A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
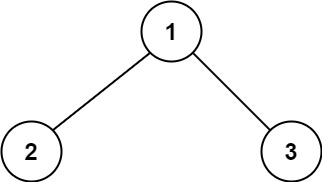
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
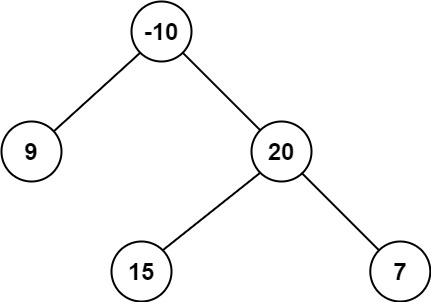
Example 2:
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
$[1, 3*10^4]$ . 1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
題目給了一個二元樹根結點 root
定義一個 path 的 sum 代表把在 path 上所有的結點值相加
找出一個樹的 path 所能形成最大 sum,且每個結點在路徑只能出現一次
這個問題的核心在於要如何找出最大值
透過累計的方式我們可以從 root 結點來分析
從 root 拆解出, 從root 結點分岔 + 從 root 點不分岔兩種包含 root 結點方式
而這個問題,可以用DFS 來做探訊
假設不做分岔的方法是 maxSum
累計量 accum = max(accum, root.Val + Max(maxSum(root.left) , maxSum(root.Right))
對包含 root 的樹去找 maxSum(root) = root.Val + Max(maxSum(root.left) , maxSum(root.Right) )
這樣只要走訪完整棵樹即為最大值, 時間複雜度O(n)
參考下圖
class Solution {
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
accumResult = root.val;
MaxSum(root);
return accumResult;
}
public int MaxSum(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftMax = MaxSum(root.left);
int rightMax = MaxSum(root.right);
// leftMax = choose or not choose maximum
leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, 0);
rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, 0);
// split Max = not split result or (leftMax + root.val + rightMax)
accumResult = Math.max(accumResult, leftMax + root.val + rightMax);
// not split result = root.val + Max(leftMax, rightMax)
return root.val + Math.max(leftMax, rightMax);
}
}- Understand DFS
- Know how to divide the question
- Understand what problem to solve
- Analysis Complexity