Table of Contents
Are you using Op5? Perhaps you do most of your work from the command-line and want to be able to do the most common Op5 tasks without logging in to a web-gui?
Or you want to start monitoring the newly installed hosts with Op5 using your ansible/chef/whatever config management tool?
Those two use-cases were my biggest itches when I first started to use saved curl commands to interact with the REST-api and soon op5util.rb was born.
The design nowdays is reasonably modular so new functions can be easily added as needed, pull requests are happily accepted.
I use op5util daily in a production environment, but it comes with no warranties.
Currently op5util have implemented these functions:
- Add a new host to be monitored by Op5
- Add a existing host to more hostgroups
- Schedule downtime for a host
- Acknowledge alarms for host/service
- Show status summary of all services/host and summary of service per host
- Show status summary of services for a host and list all services w. status for a host
- Schedule forced checks of a host and the hosts services to be done now
- List all hostgroups available, including members and service checks
- List all hosts, with optioinal detailed info
- Autocomplete template for bash/zsh is included
A few usage example and the output from op5util.
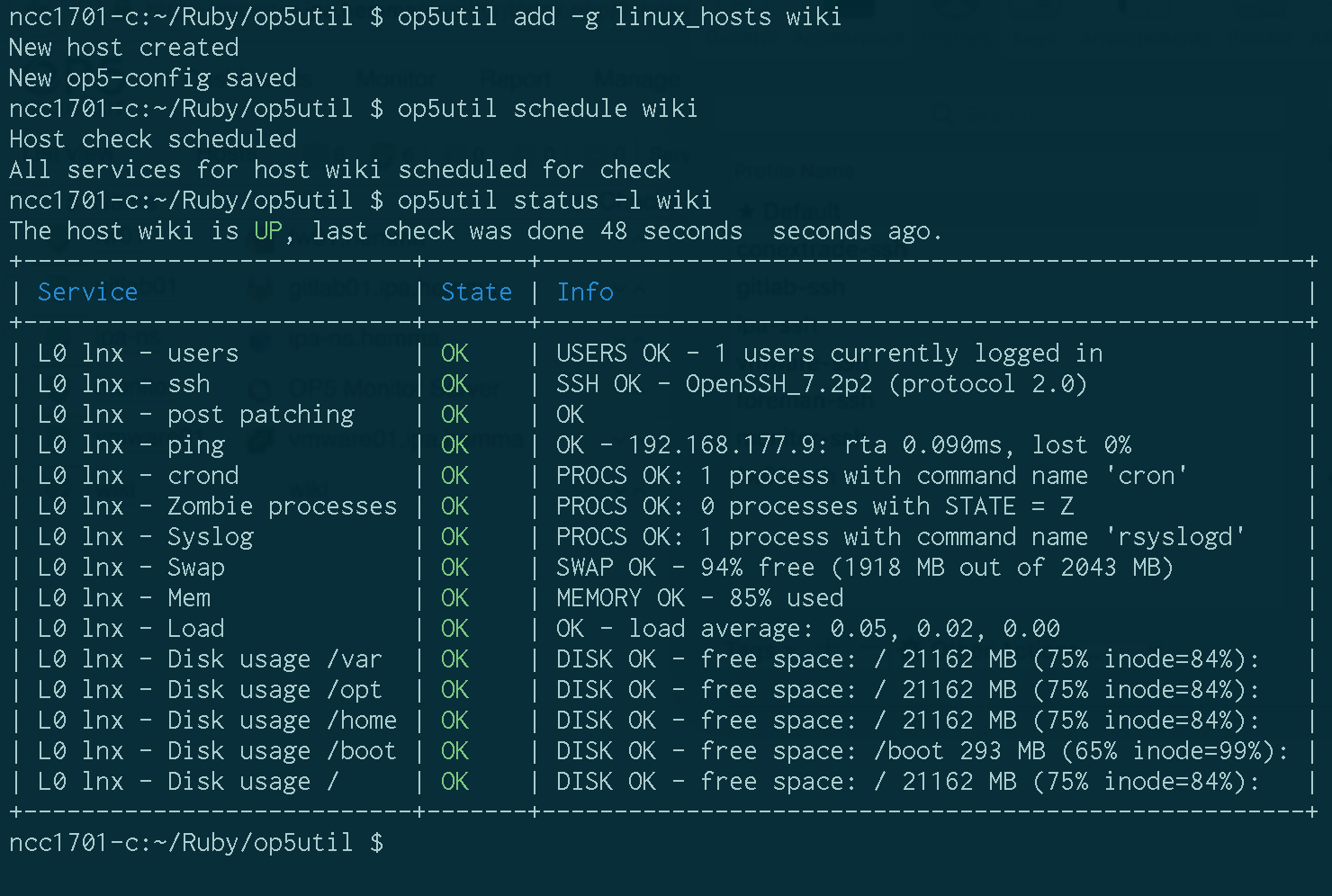
Adding a host using op5util add -g linux_hosts wiki and at the same time assigning
membership in the linux_hosts hostgroup for the host, so some standard service checks are
defined.
