The goal of this tool is to provide a quick and easy way to execute Keras models on machines or setups where utilizing TensorFlow/Keras is impossible. Specifically, in my case, to replace SNPE (Snapdragon Neural Processing Engine) for inference on phones with Python.
- Models:
- Sequential
- Layers:
- Dense
- Dropout
- Will be ignored during inference (SNPE 1.19 does NOT support dropout with Keras!)
- SimpleRNN
- Batch predictions do not currently work correctly.
- GRU
- Important: The current GRU support is based on
GRU v3in tf.keras 2.1.0. It will not work correctly with older versions of TensorFlow if not usingimplementation=2(example). - Batch prediction untested
- Important: The current GRU support is based on
- BatchNormalization
- Works with all supported layers
- Activations:
- ReLU
- LeakyReLU (supports custom alphas)
- Sigmoid
- Softmax
- Tanh
- Linear/None
The project to do list can be found here.
- Super quick conversion of your models. Takes less than a second. 🐱👤
- Usually reduces the size of Keras models by about 69.37%. 👌
- In some cases, prediction is quicker than Keras or SNPE (dense models). 🏎
- RNNs: Since we lose the GPU using NumPy, predictions may be slower
- Stores the weights and biases of your model in a separate compressed NumPy file. 👇
Benchmarks can be found in BENCHMARKS.md.
pip install keras-konverter
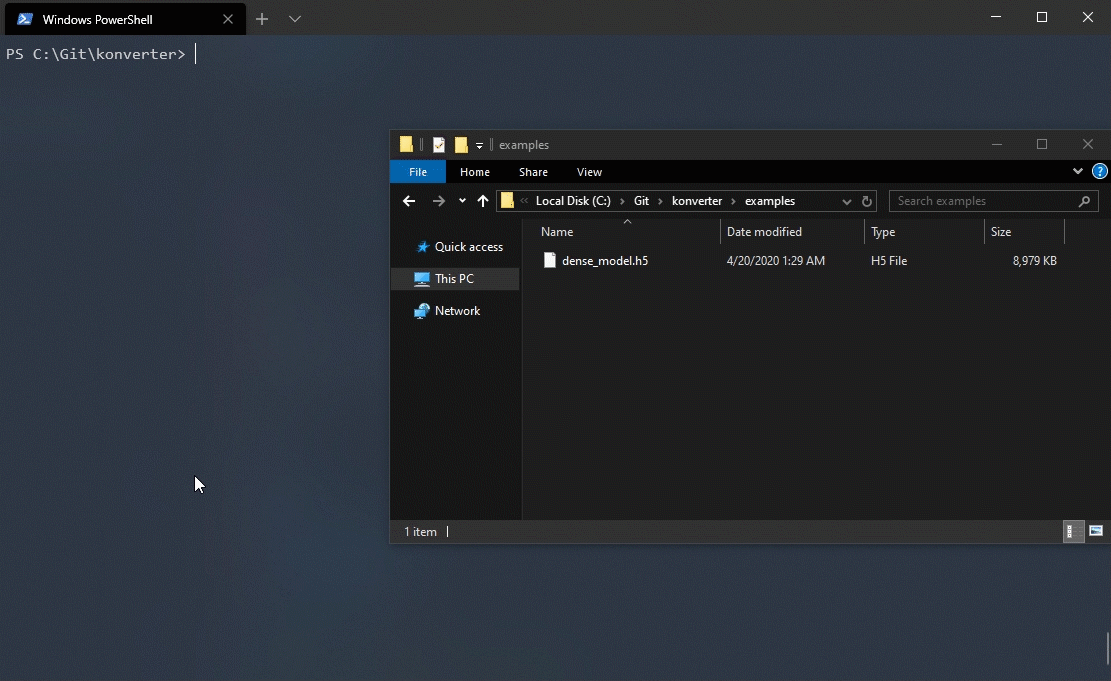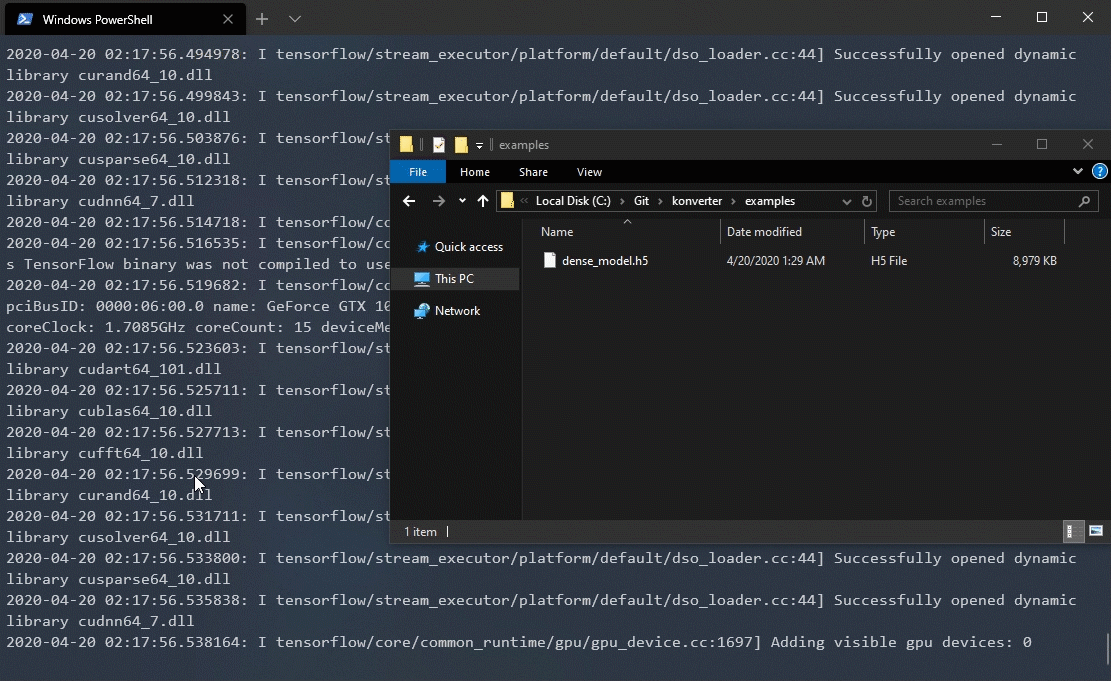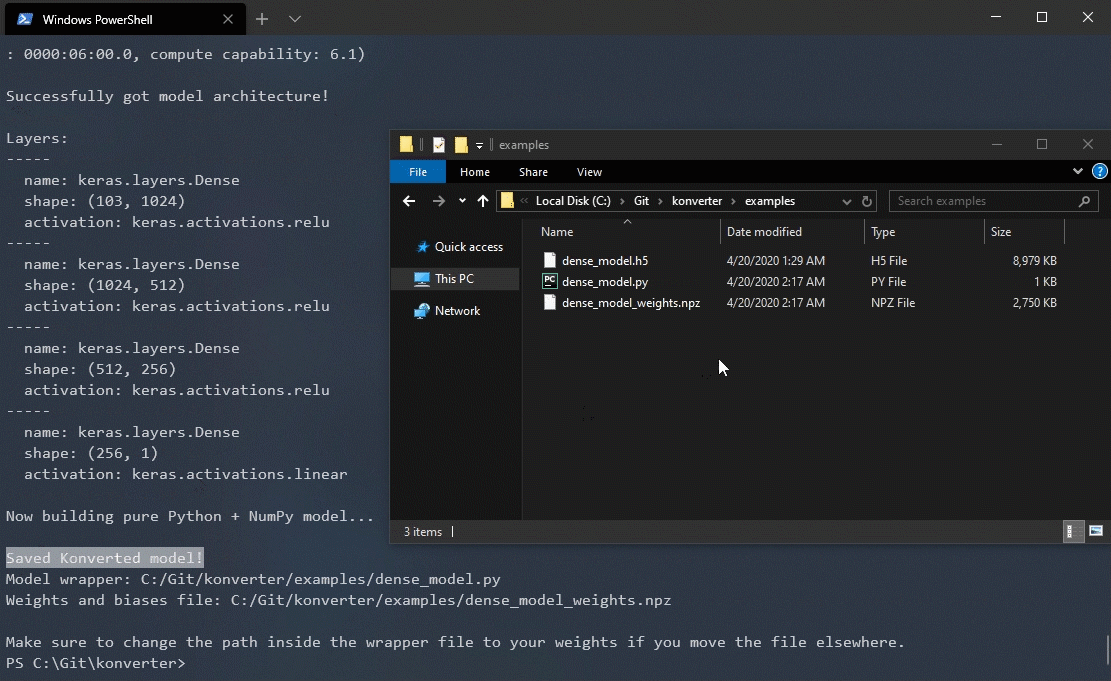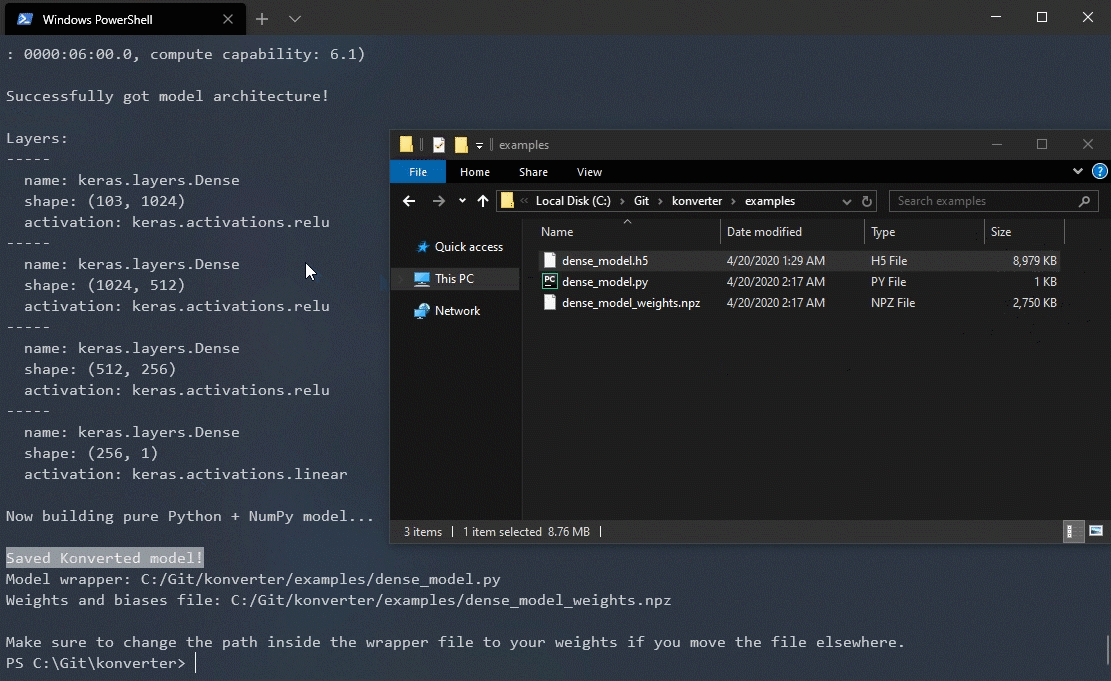
konverter examples/test_model.h5 examples/test_model.py (py suffix is optional)
Type konverter to get all possible arguments and flags!
- Arguments 💢:
