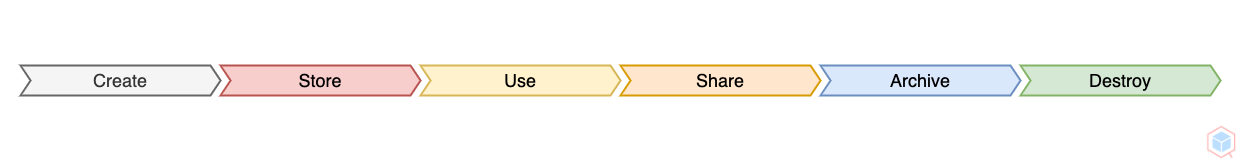
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is a policy-based model for managing data in an organization
Data is collected or generated in various ways and then analyzed if it's relevant or irrelevant (Data here could be structured or unstructured)
- What data needs to be captured?
- What is the data type (public, private, restricted)?
Data is stored in the company's data infrastructure
- What storage will be used?
- Does it meet the privacy and governmental requirements?
Data is now available for users in a format that they understand.
- What do you want from the data?
- How is data shared and used?
If data is no longer active, then archive it. Otherwise, it will be destroyed (It's better to archive first because some data will; still, this depends on the usefulness and sensitivity of the data)
- Do you need the data in the future?
- How long is the required retention period?
Archived Data is purged when it meets the required retention period (No longer benefits the company) and destroyed securely (The more you keep data, it will increase the data management cost)
- Is data still active or benefit the company?
- How is data destroyed?
24a781c4-5847-41b7-b764-ecd73862707c