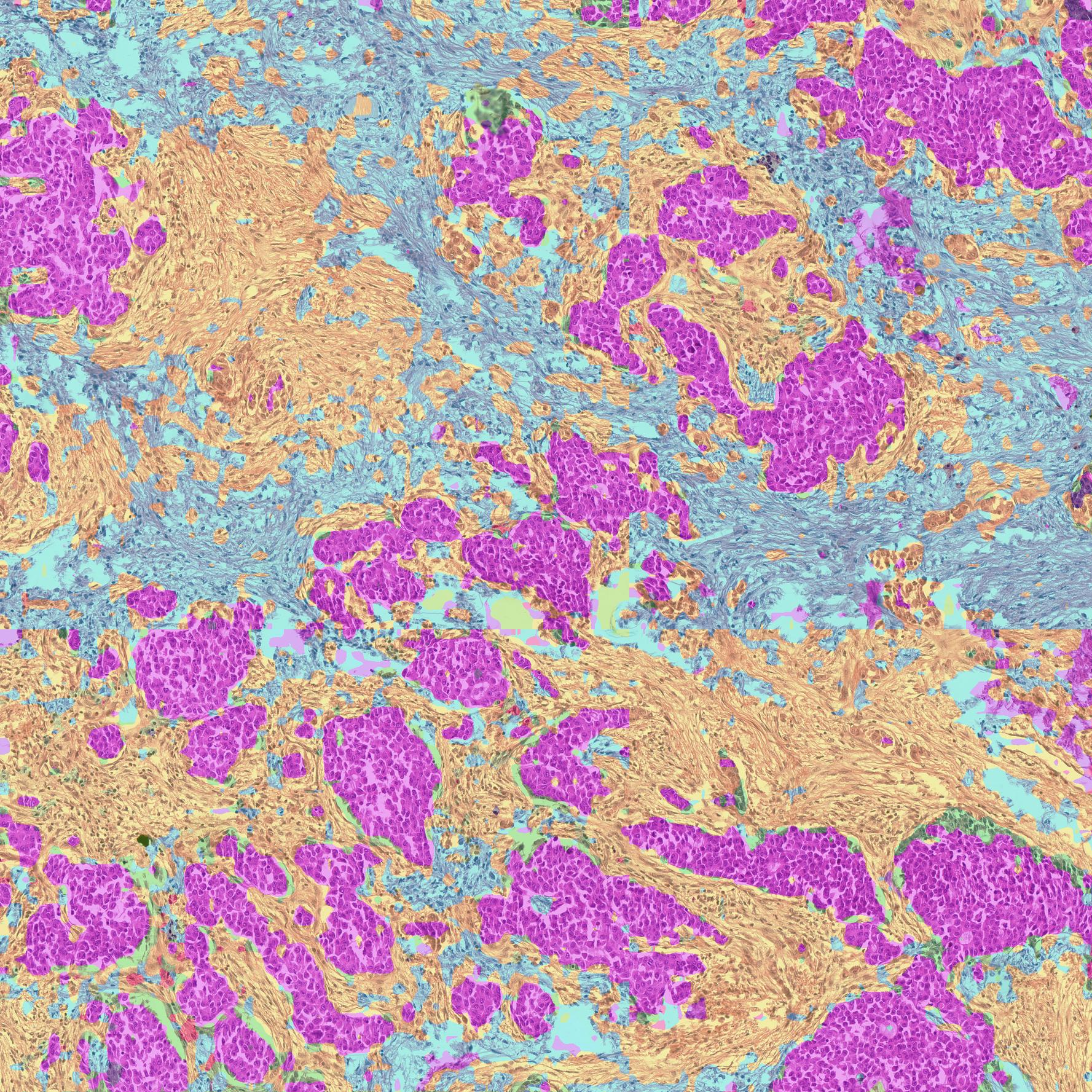
🧠 Utilize pathology foundational models for unsupervised semantic segmentation.
🏷️ No need for any annotated data!
🚀 Generates powerful H&E image segmentation, for a configurable number of semantic classes.
📄 See our paper here.
pip install segf
This is a python library from DeePathology that utilizes pathology foundational models for unsupervised semantic segmentation.
This lets you generate unsupervised semantic segmentation for pathology H&E images, with a configurable number of semantic classes.
F-Seg does this by performing Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) on the model's activations, to create a segmentation mask corresponding to a set of pre-defined feature representations.
You need two things to run F-Seg:
- A pre-trained foundational model.
- A group of representing 1D embeddings extracted from the model for different concepts. This can be done by extracting embeddings from the model, and then clustering them.
The example below uses the UNI model. We prepared cluster centers of two popular foundational models, the UNI and the Prov-GigaPath models, for different number of clusters k.
See the notebook for more advanced usage.
pip install segffrom fseg import FSeg
from huggingface_hub import login
token = "<your_token>"
login(token=token)
## A reshape transform for the UNI model
class TransformerReshapeTransform:
def __init__(self):
self.input_tensor_shape = None
def __call__(self, tensor):
result = torch.nn.ReLU()(tensor[:, 1:, :].reshape(tensor.size(0),
self.input_tensor_shape[2] // 16,
self.input_tensor_shape[3] // 16,
tensor.size(2)))
# Bring the channels to the first dimension, like in CNNs.
result = result.transpose(2, 3).transpose(1, 2)
return result
model = timm.create_model(
"hf-hub:MahmoodLab/uni", pretrained=True, init_values=1e-5, dynamic_img_size=True)
target_layer = model.blocks[-1]
transform = TransformerReshapeTransform()
unsupervised_seg = FSeg(
model=model,
target_layer=target_layer,
reshape_transform=reshape_transform
)
#Load pre-computed model embeddings:
model_embeddings = np.load("./model_embeddings/uni.joblib")
#Define the number of clusters and prepare the concepts:
concepts = model_embeddings[64]
segmentation_prediction = unsupervised_seg.predict_project_concepts(input_tensor, concepts)If you use this code in your research, please cite using this BibTeX:
@article{gildenblat2024segmentation,
title={Segmentation by Factorization: Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation for Pathology by Factorizing Foundation Model Features},
author={Gildenblat, Jacob and Hadar, Ofir},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.05697},
year={2024}
}