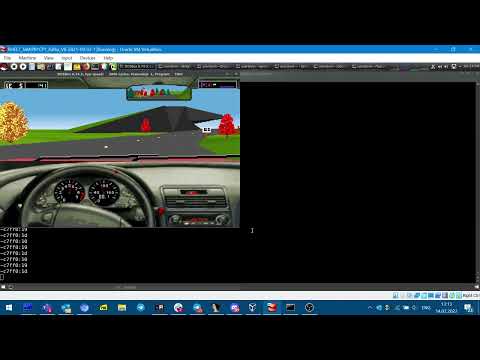
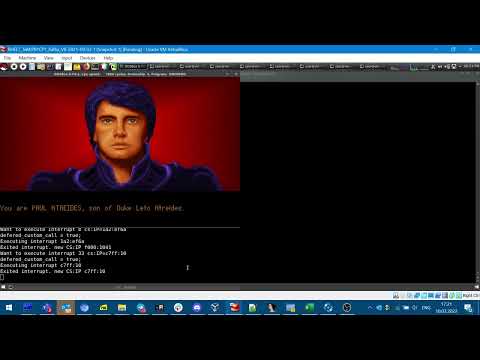
Masm2c is a tool designed to translate 16-bit x86 assembly code (often used in DOS games) to C and SDL, enabling easier porting, analysis, and modification.
It is a Source-to-source translator that generates fake-assembler instructions which can be compiled with a C compiler and executed.
(There is no working decompiler for 16 bit DOS code yet, because of DOS segmentation model, etc)
Example results:
The following assembler example:
_DATA segment use16 word public 'DATA'
_msg db 'Hello World!',10,13,'$'
_DATA ends
_TEXT segment use16 word public 'CODE'
assume cs:_TEXT,ds:_DATA
start proc near
sti ; Set The Interrupt Flag
cld ; Clear The Direction Flag
push _data
pop ds
mov ah,9 ; AH=09h - Print DOS Message
mov dx,offset _msg ; DS:EDX -> $ Terminated String
int 21h ; DOS INT 21h
mov ax,4c00h ; AH=4Ch - Exit To DOS
int 21h ; DOS INT 21h
start endp
_TEXT ends
end start
Converts to a compilable and working C++ code:
start:
R(STI); // 12 sti
R(CLD); // 13 cld
R(PUSH(seg_offset(_data))); // 14 push _data
R(POP(ds)); // 15 pop ds
R(ah = 9;); // 16 mov ah,9
R(dx = offset(_data,_msg);); // 17 mov dx,offset _msg
R(_INT(0x21)); // 18 int 21h
R(ax = 0x4c00;); // 20 mov ax,4c00h
R(_INT(0x21)); // 21 int 21h
struct Memory m = {
{0}, // padding
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, // segment _data
{'H','e','l','l','o',' ','W','o','r','l','d','!','\n','\r','$'}, // _msg
...The translation flow:
It can make IDA Pro output assembler listing to be recompilable by instrumented executing on emulator and compare each instruciton with emulated libdosbox.
Features:
- 386 instructions (except FPU) are supported (well tested with QEMU tests). x86 flags: Carry, Zero, Sign, Overflow are supported
- Segment memory model and 16bit offsets
- Internal SDL target: some BIOS/DOS Int 10h, 21h interrupts, DOS memory manager, and stack emulation CGA text mode is supported using Curses (PDcurses or NCurses). VGA 320x200x256 support (partial)
- Libdosbox target: Full interrupts, hardware support.
- structures support
- parser is based on Masm EBNF grammar
- segment can be merged same as Masm do it during linking: Many .asm sources can be converted individually and linked together using modern linker
Prerequisites:
- Python 3.9 or later: Ensure you have Python installed on your system.
- Assembly Source Code: You'll need the assembly code you want to translate. Masm2c supports MASM 6 syntax and IDA Pro's .lst files. (your code should be compilable with uasm(jwasm)/masm6, link5/tlink and work under DOS.)
Installation:
Install Dependencies: Use pip to install the required libraries:
pip install -r requirements.txt
This will install lark, jsonpickle, and other necessary packages.
Usage:
-
Basic Translation: To translate an assembly file (e.g., game.asm) to C, use the masm2c.py script:
python masm2c.py game.asmThis generates C++ source files (e.g., game.cpp and game.h) and a .seg file containing segment information.
-
Merging Procedures:
- Masm2c provides different options for handling procedure merging, it helps to get working code in case there are jumps between procedures.
- It controlled by the -m or --mergeprocs flag:
- separate (default): Procedures are kept separate, and jumps between them use a global dispatch function.
- persegment: Procedures within the same segment are merged.
- single: All procedures are merged into a single function.
-
Specifying Load Segment:
- It helps to temporary emulate a specific code memory location to speedup conversion (e.g., DOSBox loading an .exe at 0x1a2), use the -lo or --loadsegment flag to specify the segment:
python masm2c.py -lo 0x1a2 game.asm- For .com files loaded by DOSBox, use the -AT flag.
-
Generating Globals Listing:
-
To generate a file with a listing of all global variables, labels, and procedures, use the -FL or --list flag:
python masm2c.py -FL game.asm- This creates a file named game.list containing the information.
-
Output Files:
- C++ Source Files (.cpp and .h): These files contain the translated C code equivalent to your assembly source.
- Segment File (.seg): This file stores information about the segments in your assembly code. It can be used for merging data segments from multiple input files.
Tips:
- For better disassembly and translation, consider using tools like libDOSBox to collect runtime information (e.g., segment register values, memory access patterns).
- Masm2c scripts can help convert libDOSBox traces into annotations for disassemblers like IDA Pro.
(3rd-party code used from: ASM2C (x86 instruction emulation), tasm-recover (from SCUMMVM project; highly modified), QEMU x86 instructions test suit, FreeDOS memory manager.)
License: GPL2+
TODO:
- full macros support
- add FPU instructions support (may use linux 387 emulator)
Another use case: you can compile output of masm2c (C code) for 32 bit plarform with optimization; and decompile to get cleaner C code without dead code like x86 flags handling.
Assembler source code for Stunts game
https://github.com/xor2003/restunts
Assembler source code for Tornado flight sim https://github.com/xor2003/tornado-dos-flightsim
See list of DOS games with debug information http://bringerp.free.fr/forum/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=128
IDA Pro Free you can find here [https://www.scummvm.org/news/20180331/
](https://www.scummvm.org/news/20180331/)
Famous reverse engenerred MOD, S3M player. Currently platform DOS (ASM), SDL2 © There is disassembled source code for MASM, Nasm, C which can be built and running
TODO: finish sound support on SDL, finish porting (keyboard, graphics mode,...)
- get PDCurses or other curses library+headers, SDL2, mingw32 + a lot of luck
- build_mingw.bat
- execute: iplay_m_.exe HACKER4.S3M
Or just get prebuilt from release page
If you want to help me please contribute or send BTC to:
BTC: bc1qyaxs8dqn7mglp9w9zyvkfpz888x3aknr0jnsmx