To avoid waiting for checks to be performed on the new host, we tell Op5 to check the new
host and it's services right away with the command op5util schedule wiki, and after
only a short wait we can take a look at the detailed host status with op5util status -l wiki.
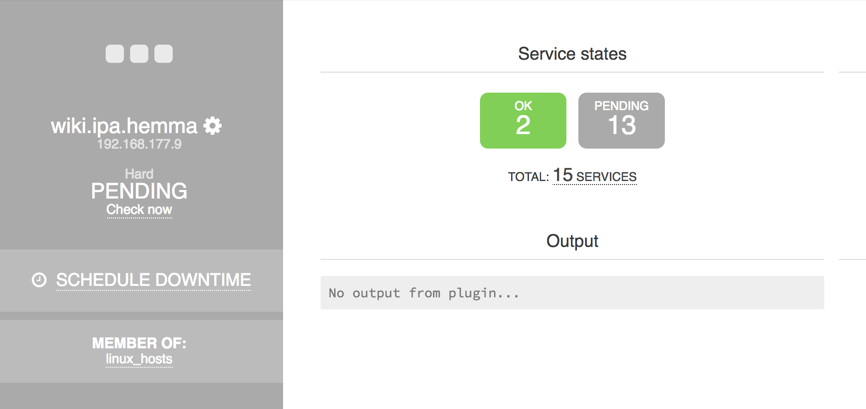
The newly added host in normal web-gui.
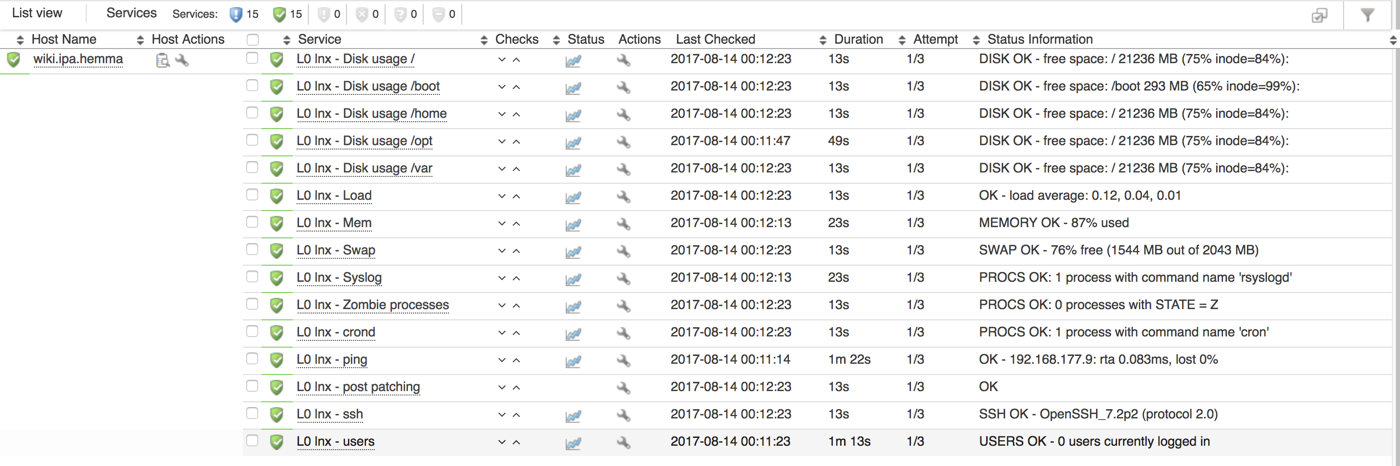
And the same host in a Op5 listview with service state after services was checked, as comparison with the terminal output by op5util.
