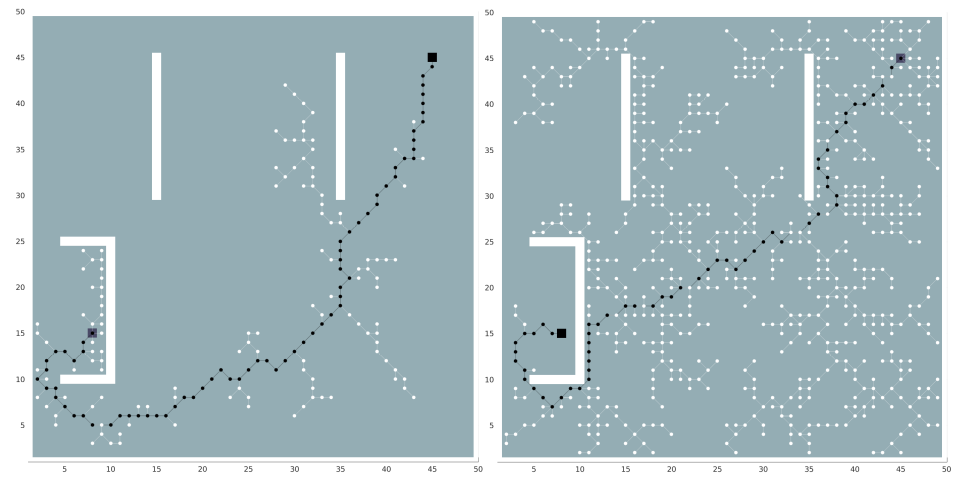
MATLAB implementation of a sampling-based planning algorithm, the rapidly- exploring random trees (RRT), as described in S. M. LaValle, “Rapidly-exploring random trees: A new tool for path planning,” 1998.
LaValle in his paper doesn’t specify which state sampling distribution, nearest-neighbors query, path search, motion and collision detection algorithms/methods should be used. Therefore the algorithm is implemented using a modular approach allowing easily the integration of state of the art algorithms for each one of these components.
In this particular implementation the open modules discussed above were addressed in the following way:
- the random state is drawn from an uniform distribution for 90% of the time and for the remaining 10% of the time the goal state is assigned as the random state. This strategy proved to be the one that quickly connected the initial and goal states, since for a pure random strategy the growth of the tree is always blind never taking into account the purpose of the algorithm.
- to find the nearest neighbor was used the euclidean distance, however it could easily have been used the mahalanobis or the minkowski distance.
- since the environment is discretized, it is assumed that the robot may move in eight different directions (N,S,E,W,NE,NW,SE,SW). Furthermore to simplify the implementation, it was set a fixed step size of one cell.
- in order to find the optimal path to follow, after the tree is built, it was used A star to search through the outputted tree and returning the shortest path. In the implemented tree it was accounted for weights in each edge making it possible to quickly find, for instance, the fastest path, instead of the shortest.