-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Species delimitation using Markov Chain Monte Carlo
#Usage
We provide a Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling method for assessing the confidence of the Maximum Likelihood delimitation scheme. The MCMC method is activated with the --mcmc switch followed by the number of MCMC steps and the switch for either the PTP model (--single) or the mPTP model (--multi). The user may define a number of additional parameters for the MCMC sampling as explained below.
##Overview of Command-line Parameters
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
--mcmc INT |
Support values for the delimitation (INT steps). |
--mcmc_sample INT |
Sample every INT iteration (default: 1000). |
--mcmc_log |
Log samples and create SVG plot of log-likelihoods. |
--mcmc_burnin INT |
Ignore all MCMC steps below threshold. |
--mcmc_chains INT |
Run multiple chains. |
--mcmc_credible REAL |
Credible interval. |
--mcmc_startnull |
Start each chain with the null model (one single species). |
--mcmc_startrandom |
Start each chain with a random delimitation. |
--mcmc_startml |
Start each chain with the delimitation obtained by the Maximum-likelihood heuristic. |
The following command-line would execute a single MCMC analysis with 1 million steps and the mPTP :
$ mptp --tree_file tree_filename --output_file output_filename --mcmc 1000000 --multi --minbr 0.0009330519Writing all MCMC samples into file is unnecessary and may produce large svg plot files (see output files). The --mcmc_sample option can be used for reducing the frequency of the MCMC sampling. For example, with the following command only the sampling frequency is set to 1/100, therefore 10000 files will be written in the output file.
$ mptp --tree_file tree_filename --output_file output_filename --mcmc 1000000 --multi --minbr 0.0009330519 --mcmc_sample 100To assess convergence (see convergence), it is important to run at least two independent MCMC analyses. This can be done in one mptp execution with the command --mcmc_chains followed by the number of analysis you want to run. It is highly recommended to run at least two independent runs, as shown in the example below.
$ mptp --tree_file tree_filename --output_file output_filename --mcmc 1000000 --multi --minbr 0.0009330519 --mcmc_sample 100 --mcmc_chains 2Another important point in assessing convergence is to use different starting delimitations. By default, the starting point for each MCMC run is a randomly generated delimitation (--mcmc_startrandom). However a user may choose to start from the ML delimitation scheme (--mcmc_startml) or the null model, which assumes that all branch lengths fit a single exponential distribution.
#Output Files
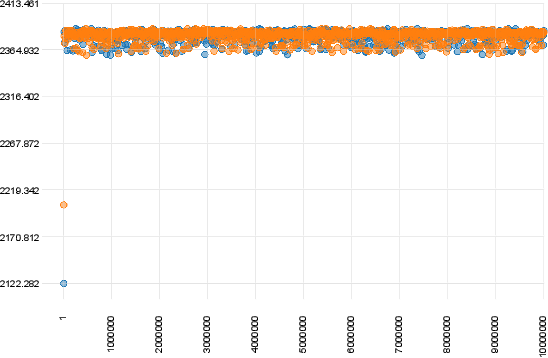
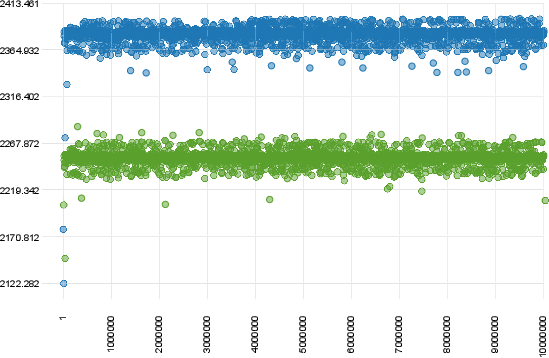
#Examples of Convergence
The figure below shows a case of convergence of two chains that were ran for 10 million generations with a sampling frequency of 10000.