- by Sasha Rush - srush_nlp (with Marcos Treviso)
When learning a tensor programming language like PyTorch or Numpy it is tempting to rely on the standard library (or more honestly StackOverflow) to find a magic function for everything. But in practice, the tensor language is extremely expressive, and you can do most things from first principles and clever use of broadcasting.
This is a collection of 21 tensor puzzles. Like chess puzzles these are not meant to simulate the complexity of a real program, but to practice in a simplified environment. Each puzzle asks you to reimplement one function in the NumPy standard library without magic.
I recommend running in Colab. Click here and copy the notebook to get start.
If you are interested, there is also a youtube walkthrough of the puzzles
!pip install -qqq torchtyping hypothesis pytest git+https://github.com/danoneata/chalk@srush-patch-1
!wget -q https://github.com/srush/Tensor-Puzzles/raw/main/lib.pyfrom lib import draw_examples, make_test, run_test
import torch
import numpy as np
from torchtyping import TensorType as TT
tensor = torch.tensor- These puzzles are about broadcasting. Know this rule.
-
Each puzzle needs to be solved in 1 line (<80 columns) of code.
-
You are allowed @, arithmetic, comparison,
shape, any indexing (e.g.a[:j], a[:, None], a[arange(10)]), and previous puzzle functions. -
You are not allowed anything else. No
view,sum,take,squeeze,tensor. -
You can start with these two functions:
def arange(i: int):
"Use this function to replace a for-loop."
return torch.tensor(range(i))
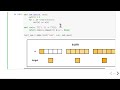
draw_examples("arange", [{"" : arange(i)} for i in [5, 3, 9]])# Example of broadcasting.
examples = [(arange(4), arange(5)[:, None]) ,
(arange(3)[:, None], arange(2))]
draw_examples("broadcast", [{"a": a, "b":b, "ret": a + b} for a, b in examples])def where(q, a, b):
"Use this function to replace an if-statement."
return (q * a) + (~q) * b
# In diagrams, orange is positive/True, where is zero/False, and blue is negative.
examples = [(tensor([False]), tensor([10]), tensor([0])),
(tensor([False, True]), tensor([1, 1]), tensor([-10, 0])),
(tensor([False, True]), tensor([1]), tensor([-10, 0])),
(tensor([[False, True], [True, False]]), tensor([1]), tensor([-10, 0])),
(tensor([[False, True], [True, False]]), tensor([[0], [10]]), tensor([-10, 0])),
]
draw_examples("where", [{"q": q, "a":a, "b":b, "ret": where(q, a, b)} for q, a, b in examples])Compute ones - the vector of all ones.
def ones_spec(out):
for i in range(len(out)):
out[i] = 1
def ones(i: int) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_ones = make_test("one", ones, ones_spec, add_sizes=["i"])# run_test(test_ones)Compute sum - the sum of a vector.
def sum_spec(a, out):
out[0] = 0
for i in range(len(a)):
out[0] += a[i]
def sum(a: TT["i"]) -> TT[1]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_sum = make_test("sum", sum, sum_spec)# run_test(test_sum)Compute outer - the outer product of two vectors.
def outer_spec(a, b, out):
for i in range(len(out)):
for j in range(len(out[0])):
out[i][j] = a[i] * b[j]
def outer(a: TT["i"], b: TT["j"]) -> TT["i", "j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_outer = make_test("outer", outer, outer_spec)# run_test(test_outer)Compute diag - the diagonal vector of a square matrix.
def diag_spec(a, out):
for i in range(len(a)):
out[i] = a[i][i]
def diag(a: TT["i", "i"]) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_diag = make_test("diag", diag, diag_spec)# run_test(test_diag)Compute eye - the identity matrix.
def eye_spec(out):
for i in range(len(out)):
out[i][i] = 1
def eye(j: int) -> TT["j", "j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_eye = make_test("eye", eye, eye_spec, add_sizes=["j"])# run_test(test_eye)Compute triu - the upper triangular matrix.
def triu_spec(out):
for i in range(len(out)):
for j in range(len(out)):
if i <= j:
out[i][j] = 1
else:
out[i][j] = 0
def triu(j: int) -> TT["j", "j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_triu = make_test("triu", triu, triu_spec, add_sizes=["j"])# run_test(test_triu)Compute cumsum - the cumulative sum.
def cumsum_spec(a, out):
total = 0
for i in range(len(out)):
out[i] = total + a[i]
total += a[i]
def cumsum(a: TT["i"]) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_cumsum = make_test("cumsum", cumsum, cumsum_spec)# run_test(test_cumsum)Compute diff - the running difference.
def diff_spec(a, out):
out[0] = a[0]
for i in range(1, len(out)):
out[i] = a[i] - a[i - 1]
def diff(a: TT["i"], i: int) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_diff = make_test("diff", diff, diff_spec, add_sizes=["i"])# run_test(test_diff)Compute vstack - the matrix of two vectors
def vstack_spec(a, b, out):
for i in range(len(out[0])):
out[0][i] = a[i]
out[1][i] = b[i]
def vstack(a: TT["i"], b: TT["i"]) -> TT[2, "i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_vstack = make_test("vstack", vstack, vstack_spec)# run_test(test_vstack)Compute roll - the vector shifted 1 circular position.