input_model: Either the the location of your tf.keras .h5 model, or a preloaded Sequential model if using with Python. This is requiredoutput_file: Optional file path for your output model, along with the weights file. Default is same name, same directory
- Flags 🎌:
--indent, -i: How many spaces to use for indentation, default is 2--silent, -i: Whether you want Konverter to silently Konvert--no-watermark, -nw: Removes the watermark prepended to the output model file
All parameters with defaults: konverter.konvert(input_model, output_file=None, indent=2, silent=False, no_watermark=False, tf_verbose=False)
>>> import konverter
>>> konverter.konvert('examples/test_model.h5', output_file='examples/test_model')Note: The model file will be saved as f'{output_file}.py' and the weights will be saved as f'{output_file}_weights.npz' in the same directory. Make sure to change the path inside the model wrapper if you move the files after Konversion.
That's it! If your model is supported (check Supported Keras Model Attributes), then your newly converted Konverter model should be ready to go.
To predict: Import your model wrapper and run the predict() function. ❗Always double check that the outputs closely match your Keras model's❗ Automatic verification will come soon. For the integrity of the predictions, always make sure your input is a np.float32 array.
import numpy as np
from examples.test_model import predict
predict([np.random.rand(3).astype(np.float32)])Thanks to @apiad you can now use Poetry to install all the needed dependencies for this tool! However the requirements are a pretty short list:
- It seems most versions of TensorFlow that include Keras work perfectly fine. Tested from 1.14 to 2.2 using Actions and no issues have occurred. (Make sure you use implementation 2/v3 with GRU layers if not on TF 2.x)
