<div>
<h1>Sample</h1>
<ul>
<li>
Animals<button onClick={() => setQuery("animals")}>Change</button>
</li>
<li>
Flowers<button onClick={() => setQuery("flowers")}>Change</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
);
}npm install react-router-dom
import React from "react";
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Switch,
Route,
Link
} from "react-router-dom";
export default function App() {
return (
<Router>
<div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/about">About</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/users">Users</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
{/* A <Switch> looks through its children <Route>s and
renders the first one that matches the current URL. */}
<Switch>
<Route path="/about">
<About />
</Route>
<Route path="/users">
<Users />
</Route>
<Route path="/">
<Home />
</Route>
</Switch>
</div>
</Router>
);
}
function Home() {
return <h2>Home</h2>;
}
function About() {
return <h2>About</h2>;
}
function Users() {
return <h2>Users</h2>;
}- State Management
- Reducer, Context and Other things
- Example
const NamesContext = React.createContext();
function nameReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "saveAnimalNames": {
return { animalNames: state.animalNames };
}
case "saveHumanNames": {
return { humanNames: state.humanNames };
}
default: {
throw new Error(`Unhandled action type: ${action.type}`);
}
}
}
function NamesProvider({ children }) {
const [state, dispatch] = React.useReducer(namesProducer, { count: 0 });
}- CSS Framework
- Usage of Bootstrap and tailwind
- Redux
- Redux Uses
- Actions
- Reducers
- Store
npm install redux
npm install react-redux- todo list using redux
- middleware
- Logger
- Thunk - asynchronous
- Weather App
- ECommerce APP
- TypeScript Basics