-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Usage BUDO creator
The Excel-Table folder contains two Excel tables (BUDO_Creator_english.xlsx and BUDO_Creator_german.xlsx). Thus, the user can choose in which language he wants to operate the tool. Currently, only English and German are implemented. All data exported from the database are hidden. It is not recommended to change anything in this data.
You start at the BUDO Key worksheet, where you can create your individual BUDO keys.
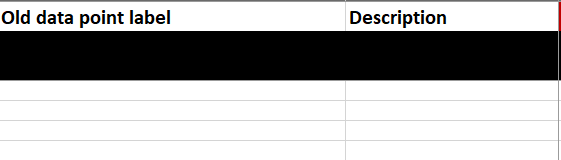
If old existing data point names exist that should be converted to BUDO, then these can be entered at the beginning in column A under Old data point label. Since in building automation systems a lot of information about the data point is also contained in a description, this can also be entered in the Description column.
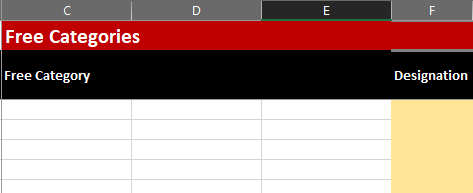
By Free Categories we mean categories that do not necessarily appear in every data point key or are very specific. These can also be mapped in a standardized way, but are separated from the standardized categories.
The article Categories gives an overview of all available categories. The article Documentation free categories (English) and Dokumentation freie Kategorien (German) in turn gives an overview of the available vocabulary in the Free Categories.
A selection field is available three times in the free categories. Selection field 1 appears from the beginning. Selection fields 2 and 3 are filled after selection fields 1 and 2 have been selected. These three selection fields are necessary, because a number of the free categories have a lot of selection possibilities, which are otherwise not possible to map.
For example, Building can be selected in selection field 1. In selection field 2 this can be specified to residential building and in selection field 3 the retirement home can be selected.
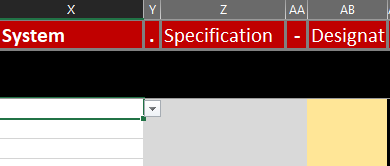
There are three levels in which a system can be built (system, subsystem and subsubsystem). All three levels work in the same way. How the levels are to be distributed is up to the person who manages the structure of the data point names.
The system consists of a selection of the central system (e.g. boiler) and a selection of the specification of the central system (e.g. condensing boiler). To these can be added a number (e.g. 01), or a specific name (e.g. Main) as designation.
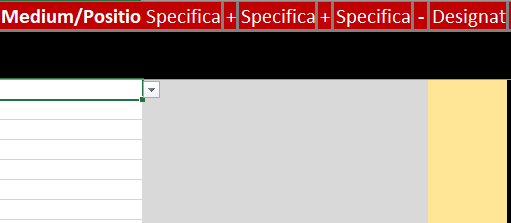
The category Medium/Position consists of five parts, the central medium, three specifications and one designation. First the central medium is selected (e.g. water). This can be described in more detail in the first specification (e.g. water -> hot water). Specification 2 and 3 have the same vocabulary. Here also positions (e.g. middle, outlet) but also functions (e.g. leakage) can be defined. At the end, the medium can be described in more detail with the help of a designation.
The category Signal Type consists of the central signal type (e.g. measured value), a maximum of three specifications and the designation. The central signal type can then be further specified (measured value -> temperature). Specification 3 and 4 have the same vocabulary. Here the signal type can be defined more precisely (e.g. chill or heating). At the end a designation (e.g. 01) can be added.
The input and output from the control device can be defined in the function type. This is important for the documentation of the control itself. The function type consists only of the central function type and a designation.
Virtual in- and outputs can also be defined in the Function Type. If simulations or model interfaces are used, they can be declared as simulated here.
Depending on the usage, it may make sense to put free categories at the end. This is possible with the BUDO Creator.
Only two settings can be changed in the 'Save' worksheet. The special character for the separator of the standard part of BUDO (default: §) and the special character as separator for the respective specification of BUDO (default: +).