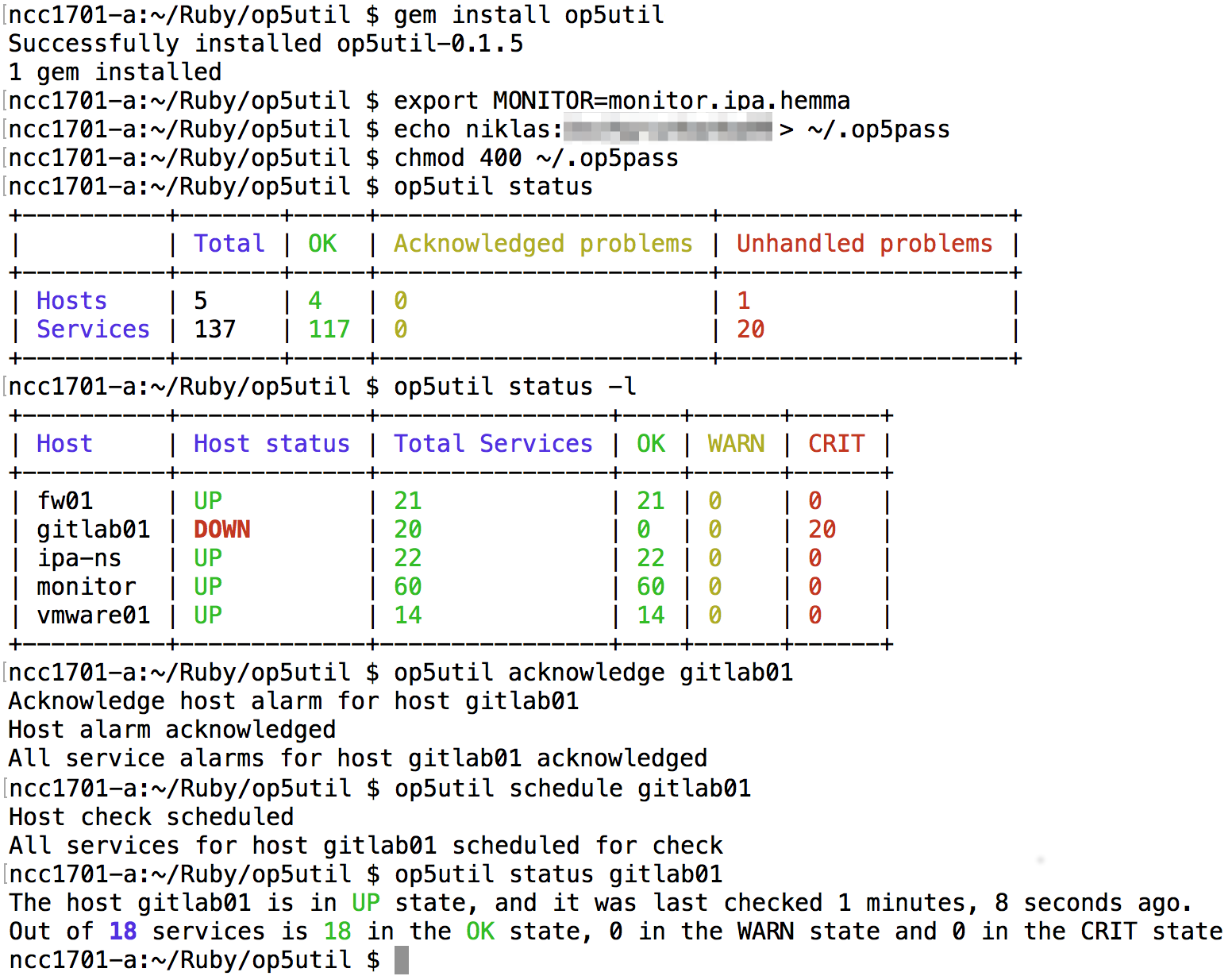
Op5util is installed using gem install op5util
The export of the environment variable MONITOR and saving credentials in the in the .op5pass
file is to avoid using the command-line flags -m monitor.ipa.hemma -u user -p password
on every command.
First check the overall status with the command op5util status, as one host is down we request
more info to be displayed with op5util status -l, and we see that the host gitlab01 is down, to
acknowledge the alarms, op5util acknowledge gitlab01.
Once the problem is resolved and the host is up, op5util schedule gitlab01, because impatience,
and a final check with op5util status gitlab01.
Install instructions are intended for and tested on a fresh install of ubuntu 16.04.
Op5util is distributed as a ruby gem, so first ruby must be installed.
user@host:~$ sudo apt-get install -y rubyUse the command gem install to install op5util, sudo is needed. This will automatically install op5util and the other gems that op5util depends on.
user@host:~$ sudo gem install op5utilThe latest version is 0.1.7, you can verify that op5util is installed correctly using:
user@host:~$ gem list --details op5util
*** LOCAL GEMS ***
op5util (0.1.6)
Author: Niklas Paulsson
Homepage: https://github.com/np422/Op5util
License: MIT License
Installed at: /var/lib/gems/2.3.0
A utility to do common Op5 administration from the commandlineThe rubygem homepage for op5util is available at: https://rubygems.org/gems/op5util
There is no man-page, but the built in help text should do the job.
If you enter the command op5util help the top-level documentation is displayed.
Help for a op5util command is diplayed with op5util help <command>, examples are
present below.
NAME
op5util - A small utility to perform common Op5 administration tasks from the command line
About authentication, if you supply username/password as command-line flags they will be
used first. If username/password options isn't supplied on the command-line, the environment
variables OP5USER and OP5PASS will be used. If there are no environment variables present,
the file ~/.op5pass (or --authfile=, or environment OP5AUTHFILE) will be read. The file
format is a single line with username and password separated by a : (colon). The supplied
credentials shoud be an account with administrative privileges.