def roll_spec(a, out):
for i in range(len(out)):
if i + 1 < len(out):
out[i] = a[i + 1]
else:
out[i] = a[i + 1 - len(out)]
def roll(a: TT["i"], i: int) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_roll = make_test("roll", roll, roll_spec, add_sizes=["i"])# run_test(test_roll)Compute flip - the reversed vector
def flip_spec(a, out):
for i in range(len(out)):
out[i] = a[len(out) - i - 1]
def flip(a: TT["i"], i: int) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_flip = make_test("flip", flip, flip_spec, add_sizes=["i"])# run_test(test_flip)Compute compress - keep only masked entries (left-aligned).
def compress_spec(g, v, out):
j = 0
for i in range(len(g)):
if g[i]:
out[j] = v[i]
j += 1
def compress(g: TT["i", bool], v: TT["i"], i:int) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_compress = make_test("compress", compress, compress_spec, add_sizes=["i"])# run_test(test_compress)Compute pad_to - eliminate or add 0s to change size of vector.
def pad_to_spec(a, out):
for i in range(min(len(out), len(a))):
out[i] = a[i]
def pad_to(a: TT["i"], i: int, j: int) -> TT["j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_pad_to = make_test("pad_to", pad_to, pad_to_spec, add_sizes=["i", "j"])# run_test(test_pad_to)Compute sequence_mask - pad out to length per batch.
def sequence_mask_spec(values, length, out):
for i in range(len(out)):
for j in range(len(out[0])):
if j < length[i]:
out[i][j] = values[i][j]
else:
out[i][j] = 0
def sequence_mask(values: TT["i", "j"], length: TT["i", int]) -> TT["i", "j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
def constraint_set_length(d):
d["length"] = d["length"] % d["values"].shape[1]
return d
test_sequence = make_test("sequence_mask",
sequence_mask, sequence_mask_spec, constraint=constraint_set_length
)# run_test(test_sequence)Compute bincount - count number of times an entry was seen.
def bincount_spec(a, out):
for i in range(len(a)):
out[a[i]] += 1
def bincount(a: TT["i"], j: int) -> TT["j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
def constraint_set_max(d):
d["a"] = d["a"] % d["return"].shape[0]
return d
test_bincount = make_test("bincount",
bincount, bincount_spec, add_sizes=["j"], constraint=constraint_set_max
)# run_test(test_bincount)Compute scatter_add - add together values that link to the same location.
def scatter_add_spec(values, link, out):
for j in range(len(values)):
out[link[j]] += values[j]
def scatter_add(values: TT["i"], link: TT["i"], j: int) -> TT["j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
def constraint_set_max(d):
d["link"] = d["link"] % d["return"].shape[0]
return d
test_scatter_add = make_test("scatter_add",
scatter_add, scatter_add_spec, add_sizes=["j"], constraint=constraint_set_max
)# run_test(test_scatter_add)Compute flatten
def flatten_spec(a, out):
k = 0
for i in range(len(a)):
for j in range(len(a[0])):
out[k] = a[i][j]
k += 1
def flatten(a: TT["i", "j"], i:int, j:int) -> TT["i * j"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_flatten = make_test("flatten", flatten, flatten_spec, add_sizes=["i", "j"])# run_test(test_flatten)Compute linspace
def linspace_spec(i, j, out):
for k in range(len(out)):
out[k] = float(i + (j - i) * k / max(1, len(out) - 1))
def linspace(i: TT[1], j: TT[1], n: int) -> TT["n", float]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_linspace = make_test("linspace", linspace, linspace_spec, add_sizes=["n"])# run_test(test_linspace)Compute heaviside
def heaviside_spec(a, b, out):
for k in range(len(out)):
if a[k] == 0:
out[k] = b[k]
else:
out[k] = int(a[k] > 0)
def heaviside(a: TT["i"], b: TT["i"]) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_heaviside = make_test("heaviside", heaviside, heaviside_spec)# run_test(test_heaviside)Compute repeat
def repeat_spec(a, d, out):
for i in range(d[0]):
for k in range(len(a)):
out[i][k] = a[k]
def constraint_set(d):
d["d"][0] = d["return"].shape[0]
return d
def repeat(a: TT["i"], d: TT[1]) -> TT["d", "i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_repeat = make_test("repeat", repeat, repeat_spec, constraint=constraint_set)Compute bucketize
def bucketize_spec(v, boundaries, out):
for i, val in enumerate(v):
out[i] = 0
for j in range(len(boundaries)-1):
if val >= boundaries[j]:
out[i] = j + 1
if val >= boundaries[-1]:
out[i] = len(boundaries)
def constraint_set(d):
d["boundaries"] = np.abs(d["boundaries"]).cumsum()
return d
def bucketize(v: TT["i"], boundaries: TT["j"]) -> TT["i"]:
raise NotImplementedError
test_bucketize = make_test("bucketize", bucketize, bucketize_spec,
constraint=constraint_set)What is the smallest you can make each of these?
import inspect
fns = (ones, sum, outer, diag, eye, triu, cumsum, diff, vstack, roll, flip,
compress, pad_to, sequence_mask, bincount, scatter_add)
for fn in fns:
lines = [l for l in inspect.getsource(fn).split("\n") if not l.strip().startswith("#")]
if len(lines) > 3:
print(fn.__name__, len(lines[2]), "(more than 1 line)")
else:
print(fn.__name__, len(lines[1]))ones 29
sum 29
outer 29
diag 29
eye 29
triu 29
cumsum 29
diff 29
vstack 29
roll 29
flip 29
compress 29
pad_to 29
sequence_mask 29
bincount 29
scatter_add 29