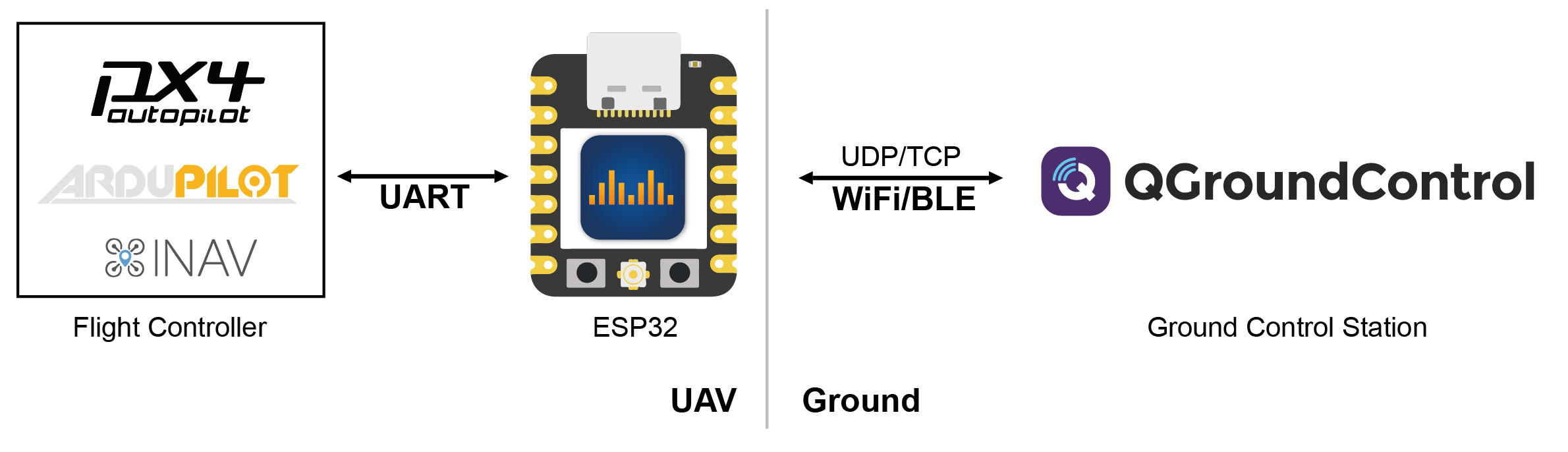
DroneBridge enabled firmware for the popular ESP32 modules from Espressif Systems. Probably the cheapest way to communicate with your drone, UAV, UAS, ground based vehicle or whatever you may call them.
Also allows for a fully transparent serial to wifi pass through with variable packet size (Continuous stream of data required).
DroneBridge for ESP32 is a telemetry/low data rate only solution. There is no support for cameras connected to the ESP32 since it does not support video encoding.
- Bi-directional link: MAVLink, MSP & LTM
- Affordable: ~7€
- Up to 150m range
- Weight: <10 g
- Supported by: DroneBridge for Android (app), mwptools, QGroundControl, impload etc.
- Easy to set up: Power connection + UART connection to flight controller
- Fully configurable through easy to use web interface
- Parsing of LTM & MSPv2 for more reliable connection and less packet loss
- Fully transparent telemetry downlink option for continuous streams like MAVLink or and other protocol
- Reliable, low latency, light weight
- Upload mission etc.
Tested with: DOIT ESP32 module
Blackbox concept. UDP & TCP connections possible. Automatic UDP uni-cast of messages to port 14550 to all connected devices/stations. Allows additional clients to register for UDP. Client must send a packet with length > 0 to UDP port of ESP32.
First download the latest release from this repository. You can find them here.
For flashing there are many ways of doing this. To easy ones are shown below.
recommended
pip install esptool- Connect via USB/Serial. Find out the serial port via
dmesgon linux or device manager on windows. In this example the serial connection to the ESP32 is on COM4 (in Linux e.g./dev/ttyUSB0). esptool.py -p COM4 -b 460800 --after hard_reset write_flash 0x1000 bootloader.bin 0x8000 partition-table.bin 0x10000 db_esp32.bin. You might need to press the boot button on your ESP to start the upload/flash process. On Windowsesptool [...](with out.py) seems to work
Look here for more detailed information
- Get it here
- Select the firmware, bootloader & partition table and set everything as below
- Hit Start and power cycle your ESP32 after flashing
- Connect UART of ESP32 to a 3.3V UART of your flight controller.
- Set the flight controller port to the desired protocol.
(Power the ESP32 module with a stable 5-12V power source) Check out manufacturer datasheet! Only some modules can take more than 3.3V/5V on VIN PIN
Defaults: UART2 (RX2, TX2 on GPIO 16, 17)
- Connect to the wifi
DroneBridge ESP32with passworddronebridge - In your browser type:
dronebridge.local(Chrome:http://dronebridge.local) or192.168.2.1into the address bar. You might need to disable the cellular connection to force the browser to use the wifi connection - Configure as you please and hit
save
Configuration Options:
Wifi password: Up to 64 character longUART baud rate: Same as you configured on your flight controllerGPIO TX PIN Number&GPIO RX PIN Number: The pins you want to use for TX & RX (UART). See pin out of manufacturer of your ESP32 device Flight controller UART must be 3.3V or use an inverter.UART serial protocol: MultiWii based or MAVLink based - configures the parserTransparent packet size: Only used with 'serial protocol' set to transparent. Length of UDP packetsLTM frames per packet: Buffer the specified number of packets and send them at once in one packet
Most options require a restart/reset of ESP32 module
- Use the Android app to display live telemetry data. Mission planning capabilities for MAVLink will follow.
- The ESP will auto broadcast messages to all connected devices via UDP to port 14550. QGroundControl should auto connect
- Connect via TCP on port 5760 or UDP on port 14550 to the ESP32 to send & receive data with a GCS of your choice. In case of a UDP connection the GCS must send at least one packet (e.g. MAVLink heart beat etc.) to the UDP port of the ESP32 to register as an end point.
You will need the Espressif SDK: esp-idf + toolchain (compile it yourself). Check out their website for more info and on how to set it up. The code is written in pure C using the esp-idf (no arduino libs).
This project uses the v4.0 branch of ESP-IDF
Compile and flash by running: idf.py build, idf.py flash