This application uses the REST-api described at https://your.op5.sever/api/help. Although
TLS/SSL is used, no verification of the certificate is done as most Op5-servers have a
self-signed certificate.
SYNOPSIS
op5util [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION
0.1.8
GLOBAL OPTIONS
-f, --authfile=authfile - Authfile containing "username:password" used to authenticate with Op5
server, enviromnent variable OP5AUTHFILE will override the default
value (default: ~/.op5pass)
--help - Show this message
-m, --monitor=monitor - Hostname or IP-address of the Op5 monitor server, if not supplied
the environment variable MONITOR will be used (default: none)
-p, --password=password - Password used to authenticate with the Op5 server, if not supplied
the environment variable OP5PASS will be used (default: none)
-u, --username=username - Username used to authenticate with the Op5 server, if not supplied
the environment variable OP5USER will be used (default: none)
--version - Display the program version
COMMANDS
acknowledge - Acknowledge outstanding host and service alarms, without host - *ALL*
outstanding alarms and services are acknowledged, ackn is "sticky" - it
lasts until host/service recovery.
add - Add a new host to be monitored by the Op5 server
add_hostgroups - Add host to a new hostgroup(s)
autocomplete - Show instruction on howto setup tab autocomplete for op5util in your shell
commit - Commit any pending changes
downtime - Schedule fixed downtime for (a) host(s) , multiple hosts in a comma separated list
help - Shows a list of commands or help for one command
hosts - List all hosts, or detailed information about a single host
hostgroups - List hostgroups, optionally with member and service info, Usage examples:
'op5util hostgroups' to list all hostgroups, 'op5util hostgroups -l linux_hosts'
to list members and services for the linux_hosts hostgroup
schedule - Schedule host and all host services checks to be performed swiftly for the given host
status - Show monitoring status, if no host is given all hosts/services are included
NAME
add - Add a new host to be monitored by the Op5 server
SYNOPSIS
op5util [global options] add [command options] hostname
DESCRIPTION
The host is added using mostly default values for max_check_attempts (3),
notification_interval (0, aka notify once), notification_period (24x7), etc
using the default-host-template. For most off-the-shelf newly installed
servers these values usually are sufficient and can be fine-tuned using
the web-gui if so should be needed.
COMMAND OPTIONS
-a, --alias=arg - Alias for host, defaults to hostname with the domain name
removed (default: none)
-c, --contactgroups=arg - Contact groups for host, defaults to "support_group" (may
be used more than once, default: ["support-group"])
-g, --hostgroups=arg - Hostgroup(s) to which the new host will be added (may be
used more than once, default: none)
-i, --ipaddr=arg - IP-address of host, resolved with DNS from hostname if
not supplied (default: none)
A lot remains, the code really should be refactored and DRY'ied up, the commands probably need some re-thinking, more automated pre-release tests, more documentation and perhaps even adding some more functions, but the current version of op5util is already useful to me in my day-time job, perhaps it also could be useful to other Op5 administrators?
Please, give my repo a github star or drop me line if you find this utility useful. You can contact me at niklasp@.com
And please feel free to leave bug-reports or feature requests as issues in this repo.
Option to schedule downtime of many hosts in i comma separated list from a single command.
New command 'commit' that commits any pending/unsaved changes done previously, combined with the option --no-commit on the add_host and add_hostgroup commands.
New command 'hosts' which lists hosts, included example of ansible playbook in documentation.
Added template for shell autocomplete of op5util command (bash/zsh)
Gemspec filespec corrected to avoid unnecessary large .gem-files.
Environment variable OP5AUTHFILE possible to use instead of --authfile, check permission of authfile and refuse to start if readable by other than owner.
Use the example below as a source of inspiration on how op5util can be used from an ansible playbook.
In this example the variable 'hostgroups', which should be a list, will be used to assign hostgroups, otherwise the default hostgroup 'linux_hosts' will be assigned.
---
- hosts: monitoring-clients
gather_facts: false
serial: 1
vars:
op5_user: 'user'
op5_password: 'password'
op5_server: 'op5server'
tasks:
- name: Check if Op5 registration is needed
shell: op5util -u {{ op5_user }} -p {{ op5_password }} -m {{ op5_server }} hosts
register: var_op5_hosts
delegate_to: localhost
- set_fact:
op5_hosts: "{{ var_op5_hosts.stdout_lines }}"
- name: Register client with Op5 monitoring server
shell: op5util -u {{ op5_user }} -p {{ op5_password }} -m {{ op5_server }} add -g {{ hostgroups | default([ 'linux_hosts' ]) | join(' -g ') }} {{ inventory_hostname }}
delegate_to: localhost
when: inventory_hostname not in op5_hosts