- Important: You must create your models with tf.keras currently (not keras)
- Python >= 3.6 (for the glorious f-strings!)
To install all needed dependencies, simply cd into the base directory of Konverter, and run:
poetry install --no-dev
If you would like to use this version of Konverter (not from pip), then you may need to also run poetry shell after to enter poetry's virtualenv environment. If you go down this path, make sure to remove --no-dev so TensorFlow installs in the venv!
-
Dimensionality of input data:
When working with models using
softmax, the dimensionality of the input data matters. For example, predicting on the same data with different input dimensionality sometimes results in different outputs:>>> model.predict([[1, 3, 5]]) # keras model, correct output array([[14.792273, 15.59787 , 15.543163]]) >>> predict([[1, 3, 5]]) # Konverted model, wrong output array([[11.97839948, 18.09931636, 15.48014805]]) >>> predict([1, 3, 5]) # And correct output array([14.79227209, 15.59786987, 15.54316282])
If trying a batch prediction with classes and
softmax, the model fails completely:>>> predict([[0.5], [0.5]]) array([[0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]])
Always double check that predictions are working correctly before deploying the model.
-
Batch prediction with SimpleRNN (and possibly all RNN) layers
Currently, the converted model has no way of determining if you're feeding a single prediction or a batch of predictions, and it will fail to give the correct output in certain cases (more likely with recurrent layers and softmax dense outputs layers). Support will be added soon.